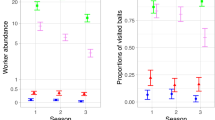
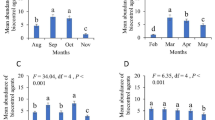
Abstract
Harmonia axyridis Pallas is a generalist predator native to Asia. It has been released both for classical and neoclassical biological control programs worldwide. Its presence has led to new ecological associations and it has been associated with the decline of indigenous natural enemies, notably ladybirds. These declines have been attributed to competition for resources and intraguild predation (IGP). H. axyridis was introduced in Argentina in 1986 to control the aphid Myzus persicae, although native coccinellid species are widespread in this area. Eriopis connexa Germar is the most abundant native coccinellid in Argentina. No study has assessed the possible ecological effects of the introduction of H. axyridis on naturally occurring aphid predators in Argentinian agro-ecosystems. This study evaluated IGP between H. axyridis and E. connexa at two different aphid densities under laboratory conditions. IGP occurred in 100 % of the cases when larvae of both species were reared together at low prey density and in 67 % of the cases at high prey density; at both prey levels, H. axyridis usually acted as the IG predator. The more rapid development to second and third larval instars, larger body size, and more voracious behavior of H. axyridis compared to the native coccinellid could explain the IGP direction. This study showed the negative effect of H. axyridis on the native E. connexa under laboratory conditions, corroborated interactions between the species observed in field crops, and highlighted the impacts of this exotic predator on naturally occurring predator species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala BK, Dixon AFG (1992) Laboratory study of cannibalism and interspecific predation in ladybirds. Ecol Entomol 17:303–309
Alhmedi A, Haubruge E, Francis F (2010) Intraguild interactions and aphid predator: biological efficiency of Harmonia axyridis and Episyrphus balteatus. J Appl Entomol 134:34–44
Almeida LM, da Silva VB (2002) First record of Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae): a lady beetle native to the Palaearctic region. Rev Bras Zool 19:941–944
Almeida Sarmento R, Pallini A, Venzon M, Fonesca de Souza F, Molina-Rugama AJ, Lima de Olivera C (2007) Functional response of the predator Eriopis connexa (Coleoptera Coccinellidae) to different prey. Braz Arch Biol Tech 50:121–126
Bompard A, Jaworski CC, Bearez P, Desneux N (2013) Sharing a predator: can an invasive alien pest affect the predation on a local pest? Pop Ecol 55:433–440
Brown PMJ, Adrianse T, Bathon H, Cuppen J, Goldarazena A, Hägg T, Kenis M, Klausnitzer BEM, Kovar I, Loomans AJM, Majerus MEN, Nedved O, Pedersen J, Rabitsch W, Roy HE, Ternois V, Zakharov IA, Roy DB (2008) Harmonia axyridis in Europe: spread and distribution of a non-native coccinellid. Biocontrol 53:5–21
Brown PMJ, Thomas CE, Lombaert E, Jeffries DL, Estoup A, Lawson Handley LJ (2011) The global spread of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: coccinellidae): distribution, dispersal and routes of invasion. Biocontrol 56:623–641
Chailleux A, Bearez P, Pizzol J, Amiens-Desneux E, Ramirez-Romero R, Desneux N (2013) Potential for combined use of parasitoids and generalist predators for biological control of the key invasive tomato pest, Tuta absoluta. J Pest Sci 86:533–541
Coderre D, Lucas E, Gagne I (1995) The occurrence of Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Canada. Can Entomol 127:609–611
Cottrell TE (2004) Suitability of exotic and native lady beetle eggs (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) for development of lady beetle larvae. Biol Control 31:362–371
Cottrell TE, Yeargan KV (1998) Intraguild predation between an introduced lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: coccinellidae), and a native lady beetle, Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Kansas Entomol Soc 71:159–163
Duarte Gómez W, Zenner de Polanía I (2009) Life table of the predatory beetle Eriopis connexa connexa (Germar) (Coleoptera: coccinellidae). Rev UDCA Act & Div Cient 12:147–155
Félix S, Soares A (2004) Intraguild predation between the aphidophagous ladybird beetles Harmonia axyridis and Coccinella undecimpunctata (Coleoptera: coccinellidae): the role of body weight. Eur J of Entomol 101:237–242
Gagnon AV, Heimpel GE, Brodeur J (2011a) The ubiquity of intraguild predation among predatory Arthropods. PLoS ONE 6:e28061
Gagnon AE, Doyon J, Heimpel GE, Brodeur J (2011b) Prey DNA detection success following digestion by intraguild predators: influence of prey and predator species. Mol Ecol Res 11:1022–1032
García MF, Becerra VC, Reising CE (1999) Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Col.: coccinellidae). Estudio biológico Rev Fac Cs Agrarias 31:85–91
Gordon RD (1985) The Coleoptera (Coccinellidae) of America north of Mexico. J New York Entomol Soc 93:1–912
Grez A, Zaviezo T, Gónzalez G, Rothmann S (2010) Harmonia axyridis in Chile: a new threat. Cien Inv Agr 37:145–149
Harmon JP, Stephens E, Losey J (2007) The decline of native coccinellids (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in the United States and Canada. J Insect Conserv 11:85–94
Hautier L, San Martin G, Callier P, de Biseau JC, Grégoire JC (2011) Alkaloids provide evidence of intraguild predation on native coccinellids by Harmonia axyridis in the field. Biol Invasions 13:1805–1814
Heimpel GE, Frelich LE, Landis DA, Hopper KR, Hoelmer KA, Sezen Z, Asplen MK, Wu KM (2010) European buckthorn and Asian soybean aphid as components of an extensive invasional meltdown in North America. Biol Invasions 12:2913–2931
Hesler LS, Keickhefer RW, Beck DA (2001) First record of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in South Dakota and notes on its activity there and in Minnesota. Entomol News 112:264–270
Hokkanen H, Pimentel D (1984) New approach for selecting biological control agents. Can Entomol 116:1109–1121
Hukusima S, Kamei M (1970) Effects of various species of aphids as food on development, fecundity and longevity of Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: coccinellidae). Res Bull Fac Agric Gifu Univ 29:53–66
Ingels B, De Clercq P (2011) Effect of size, extraguild prey and habitat complexity on intraguild interactions: a case study with the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis and the hoverfly Episyrphus balteatus. Bio Control 56:871–882
Iperti G, Bertand E (2001) Hibernation of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in South-Eastern France. Acta Soc Zool Bohem 65:207–210
Jaworski CC, Bompard A, Genies L, Amiens-Desneux E, Desneux N (2013) Preference and prey switching in a generalist predator attacking local and invasive alien pests. PLoS ONE 8:82231
Koch RL (2003) The multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis: a review of its biology, uses in biological control, and non-target impacts. J Insect Sci 3:1–16
Koch RL, Venette R, Hutchison W (2006) Invasion by Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in the western hemisphere: Implications for South America. Neotrop Entomol 35:421–434
Lucas E, Coderre D, Brodeur J (1998) Intraguild predation among aphid predators: characterization and influence of extraguild prey density. Ecology 79:1084–1092
Majerus MEN, Strawson V, Roy HE (2006) The potential impacts of the arrival of the harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: coccinellidae), in Britain. Ecol Entomol 31:207–215
Michaud JP (2002) Invasion of the Florida citrus ecosystem by Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) and asymmetric competition with a native species, Cycloneda sanguinea. Environ Entomol 31:827–835
Michaud JP (2012) Coccinellids in biological control. In: Hodek I, van Emden HF, Honek A (eds) Ecology and behaviour of the ladybird beetles (Coccinellidae). Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, pp 488–519
Moreno-Ripoll R, Gabarra R, Symondson WOC, King RA, Agustí N (2014) Do the interactions among natural enemies compromise the biological control of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci? J Pest Sci 87:133–141
Moser SE, Obrycki JJ (2009) Competition and intraguild predation among three species of coccinellids (Coleoptera: coccinellidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 102:419–425
Nóia M, Borges I, Soares A (2008) Intraguild predation between the aphidophagous ladybird beetles Harmonia axyridis and Coccinella undecimpunctata (Coleoptera: coccinellidae): the role of intra and extraguild prey densities. Biol Control 46:140–146
O’Connel DM, Wratten SD, Pugh AR, Barnes AM (2012) New species association biological control? Two coccinellid species and an invasive psyllid pest in New Zealand. Biol Control 62:86–92
Obrycki JJ, Giles KL, Ormord AM (1998) Experimental assessment of interactions between larval Coleomegilla maculata and Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in field cages. Environ Entomol 27:1280–1288
Ohashi DV, Urdampilleta JD (2003) Interacción entre insectos perjudiciales y benéficos en el cultivo del tabaco de Misiones, Argentina. Rev Invest Agrícolas 32:113–124
Pell JK, Baverstock J, Roy HE, Ware RL, Majerus MEN (2008) Intraguild predation involving Harmonia axyridis: a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. Biocontrol 53:147–168
Phoofolo MW, Obrycki JJ (1998) Potential for intraguild predation and competition among predatory Coccinellidae and Chrysopidae. Entomol Exp Appl 89:47–55
Pimentel D, Levin SA, Soans AS (1975) On the evolution of energy balance in some exploiter-victim systems. Ecology 56:381–390
Polis GA, McCormick SJ (1989) Intraguild predation and competition among desert scorpions. Ecology 68:332–343
Quiroz EC, Larraín SP, Sepúlveda RP (2005) Seasonal abundance of insect vectors of viruses in two green pepper (Capsicum annum L.) ecosystems of the Coquimbo Region. Chile Agric Técnica 65:3–19
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Reed DK, Pike KS (1991) Summary of an exploration trip to South America. IOBC NR Newsl 36:16–17
Rocha de Moraes R, Lek AE, Belarmino EC (1991) Inimigos naturais de Rachiplusia nu (Guenée, 1852) e Pseudoplusia includens (Walter, 1857) (Lepidoptera: noctuidae). Pesq Agropec Bras 26:57–64
Roy HE, Wajnberg E (2008) From biological control: the ladybird Harmonia axyridis as a model species. In: Roy HE, Wajnberg E (eds) From biological control to invasion: the ladybird Harmonia axyridis as a model Species. IOBC, Dordrecht, pp 1–5
Saini ED (2004) Presencia de Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) en la provincia de Buenos Aires. Aspectos biológicos y morfológicos RIA 33:151–160
Sarmento RA, Gomes de Oliveira H, Holtz AM, Marques da Silva S, Serrão JE, Pallini A (2004) Fat body morphology of Eriopis connexa (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in function of two alimentary sources. Braz Arch Biol Technol 47:407–411
Sato S, Shinya K, Yasuda H, Kindlmann P, Dixon AFG (2008) Effects of intra and interspecific interactions on the survival of two predatory ladybirds (Coleoptera: coccinellidae) in relation to prey abundance. Appl Entomol Zool 44:215–221
Scheiner S, Gurevitch J (2001) Design and analysis of ecological experiments. Oxford University Press, New York
Silva RB, Cruz I, Zanuncio JC, Figueiredo MLC, Zanuncio TV, Serrão J (2013) Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: noctuidae) eggs as alternative food for rearing of lady beetles Eriopis connexa (Germar) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 64:101–105
van Lenteren JC, Babendreier D, Bigler F, Burgio G, Hokkanen HMT, Kuske S, Loomans AJM, Menzler-Hokkanen I, Van Rijn PCJ, Thomas MB, Tommasini MG, Zeng QQ (2003) Environmental risk assessment of exotic natural enemies used in inundative biological control. Biocontrol 48:3–38
van Lenteren JC, Bale J, Bigler E, Hokkanen HMT, Loomans AM (2006) Assessing risks of releasing exotic biological control agents of arthropod pests. Annu Rev Entomol 51:609–634
Velasco-Hernández MC, Ramirez Romero R, Cicero L, Michel C, Desneux N (2013) Intraguild predation on the whitefly parasitoid Eretmocerus eremicus by the generalist predator Geocoris punctipes: a behavioral approach. PLoS ONE 8:e80679
Ware R, Yguel B, Majerus M (2009) Effect of competition, cannibalism and intraguild predation on larval development of the European coccinellids Adalia bipunctata and the invasive species Harmonia axyridis. Ecol Entomol 34:12–19
Yasuda H, Kikuchi T, Kindlmann P, Satoru S (2001) Relationships between attack and escape rates cannibalism, and intraguild predation in larvae of two predatory ladybirds. J Insect Behav 14:373–383
Yasuda H, Evans E, Kajita Y, Urakawa K, Takizawa T (2004) Asymmetric larval interaction between introduced and indigenous ladybird in North America. Oecologia 141:722–731
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a PICT 2011 1752 grant from the Argentine National Agency for the Promotion of Science and Technology (ANPCyT) to M. Schneider. L. Mirande and M Haramboure are grateful to CONICET for doctoral fellowship. The authors thank Ing. Armando Junquera (Asociación Cooperativas Argentinas) for seeds of wheat cv. ACA 901 and Dr. Mónica Ricci (Faculty of Agronomic and Forest Sciences, UNLP) for R. padi specimens to initiate our colonies. We are grateful also to Guillermo Reboredo for his valuable assistance in the field surveys. The English editing was done by a native English speaker for Edanz Group Global Limited. We thank the two anonymous reviewers whose contributions improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. C. Weber.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirande, L., Desneux, N., Haramboure, M. et al. Intraguild predation between an exotic and a native coccinellid in Argentina: the role of prey density. J Pest Sci 88, 155–162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0597-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0597-z