Abstract
Purpose
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a state of leptin resistance which develops a vicious cycle of hyperinsulinemia and hyperleptinemia leading to aggravation of an inflammatory situation. This study was done to find out the association between IL-6, leptin and insulin in gestational diabetes among North Indian women.
Method
This cross-sectional study included 100 GDM, 100 non-GDM and 50 non-pregnant women. DIPSI (Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group India) criteria was used for screening GDM among pregnant women. GDM and non-GDM pregnant women were further categorized into three groups according to the trimester of pregnancy. Serum IL-6, leptin and insulin were measured in all the enrolled women.
Results
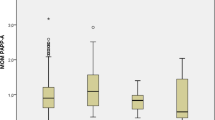
Serum IL-6 levels were significantly higher among GDM women as compared to non-GDM and non-pregnant women. Although the mean serum leptin and insulin levels were higher in GDM, but the difference was not statistically significant. When GDM and non-GDM women were categorized into three trimester, serum leptin levels were found to be significantly higher in 3rd trimester (p < 0.002) and IL-6 in 1st trimester (p < 0.017) among GDM women. No correlation was found between serum IL-6, leptin and insulin in GDM.
Conclusion
Absence of any significant association between leptin and IL-6 signifies that leptin may not be associated with inflammation in gestational diabetes. However, IL-6 may serve as an early marker for screening glucose intolerance during pregnancy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Margetic S, Gazzola C, Pegg GG, Hill RA. Leptin: a review of its peripheral actions and interactions. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002;26:1407–33.
Mantzoros CS, Magkos F, Brinkoetter M, Sienkiewicz E, Dardeno TA, Kim SY, et al. Leptin in human physiology and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;301:567–84.
Ceddia RB, Koistinen HA, Zierath JR, Sweeney G. Analysis of paradoxical observations on the association between leptin and insulin resistance. FASEB J. 2002;16:1163–76.
Al-Dahhri N, Bartlett WA, Jones AF, Kumar S. Role of leptin in glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Obes Metab. 2002;4:147–55.
Cervero A, Horcajadas JA, Dominguez F, Pellicer A, Simon C. Leptin system in embryo development and implantation: a protein in search of a function. Reprod Biomed Online. 2005;10(2):217–23.
Dos SE, Serazin V, Morvan C, Torre A, Wainer R, de Mazancourt P, et al. Adiponectin and leptin systems in human endometrium during window of implantation. Fertil Steril. 2012;97(3):771–78.
Mithal A, Bansal B, Kalra S. Gestational diabetes in India: Science and society. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;19(6):701–4.
Swaminathan G, Swaminathan A, Corsi DJ. Prevalence of gestational diabetes in India by Individual Socioeconomic, demographic, and clinical factors. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(11):e2025074.
Suhonem L, Hiilesma V, Teramo K. Glycemic control during early pregnancy and fetal malformations in women with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2000;43:79–82.
Gao XL, Yang HX, Zhao Y. Variations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, leptin and adiponectin in mid-trimester of gestational diabetes mellitus. Chin Med J (Engl). 2008;121:701–5.
Henson MC, Castracane VD. Leptin in pregnancy. Biol Reprod. 2000;63:1219–28.
Thagaard IN, Krebs L, Holm JC, Lange T, Larsen T, Christiansen M. Adiponectin and leptin as first trimester markers for gestational diabetes mellitus: a cohort study. Clin Chem Lab Med. Oct 2017;26(11):1805–12.
Perez-Perez A, Sanchez-Jimenez F, Maymo J, Duenas L, Varone J, Sanchez-Margalet C. Insulin and leptin signaling in placenta from gestational diabetic subjects. Horm Metab Res. 2015;48:62–9.
Perez-Perez A, Maym_o JL, Gambino YP, et al. Activated translation signaling in placenta from pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus: possible role of leptin. Horm Metab Res. 2013;45:436–42.
Dahlgren J. Pregnancy and insulin resistance. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2006;4(2):149–52.
Baban RS, Kasar KA, Al-Karawi IN. Fasting glucose to leptin ratio as a new diagnostic marker in patients with diabetes mellitus. Oman Med J. 2010;25(4):269–75.
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:85–97.
Kuzmicki M, Telejko B, Szamatowicz J, Zonenberg A, Nikolajuk A, Kretowski A, et al. High resistin and interleukin-6 levels are associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2009;25(4):258–63.
Sun D, Li F, Zhang Y, Xu X. Associations of the prepregnancy BMI and gestational BMI gain with pregnancy outcomes in chinese women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7:5784–9.
Kleiblova P, Dostalova I, Bartlova M, Lacinova Z, Ticha I, Krejci V, et al. Expression of adipokines and estrogen receptors in adipose tissue and placenta of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;314:150–6.
Agrawal S, Gollapudi S, Su H, Gupta S. Leptin activates human B cells to secrete TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 via JAK2/STAT3 and p38MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31:472–8
Anjalakshi C, Balaji V, Balaji MS et al. A single test procedure to diagnose gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2009; 46:51–4.
Saini V, Kataria M, Yadav A, Jain A. Role of leptin and adiponectin in gestational diabetes mellitus: a study in a north indian tertiary care hospital. Inter J Medi Update. 2015;10:11–4.
Imoh LC, Ocheke AN. Correlation between maternal weight and insulin resistance in second half of pregnancy. Niger Med J. 2014;55(6):465–8.
Pieczynska J, Płaczkowska S, Pawlik-Sobecka L, Kokot I, Sozanski R, Grajeta H. Association of Dietary Inflammatory Index with serum IL-6, IL-10, and CRP concentration during pregnancy. Nutrients. 2020;12(9):2789.
Mokhtari M, Hashemi M, Yaghmaei M, Naderi M, Shikhzadeh A, Ghavami S. Evaluation of the serum leptin in normal pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus in Zahedan, southeast Iran. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2011;284:539–42.
Saucedo R, Zarate A, Basurto L, Hernandez M, Puello E, Galvan R, et al. Relationship between circulating adipokines and insulin resistance during pregnancy and postpartum in women with gestational diabetes. Arch Med Res. 2011;42:318–23.
Simmons D, Breier BH. Fetal over nutrition in polynesian pregnancies and in gestational diabetes may lead to dysregulation of the adipoinsular axis in offspring. Diabet Care. 2002;25:1539–44.
Goel R, Chugh K, Duhan N, Ghalaut VS, Kumar HD, Sehgal PK, et al. Maternal serum leptin concentration in gestational diabetes mellitus. Imp J Interdisp Res. 2016;2(2):2454–1362.
Kautzky-Willer A, Pacini G, Tura A, Bieglmayer C, Schneider B, Ludvik B, Prager R, Waldhäusl W. Increased plasma leptin in gestational diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001;44:164–72.
Noureldeen AF, Qusti SY, Al-Seeni MN, Bagais MH. Maternal leptin, adiponectin, resistin, visfatin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in normal and gestational diabetes. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014;29:462–70.
Shalayel MHF, Al-Noaemi MC, Ahmed SA. In: Radenkovic M, editor. Insulin resistance in the third trimester of pregnancy suffering from gestational diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance. Gestational Diabetes, Croatia: In Tech; 2011 In.
Fakhrul-Alam M, Sharmin-Jahan M-H, Rakibul-Hasan Nusrat-SultanaMohona-Zaman. Insulin secretory defect may be the major determinant of GDM in lean mothers. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2020;20:100226.
Wang X, Yang T, Miao J, Liu H, Wu K, Guo J, et al. Correlation between maternal and fetal insulin resistance in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin Lab. 2018;64:945–53.
Sarma GD, Khemka VK, Sanyal R, Hossaini SSA, Mitra A. Altered interleukin 6 level in gestational diabetes across eastern India. Int J Health Clin Res. 2021;4:182–5.
Wang Q, Huang R, Yu B, Cao F, Wang H, Zhang M, et al. Higher fetal insulin resistance in chinese pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus and correlation with maternal insulin resistance. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e59845.
Yang Y, Liu L, Liu B, Li Q, Wang Z, Fan S, et al. Functional defects of regulatory T cell through interleukin 10 mediated mechanism in the induction of gestational diabetes mellitus. DNA Cell Bio. 2018;37:278–85.
Hassiakos D, Eleftheriades M, Papastefanou I, Lambrinoudaki I, Kappou D, Lavranos D, et al. Increased maternal serum interleukin-6 concentrations at 11 to 14 weeks of gestation in low-risk pregnancies complicated with gestational diabetes mellitus: development of a prediction model. Horm Metab Res. 2016;48:35–41.
Abell SK, Shorakae S, Harrison CL, Hiam D, Moreno- Asso A, Stepto NK, et al. The association between dysregulated adipocytokines in early pregnancy and development of gestational diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017;33:26–9.
Lain KY, Daftary AR, Ness RB, Roberts JM. First trimester adipocytokine concentrations and risk of developing gestational diabetes later in pregnancy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008;69:407–11.
Braga FO, Negrato CA, Matta MFBD, Carneiro JR, Gomes MB. Relationship between inflammatory markers, glycated hemoglobin and placental weight on fetal outcomes in women with gestational diabetes. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2019;63:22–9.
Simjak P, Cinkajzlova A, Anderlova K, Kloučkova J, Kratochvilova H, Lacinova Z, et al. Changes in plasma concentrations and mRNA expression of hepatokines fetuin A, fetuin B and FGF21 in physiological pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus. Physiol Res. 2018;67:531–42.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Council of Science and Technology, U.P., India (UPCST) for providing financial support during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by our Institutional (King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India) Ethical Committee. Informed and written consent was obtained from all the enrolled participants.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, N., Singh, K., Singh, N. et al. Association between serum interleukin-6, leptin and insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus – a cross- sectional study. J Diabetes Metab Disord 22, 639–648 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01188-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01188-3