Abstract
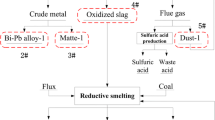
A complex copper dross containing Bi, Pb, Cu, As and Sb was processed in a 3.6 m2 industrial-scale oxygen-rich side-blown bath smelting furnace (OSBF). The products were collected and analyzed by chemical and mineralogical methods. Industrial statistical data showed that recoveries of Cu, Pb, Bi and Sb reached 87%, 96%, 97% and 60%, respectively. Slag composition indicated that the process can be divided into 2 steps, i.e., oxidative smelting and reductive smelting, due to the use of different oxygen-rich gas flow rate and enrichment. The effect of oxygen partial pressure (PO2) on the element partitioning was simulated by Factsage. The results indicated that increase of PO2 between 10–5 atm and 10–7 atm would significantly increase the partitioning of Cu, Pb, As and Sb to the slag; while element partitioning became almost independent of PO2 between 10–7.5 atm to 10–9.5 atm. Phase analysis for the slag indicated that the bath in the furnace was a “FeO”–CaO–SiO2–Al2O3–ZnO slag coexisting with solid spinels.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates C, DiMartini C (1986) Sodium treatment of copper dross. JOM 38(8):43–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03257788
Ohmsen GS (2001) Characterization of fugitive material within a primary lead smelter. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 51(10):1443–1451. https://doi.org/10.1080/10473289.2001.10464371
Xu B, Guo X, Deng Y, Xiong H, Yang B, Liu D, Jiang W (2018) Removal of sulfur from copper dross generated by refining lead. In: J-Y Hwang, T Jiang, MW Kennedy, D Gregurek, S Wang, B Zhao, O Yücel, E Keskinkilic, JP Downey, Z Peng, R Padilla (eds) 9th International symposium on high-temperature metallurgical processing, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, pp 259–267.
Klochko K (2020) Lead. mineral commodity summaries, U. S. Geol. Surv., USA, pp 94–95. https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2020/mcs2020-lead.pdf
Xiao H, Xie B, Chen L, Wang Z, Liu W, Zhang D, Yang T (2019) Metal Distribution behavior in copper dross smelting for enrichment. J Cent South Univ 50(7):1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.07.004
Guo X, Tian M, Wang S, Yan S, Wang Q, Yuan Z, Tian Q, Tang D, Li Z (2019) Element distribution in oxygen-enriched bottom-blown smelting of high-arsenic copper dross. JOM 71(11):3941–3948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03767-3
Yang C, Xu N, Jiang W, Liu D, Yang B, Liu F (2016) Recycling of copper dross by distillation and two-stage condensation in vacuum. Chin J Vac Sci Technol 36(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.13922/j.cnki.cjovst.2016.01.11
Yang M, Di J-C (2012) Pilot test on treatment of copper scum by bottom-blown furnace. China Nonferrous Metall 4:22–24
Zhang L, Wang Y-Y, Li X-B, Lu G-C, Wang Q-J (2016) Production practice of copper dross treatment with oxygen side-blowing furnace. China Nonferrous Metall 3:13–15
Chen L, Yang T, Bin S, Liu W, Zhang D, Bin W, Zhang L (2014) An efficient reactor for high-lead slag reduction process: oxygen-rich side blow furnace. JOM 66(9):1664–1669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1057-1
Cao L-B, Yang W (2017) Measures of improving the production index of copper scum reverberatory. Hunan Nonferrous Met 33(6):32–33
Bao C-J, Jia Z-H, Wu H-L, Ren Z-Y, Wei X, Wu Z-Y (2009) Industrial test for treating copper dross with converter. China Nonferrous Metall 3:27–28
Chen L, Hao Z, Yang T, Xiao H, Liu W, Zhang D, Bin S, Bin W (2015) An efficient technology for smelting low grade bismuth-lead concentrate: oxygen-rich side blow process. JOM 67(9):1997–2004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1491-8
Vernon PN, Burks SF (1997) The application of Ausmelt technology to base metal smelting, now and in the future. J S Afr Inst Min Metall 97(3):89–98
Chen L, Bin W, Yang T, Liu W, Bin S (2013) Research and industrial application of oxygen-rich side-blow bath smelting technology. In: Tao J, Hwang J-Y, Mackey PJ, Yucel O, Zhou G (eds) 4th international symposium on high-temperature metallurgical processing, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, pp 49–55
Zhang HL, Zhou CQ, Bing WU, Chen YM (2015) Numerical simulation of multiphase flow in a Vanyukov furnace. J Southern Afr Inst Mining Metall 115(5):457–463. https://doi.org/10.17159/2411-9717/2015/v115n5a14
Zhou S, Wei Y, Zhang S, Li B, Wang H, Yang Y, Barati M (2019) Reduction of copper smelting slag using waste cooking oil. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117668
Chen L, Hao Z, Yang T, Liu W, Zhang D, Zhang L, Bin S, Bin W (2015) A comparison study of the oxygen-rich side blow furnace and the oxygen-rich bottom blow furnace for liquid high lead slag reduction. JOM 67(5):1123–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1375-y
Taskinen P, Seppala K, Laulumaa J, Poijarvi J (2001) Oxygen pressure in the Outokumpu flash smelting furnace—Part 1: copper flash smelting settler. Trans Inst Min Metall Sect C-Miner Process Extr Metall 110:C94–C100
Matousek JW (2011) Oxidation potentials in lead and zinc smelting. JOM 63(12):63–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-011-0209-9
Bale CW, Bélisle E, Chartrand P, Decterov SA, Eriksson G, Gheribi AE, Hack K, Jung IH, Kang YB, Melançon J, Pelton AD, Petersen S, Robelin C, Sangster J, Spencer P, Van Ende MA (2016) FactSage thermochemical software and databases, 2010–2016. Calphad. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2016.05.002
Shishin D, Chen J, Hidayat T, Jak E (2019) Thermodynamic modeling of the Pb-As and Cu-Pb-As systems supported by experimental study. J Phase Equilibria Diffus 40(6):758–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-019-00764-6
Swinbourne DR, Kho TS (2012) Computational thermodynamics modeling of minor element distributions during copper flash converting. Metall Mater Trans B 43(4):823–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-012-9652-4
Coursol P, Cardona Valencia N, Mackey P, Bell S, Davis B (2012) Minimization of copper losses in copper smelting slag during electric furnace treatment. JOM 64(11):1305–1313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-012-0454-6
Liu H, Cui Z, Chen M, Zhao B (2016) Phase equilibria study of the ZnO-“FeO”-SiO2-Al2O3 system at PO2 10–8 atm. Metall Mater Trans B 47(2):1113–1123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0596-y
Zhao B, Hayes PC, Jak E (2010) Phase equilibria studies in the system ZnO-“FeO”-Al2O3-CaO-SiO2 relevant to imperial smelting furnace slags: Part I. Metall Mater Trans B 41(2):374–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9342-z
Zhao B, Hayes PC, Jak E (2010) Phase equilibria studies in the system ZnO-“FeO”-Al2O3-CaO-SiO2 relevant to imperial smelting furnace slags: Part II. Metall Mater Trans B 41(2):386–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9343-y
Zhao B, Hayes PC, Jak E (2011) Effects of Al2O3 and CaO/SiO2 ratio on phase equilibria in the ZnO-“FeO”-Al2O3-CaO-SiO2 system in equilibrium with metallic iron. Metall Mater Trans B 42(1):50–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9443-8
Shevchenko M, Jak E (2019) Experimental liquidus study of the binary PbO-CaO and ternary PbO-CaO-SiO2 systems. J Phase Equilibria Diffus 40(2):148–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-019-00705-3
Shevchenko M, Jak E (2019) Experimental liquidus study of the binary PbO-ZnO and ternary PbO-ZnO-SiO2 systems. Ceramics Int 45(6):6795–6803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.172
Shevchenko M, Jak E (2018) Experimental liquidus studies of the Pb-Fe-Si-O system in equilibrium with metallic Pb. Metall Mater Trans B 49(1):159–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1136-0
Chen M, Zhao B (2013) Viscosity measurement for copper smelting slags. Copper 2013: copper international conference. Santiago, Chile, pp 799–811
Acknowledgement
The financial support from National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1901604), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (No. 2018JJ3662), China Scholarship Council (No. 201706375005), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2018M632988) are gratefully acknowledged. Hunan Jinwang Bismuth Industrial Co., Ltd. is acknowledged for the industrial trial.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Sharif Jahanshahi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Xiao, H., Chen, J. et al. Oxygen-Rich Side-Blown Bath Smelting of Copper Dross: A Process Study. J. Sustain. Metall. 6, 344–354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00278-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-020-00278-3