Abstract
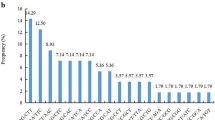
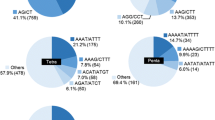
Genomic simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers are particularly valuable in studies of genetic diversity, evolution, genetic linkage map construction, quantitative trait loci tagging, and marker-assisted selection because of their multi-allelic nature, reproducibility, co-dominant inheritance, high abundance, and extensive genome coverage. The traditional methods of SSR marker development, such as genomic-SSR hybrid screening and microsatellite enrichment, have the disadvantages of high cost and complex operation. The selectively amplified microsatellite method is less costly and highly efficient as well as being simple and convenient. In this study, 252 sequences with SSRs were cloned from the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) genome from which 258 SSR loci were obtained. The average repeat number was six. There were only 10 (3.9%) mononucleotide, trinucleotide, and pentanucleotide repeats, whereas the remaining 248 (96.1%) were dinucleotide repeats, including 128 (49.6%) GT/CA repeats, 118 (45.7%) GA/CT repeats, and 2 (0.8%) AT/TA repeats. A total of 126 primer pairs (see ESM) were successfully designed of which 36 primer pairs generated polymorphic products from 12 accessions of the cultivated species, 4 related species, and 3 species of the family Euphorbiaceae. In addition, investigations based on four genomic SSRs (GAR4, ACR22, CTR25, and GTR28) by cloning and sequencing provided evidence for cross-species/genera applicability, and homologous sequences were obtained from the rubber tree and Euphorbiaceae. Further analysis about the variation of the flanking regions of the four markers was carried out.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aidi-Daslin (2002) Report on the evaluation and utilization of the 1981 IRRDB Hevea germplasm in Indonesia. IRRDB plant breeding, agronomy and socio-economics joint workshop, 28 Aug–7 Sept, Malaysia and Indonesia
Benong M (2002) Status on the evaluation and utilization of the 1981 IRRDB Hevea germplasm. IRRDB plant breeding, agronomy and socio-economics joint workshop, 28 Aug–7 Sept, Malaysia and Indonesia
Besse P, Seguin M, Legrun P, Chevallier MH, Nicolas D, Lanaud C (1994) Genetic diversity among wild and cultivated populations of Hevea brasiliensis assessed by nuclear RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet 88:199–207
Billotte N, Lagoda PJL, Risterucci A-M, Baurens F-C (1999) Microsatellite-enriched libraries: applied methodology for the development of SSR markers in tropical crops. Fruits 54:277–287
Bonnett DG, Rebetzke GJ, Spielmeyer W (2005) Strategies for efficient implementation of molecular markers in wheat breeding. Mol Breed 15:75–85
Clement-Demange A (2002) Report on the IRRDB 1981 Hevea germplasm by Cirad (France) year (2002) IRRDB plant breeding, agronomy and socio-economics joint workshop, 28 Aug–7 Sept, Malaysia and Indonesia
Collard BCY, Mackill DJ (2008) Marker-assisted selection: an approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century. Philos Trans R Soc B 363:557–572
Davierwala AP, Ramakrishna W, Chowdari V, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2001) Potential of (GATA)n microsatellites from rice for inter-and intraspecific variability studies. BMC Evol Biol 1:7
Dreisigacker S, Zhang P, Warburton ML, Ginkel MV (2004) SSR and pedigree analyses of genetic diversity among CIMMYT wheat lines targeted to different megaenvironments. Crop Sci 44:381–388
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2002) Solation of EST-derived microsatellite markers for genotyping the A and B genomes of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:399–407
Feng SP, Li WG, Huang HS, Wang JY, Wu YT (2009) Development, application and cross-species/genera transferability of EST-SSR makers for rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Mol Breed 23:85–97
Ferguson ME, Burow MD, Schulze SR, Bramel PJ, Paterson AH, Kresovich S, Mitchell S (2004) Microsatellite identification and characterization in peanut (A. hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 108:1064–1070
Field D, Wills C (1996) Long, polymorphism microsatellite in simple organisms. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 263:209–215
Friedt W, Ordon F (2007) Molecular marker for gene pyramiding and disease resistance breeding in barley. Genomics-assisted crop improvement, pp 81–101
Gao LF, Tang J, Li H, Jia J (2003) Analysis of microsatellites in major crops assessed by computational and experimental approaches. Mol Breed 113:163–185
Gonzalo MJ, Oliver M, Garcia-Mas J, Monfort A, Dolcet-Sanjuan R, Katzir N, Arus P, Monforte AJ (2005) Simple-sequence repeat markers used in merging linkage maps of melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:802–811
Guen V, Lespinasse D, Oliver G, Rodier-Groud M, Pinard F, Seguin M (2003) Molecular mapping of genes conferring field resistance to South American leaf blight (Microcyclus ulei) in rubber tree. Theor Appl Genet 108:160–167
Gutierrez MV, Vaz Patto MC, Huguet T, Cubero JI, Moreno MT, Torres AM (2005) Cross-species amplification of Medicago truncatula microsatellites across three major pulse crops. Theor Appl Genet 110:1210–1217
Hancock JM (1999) Microsatellites and other simple sequences: genetic context and mutation mechanisms [A]. In: Goldstein AB, Schotterer C (eds) Microsatellites: evolution and applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 1–9
Hayden MJ, Sharp PJ (2001) Targeted development of informative microsatellites (SSR) markers. Nucleic Acids Res 29(8):e44
Huang HB, Song YQ, Hsei M, Zahorchak R, Chiu J, Teuscher C, Smith EJ (1990) Development and characterization of genetic mapping resources for the turkey (Meleagris gallopavo). J Hered 90(1):240–242
Jamnadass R, Lowe A, Dawson IK (2009) Molecular markers and the management of tropical trees: the case of indigenous fruits. Trop Plant Biol 2:1–12
Jarne P, Lagoda PJL (1996) Microsatellites, from molecules to population and back. Trends Ecol Evol 10:424–429
Johannsdottir JT, Jonasson JG, Bergthorsson JT, Amundadottir LT, Magnusson J, Egilsson V, Ingvarsson S (2000) The effect of mismatch repair deficiency on tumourigenesis; microsatellite instability affecting genes containing short repeated sequences. Int J Oncol 16(1):133–139
Jones ES, Dupal MP, K_lliker R, Drayton MC, Forster JW (2001) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Theor Appl Genet 102:405–415
Jung S, Albert A, Jesudurai C, Tomkins J, Main D (2005) Frequency, type, distribution and annotation of simple sequence repeats in Rosaceae ESTs. Funct Integr Genomics 5:136–143
Kaemmer D, Fischer D, Jarret RL, Baurens FC, Grapin A, Dambier D, Noyer JL, Lanaud C, Kahl G, Lagoda PJL (1997) Molecular breeding in the genus Musa: a strong case for STMS marker technology. Euphytica 96:49–63
Kuchel H, Rebecca Fox R, Reinheimer J, Mosionek L, Willey N, Bariana H, Jefferies S (2007) The successful application of a marker-assisted wheat breeding strategy. Mol Breed 20:295–308
Landjeva S, Korzun V, Börner A (2007) Molecular markers: actual and potential contributions to wheat genome characterization and breeding. Euphytica 156:271–296
Lekawipat N, Teerawatanasuk K, Rodier-Goud M, Seguin M, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T, Tragoonrung S (2003) Genetic diversity analysis of wild germplasm and cultivated clones of Hevea brasiliensis Müell. Arg. using microsatellite markers. J Rubb Res 6:36–47
Lespinasse D, Rodier-Goud M, Grivet L, Leconte A, Legnate H, Seguin M (2000) A saturated genetic linkage map of rubber tree (Hevea spp.) based on RFLP, AFLP, microsatellite, and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:127–138
Litt M, Luty JA (1989) Hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle action gene. Am J Hum Genet 44:391–401
Low FC, Safiah A, Hafsah J, Tan H (1996) Recent advances in the development of molecular markers for Hevea studies. J Nat Rubb Res 6:152–157
Lowe BA, Way MM, Kumpf JM, Rout J, Warner D, Johnson R, Armstrong CL, Spencer MT, Chomet PS (2006) Marker assisted breeding for transformability in maize. Mol Breed 18(3):229–239
Luo H, Boutry M (1995) Phylogenetic relationships within Hevea brasiliensis as deduced from a polymorphic mitochondrial DNA region. Theor Appl Genet 91:876–884
Matsuoka Y, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Goodman M, Doebley J (2002) Microsatellites in Zea-”variability, patterns of mutations, and use for evolutionary studies”. Theor Appl Genet 104:436–450
Morgante M, Pfeiffer A, Constacurta A, Olivieri AM, Powell W, Vendramin GG, Rafalski JA (1999) Polymorphic simple sequence repeats in nuclear and chloroplast genomes: applications to the population genetics of trees. In: Ahuja R, Boerjan W, Neale D (eds) Somatic cell genetics and molecular genetics of trees, Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 233–238
Nicot N, Chiquet V, Gandon B, Amilhat L, Legeai F, Leroy P, Bernard M, Sourdille P (2004) Study of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from wheat expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Theor Appl Genet 109:800–805
Peakall R, Gilmore S, Keys W, Morgante M, Rafalski A (1998) Cross species amplification of soybean (Glycine max) simple sequence repeat (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera: implication for transferability of SSRs in plants. Mol Biol Evol 15:1275–1287
Pinto LR, Oliveira KM, Marconi T, Garcia AAF, Ulian EC, De Souza AP (2006) Characterization of novel sugarcane expressed sequence tag microsatellites and their comparison with genomic SSRs. Plant Breed 125:378–384
Puchooa D (2004) A simple, rapid and efficient method for the extraction of genomic DNA from lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Afr J Biotechnol 3(4):253–255
Rallo R, Dorado G, Martin A (2000) Development of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in olive tree (Oleaeuropacea L.). Theor Appl Genet 101:984–989
Ramakrishna W, Davierwala AP, Gupta VS, Ranjekar PK (1998) Expansion of (GA)n dinucleotide at a microsatellite locus associated repeats (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera. Biochem Genet 36:323–327
Rivera R, Edwards KJ, Barler JHA, Arnold GM, Ayad G, Hodgkin T, Karp A (1999) Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites in Cocos nucifera L. Genome 42(4):668–675
Roder MS, Korzun K, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Saha T, Roy CB, Nazeer MA (2005) Microsatellite variability and its use in the characterization of cultivated clones of Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Breed 124:86–92
Schultes RE (1990) A brief taxonomic view of the genus Hevea. In: MRRDB (ed) Monograph, vols 14, 57. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Seguin M, Gay C, Xiong T-C, Rodier-Goud M (2002) Microsatellite markers for genome analysis of rubber tree (Hevea spp.). In: Proceedings of the IRRDB symposium 2001—biotechnology and rubber tree, Cirad, Montpellier, France, 25–28 September 2001, Montpellier, France
Squirrell J, Hollingsworth PM, Woodhead M, Russell J, Lowe AJ, Gibby M, Powell W (2003) How much effort is required to isolate nuclear microsatellites from plant? Mol Ecol 12:1339–1348
Steinkellner H, Lexer C, Turetschek E, Glossl J (1997) Conservation of (GA)n microsatellite loci between Quercus species. Mol Ecol 6:1189–1194
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422
Tokuko U, Takayuki K, Yoshihiko T, Teruyoshi N, Hiroshi Y, Wickneswari R (1998) Development and polymorphism of simple sequence repeat DNA markers for Shorea curtisii and other Dipterocarpaceae species. Heredity 81:422–428
Varghese YA (2002) Management of the 1981 IRRDB germplasm collection in India. IRRDB plant breeding, agronomy and socio-economics joint workshop, 28 Aug–7 Sept, Malaysia and Indonesia
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genetic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Venkatachalam P, Priya P, Saraswathy Amma CK, Thulaseedharan A (2004) Identification, cloning and sequencing analysis of a dwarf genomic-specific RAPD marker in rubber tree [Hevea brasiliensis (Muell.)Arg.]. Plant Cell Rep 23:327–332
Venkatachalam P, Priya P, Gireesh T, Saraswathy Amma CK, Thulaseedharan A (2006) Molecular cloning and sequencing of a polymorphic band from rubber tree [Hevea brasiliensis (Muell.) Arg.]: the nucleotide sequence revealed partial homology with proline-specific permease gene sequence. Curr Sci 90(11):1510–1515
Wetmur JG (1991) DNA probes: applications of the principles of nucleic acid hybridization. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 26:227–259
Xie H, Sui Y, Chang FQ, Xu Y, Ma RC (2006) SSR allelic variation in almond (Prunus dulcis Mill.). Theor Appl Genet 112:366–372
Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Sawamura Y, Manabe T, Kotobuki K, Hayashi T (2002) Simple sequence repeat for genetic analysis in pear. Euphytica 124:129–137
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant of CATAS-ITBB (ITBBZD0715). We wish to express our faithful thanks to Yanling Xiao (Hainan University). Many thanks also go to Bennett and Bettina’s friendly and critical reading of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Bennett.
A contribution to the Special Issue: Plant Biotechnology in Support of the Millennium Development Goals.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, F., Wang, BH., Feng, SP. et al. Development, characterization, and cross-species/genera transferability of SSR markers for rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Plant Cell Rep 30, 335–344 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0908-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0908-7