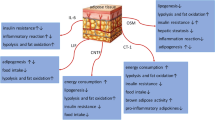
Abstract
Childhood obesity is a chronic inflammatory epidemic that affects children worldwide. Obesity affects approximately 1 in 5 children worldwide. Obesity in children can worsen weight gain and raise the risk of obesity-related comorbidities like diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). It can also negatively impact the quality of life for these children. Obesity disrupts immune system function, influencing cytokine (interleukins) balance and expression levels, adipokines, and innate and adaptive immune cells. The altered expression of immune system mediators, including interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8), interleukin-17 (IL-17), interleukin-18 (IL-18), transforming growth factor (TGF), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and others, caused inflammation, progression, and the development of pediatric obesity and linked illnesses such as diabetes and NAFLD. Furthermore, anti-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-2 (IL-2), have been shown to have anti-diabetes and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) anti-diabetic and pro-NAFLFD properties, and interleukin-10 (IL-10) has been shown to have a dual role in managing diabetes and anti-NAFLD. In light of the substantial increase in childhood obesity-associated disorders such as diabetes and NAFLD and the absence of an effective pharmaceutical intervention to inhibit immune modulation factors, it is critical to consider the alteration of immune system components as a preventive and therapeutic approach. Thus, the current review focuses on the most recent information regarding the influence of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (interleukins) and their molecular mechanisms on pediatric obesity-associated disorders (diabetes and NAFLD). Furthermore, we discussed the current therapeutic clinical trials in childhood obesity-associated diseases, diabetes, and NAFLD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- IL-1:
-
Interleukin-1
- IL-2:
-
Interleukin-2
- IL-3:
-
Interleukin-3
- IL-4:
-
Interleukin-4
- IL-5:
-
Interleukin-5
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-7:
-
Interleukin-7
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- IL-9:
-
Interleukin-9
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin-10
- IL-11:
-
Interleukin-11
- IL-12:
-
Interleukin-12
- IL-13:
-
Interleukin-13
- IL-14:
-
Interleukin-14
- IL-15:
-
Interleukin-15
- IL-16:
-
Interleukin-16
- IL-17:
-
Interleukin-17
- IL-18:
-
Interleukin-18
- IL-21:
-
Interleukin-21
- IL-23:
-
Interleukin-23
- GM-CSF:
-
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
- MIG:
-
Monokine Induced by Gamma
- IP-10:
-
Interferon Gamma-Induced Protein 1
- TGF-1β:
-
Transforming Growth Factor -I beta
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-Gamma
- LDL:
-
Low-Density Lipoproteins
- HDL:
-
High-Density Lipoproteins
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1
- AST:
-
Aspartate Aminotransferase
- ALT:
-
Alanine Transaminase
- JAK/STAT3:
-
Janus Kinase/Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 3
- HOMA-IR:
-
Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance
- TNFSF:
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily
- PDFF:
-
Proton Density Fat-Fraction
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- GDF15:
-
Growth Differentiation Factor 15
References
Collaboration NRF. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–42.
World Health Organization. Draft recommendations for the prevention and management of obesity over the life course, including potential targets. 2021.
Lange SJ, Kompaniyets L, Freedman DS, Kraus EM, Porter R, et al. Longitudinal trends in Body Mass Index before and during the COVID-19 pandemic among persons aged 2–19 years — United States, 2018–2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1278–83.
Ling J, Chen S, Zahry NR, Kao TSA. Economic burden of childhood overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2023;24:e13535.
Carsley S, Tu K, Parkin PC, Pullenayegum E, Birken CS. Overweight and obesity in preschool aged children and risk of mental health service utilization. Int J Obes. 2019;43:1325–33.
Mamrot P, Hanć T. The association of the executive functions with overweight and obesity indicators in children and adolescents: a literature review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019;107:59–68.
Davies S. Time to Solve Childhood Obesity: An Independent Report by the Chief Medical Officer. 2019.
Duan Y, Luo J, Pan X, Wei J, Xiao X, Li J, et al. Association between inflammatory markers and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Front Public Heal. 2022;10:991393.
Tagi VM, Giannini C, Chiarelli F. Insulin resistance in children. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:1–13.
Chait A, den Hartigh LJ. Adipose tissue distribution, inflammation and its metabolic consequences, including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:1–41.
Powell-Wiley TM, Poirier P, Burke LE, Després JP, Gordon-Larsen P, Lavie CJ, et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:E984–1010.
Yang F, Dawes P, Leroi I, Gannon B. Measurement tools of resource use and quality of life in clinical trials for dementia or cognitive impairment interventions: a systematically conducted narrative review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;33:e166–76.
Liu C, Chu D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, George J, Young HA, Liu G. Cytokines: from clinical significance to quantification. Adv Sci. 2021;8:2004433.
Marshall JS, Warrington R, Watson W, Kim HL. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018;14:49.
Ragab D, Salah Eldin H, Taeimah M, Khattab R, Salem R. The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1–4.
Amere Subbarao S. Cancer vs. SARS-CoV-2 induced inflammation, overlapping functions, and pharmacological targeting. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29:343–66.
Bhasin E, Mishra S, Pathak G, Chauhan PS, Kulshreshtha A. Cytokine database of stress and metabolic disorders (CdoSM): a connecting link between stress and cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes and obesity. 3 Biotech. 2022;12:1–12.
Kany S, Vollrath JT, Relja B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:6008.
Wautier JL, Wautier MP. Pro- and anti-inflammatory prostaglandins and cytokines in humans: a Mini Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:9647.
Mărginean CO, Meliţ LE, Huțanu A, Ghiga DV, Săsăran MO. The adipokines and inflammatory status in the era of pediatric obesity. Cytokine. 2020;126:4–9.
Feldman A, Aigner E, Weghuber D, Paulmichl K. The potential role of iron and copper in pediatric obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:7.
Ullah A, Ud Din A, Ding W, Shi Z, Pervaz S, Shen B. A narrative review: CXC chemokines influence immune surveillance in obesity and obesity-related diseases: type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023;4:611–31.
Moghbeli M, Khedmatgozar H, Yadegari M, Avan A, Ferns GA, Ghayour Mobarhan M. Cytokines and the immune response in obesity-related disorders. Adv Clin Chem. 1st ed. 2021. p. 135–68.
Peña A, Olson ML, Ayers SL, Sears DD, Vega-López S, Colburn AT, et al. Inflammatory mediators and type 2 diabetes risk factors before and in response to Lifestyle intervention among latino adolescents with obesity. Nutrients. 2023;15:2442.
Stoppa-Vaucher S, Dirlewanger MA, Meier CA, De Moerloose P, Reber G, Roux-Lombard P, et al. Inflammatory and prothrombotic states in obese children of European descent. Obesity. 2012;20:1662–8.
Ruotsalainen E, Salmenniemi U, Vauhkonen I, Pihlajam̈aki J, Punnonen K, Kainulainen S, et al. Changes in inflammatory cytokines are related to impaired glucose tolerance in offspring of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2714–20.
Aygun AD, Gungor S, Ustundag B, Gurgoze MK, Sen Y. Proinflammatory cytokines and leptin are increased in serum of prepubertal obese children. Mediators Inflamm. 2005;2005:180–3.
Rohm TV, Meier DT, Olefsky JM, Donath MY. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity. 2022;55:31–55.
Nicol LE, Grant WF, Comstock SM, Nguyen ML, Smith MS, Grove KL, et al. Pancreatic inflammation and increased islet macrophages in insulin-resistant juvenile primates. J Endocrinol. 2013;217:207–13.
Almheiri A, Alhammadi A, AlShehhi, Fatima Mohammad A, Alshamsi R, Alzaman K, Jabeen S, et al. Biomarkers for Prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and Associated complications. Am J Heal Med Nurs Pract. 2023;9:pp1–21.
Flisiak-Jackiewicz M, Bobrus-Chociej A, Tarasów E, Wojtkowska M, Białokoz-Kalinowska I, Lebensztejn DM. Predictive Role of Interleukin-18 in Liver Steatosis in Obese Children. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;2018.
Dong G, Liang L, Fu J, Zou C. Serum interleukin-18 levels are raised in diabetic ketoacidosis in Chinese children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Indian Pediatr. 2007;44:732–6.
Svensson J, Eising S, Hougaard DM, Mortensen HB, Skogstrand K, Simonsen LB, et al. Few differences in cytokines between patients newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes and their healthy siblings. Hum Immunol. 2012;73:1116–26.
Heier M, Margeirsdottir HD, Brunborg C, Hanssen KF, Dahl-Jørgensen K, Seljeflot I. Inflammation in childhood type 1 diabetes: influence of glycemic control. Atherosclerosis. 2015;238:33–7.
Harms RZ, Yarde DN, Guinn Z, Lorenzo-Arteaga KM, Corley KP, Cabrera MS, et al. Increased expression of IL-18 in the serum and islets of type 1 diabetics. Mol Immunol. 2015;64:306–12.
Jung C, Gerdes N, Fritzenwanger M, Figulla HR. Circulating levels of interleukin-1 family cytokines in overweight adolescents. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:1–7.
Khalil RG, Abdel-Moneim A, Yousef AI, Abdel-Rahman H, Zanaty MI, El-Sayed A. Association of interleukin-2, interleukin-21 and interleukin-23 with hyperlipidemia in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48:5421–33.
Iacomino G, Siani A. Role of microRNAs in obesity and obesity-related diseases. Genes Nutr. 2017;12:1223.
Mohany KM, Rugaie O, Al, Al-wutayd O, Al-nafeesah A. Investigation of the levels of circulating miR-29a, miR-122, sestrin 2 and inflammatory markers in obese children with/without type 2 diabetes: a case control study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021;21:21.
Reinehr T. Inflammatory markers in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. p. 100–7.
Smitka K, Marešová D. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ: an update on pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory microenvironment. Prague Med Rep. 2015;116:87–111.
Hagman E, Besor O, Hershkop K, Santoro N, Pierpont B, Mata M, et al. Relation of the degree of obesity in childhood to adipose tissue insulin resistance. Acta Diabetol. 2019;56:219–26.
Flores-Cortez YA, Barragán-Bonilla MI, Mendoza-Bello JM, González-Calixto C, Flores-Alfaro E, Espinoza-Rojo M. Interplay of retinol binding protein 4 with obesity and associated chronic alterations (review). Mol Med Rep. 2022;26:244.
Balagopal P, Graham TE, Kahn BB, Altomare A, Funanage V, George D. Reduction of elevated serum retinol binding protein in obese children by lifestyle intervention: Association with subclinical inflammation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1971–4.
Camilli C, Hoeh AE, De Rossi G, Moss SE, Greenwood J. LRG1: an emerging player in disease pathogenesis. J Biomed Sci. 2022;29:1–29.
Alhammad R, Abu-Farha M, Hammad MM, Thanaraj TA, Channanath A, Alam-Eldin N, et al. Increased LRG1 levels in overweight and obese adolescents and its association with Obesity Markers, including leptin, Chemerin, and high sensitivity C-Reactive protein. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:1–11.
El-Alameey IR, Fadl NN, Abdel Hameed ER, Sherif LS, Ahmed HH. Clinical relevance of transforming growth factor-β1, interleukin-6 and haptoglobin for prediction of obesity complications in prepubertal Egyptian children. Maced J Med Sci. 2015;3:105–10.
Serbis A, Giapros V, Challa A, Chaliasos N, Siomou E. Elevated 1-hour post-load plasma glucose identifies obese youth with abnormal glucose metabolism and an unfavourable inflammatory profile. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;89:757–64.
Lopez-Sandoval J, Sanchez-Enriquez S, Rivera-Leon EA, Bastidas-Ramirez BE, Garcia-Garcia MR, Gonzalez-Hita ME. Cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents: role of insulin resistance and obesity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 2018;14:330–7.
Oluwagbemigun K, Buyken AE, Alexy U, Schmid M, Herder C, Nöthlings U. Developmental trajectories of body mass index from childhood into late adolescence and subsequent late adolescence-young adulthood cardiometabolic risk markers. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18:1–14.
Snell-Bergeon JK, West NA, Mayer-Davis EJ, Liese AD, Marcovina SM, D’Agostino RB, et al. Inflammatory markers are increased in youth with type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH case-control study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95:2868–76.
G B, U M. Selected cytokines (Il-6, Il-8, Il-10, MCP-1, TNF-alpha) in children and adolescents with atherosclerosis risk factors: obesity, hypertension, diabetes. Wiad Lek (Warsaw Pol 1960). 2003;56:109–16.
Nascimento H, Vieira E, Coimbra S, Catarino C, Costa E, Bronze-Da-Rocha E, et al. Adipokine gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Portuguese obese adolescents: associations with plasma concentrations of adiponectin, resistin, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. Child Obes. 2016;12:300–13.
Tam CS, Garnett SP, Cowell CT, Heilbronn LK, Lee JW, Wong M, et al. IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 levels in healthy weight and overweight children. Horm Res Paediatr. 2010;73:128–34.
Utsal L, Tillmann V, Zilmer M, Mäestu J, Purge P, Jürimäe J, et al. Elevated serum IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, CRP, and IFN-γ levels in 10- to 11-year-old boys with increased BMI. Horm Res Paediatr. 2012;78:31–9.
Moschen HTAR. Christian. Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol Med. 2008;103:398–406.
Zhang C. The role of inflammatory cytokines in endothelial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103:398–406.
Erbaǧci AB, Tarakçioǧlu M, Coşkun Y, Sivasli E, Sibel Namiduru E. Mediators of inflammation in children with type I diabetes mellitus: cytokines in type I diabetic children. Clin Biochem. 2001;34:645–50.
Roth CL, Kratz M, Ralston MM, Reinehr T. Changes in adipose-derived inflammatory cytokines and chemokines after successful lifestyle intervention in obese children. Metabolism. 2011;60:445–52.
Herder C, Baumert J, Thorand B, Martin S, Löwel H, Kolb H, et al. Chemokines and incident coronary heart disease: results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg case-cohort study, 1984–2002. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2147–52.
Zeyda M, Farmer D, Todoric J, Aszmann O, Speiser M, Györi G, et al. Human adipose tissue macrophages are of an anti-inflammatory phenotype but capable of excessive pro-inflammatory mediator production. Int J Obes. 2007;31:1420–8.
Zeyda M, Stulnig TM. Adipose tissue macrophages. Immunol Lett. 2007;112:61–7.
Bhatt SP, Guleria R, Kabra SK. Metabolic alterations and systemic inflammation in overweight/obese children with obstructive sleep apnea. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:1–14.
Lima RS, Mattos RT, Medeiros NI, Kattah FM, Julya R, Nascimento S, et al. CXCL8 expression and methylation are correlated with anthropometric and metabolic parameters in childhood obesity. Cytokine. 2021;143:155538.
Abdelhamid ER, Kamhawy AH, Ahmed HH, Abu Shady MM, Eladawy R, Megawer AS, et al. Role of inflammatory cytokines in obese and nonobese Diabetic Children. Maced J Med Sci. 2020;8:858–65.
Kupca S, Jurka A, Marksa I, Rinkuza I, Sipols AJ, Rumba-Rozenfelde I. Inflammatory cytokine IFNγ, IL-6, and IL-10 association with childhood obesity. Proc Latv Acad Sci Sect B Nat Exact Appl Sci. 2021;75:387–91.
ES AA, D FEA, H DA, M DS, AA MGED, E NA, et al. Utility of Adipokines and IL-10 in Association with Anthropometry in prediction of insulin resistance in obese children. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15:3231–41.
Lauridsen JK, Olesen RH, Vendelbo J, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Bibby BM, et al. High BMI levels associate with reduced mRNA expression of IL10 and increased mRNA expression of iNOS (NOS2) in human frontal cortex. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1044–7.
Yao CJ, Du W, Chen HB, Xiao S, Wang CH, Fan ZL. Associations of IL-10 gene polymorphisms with acute myeloid leukemia in Hunan, China. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2439–42.
Kulshrestha H, Gupta V, Mishra S, Mahdi AA, Awasthi S, Kumar S. Interleukin-10 as a novel biomarker of metabolic risk factors. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. 2018;12:543–7.
Chang JS, Bai CH, Huang ZC, Owaga E, Chao KC, Chang CC, et al. Interleukin 10 and clustering of metabolic syndrome components in pediatrics. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014;44:384–94.
Liu Y, Xu D, Yin C, Wang S, Wang M, Xiao Y. IL-10/STAT3 is reduced in childhood obesity with hypertriglyceridemia and is related to triglyceride level in diet-induced obese rats. BMC Endocr Disord. 2018;18:1–9.
Toubal A, Kiaf B, Beaudoin L, Cagninacci L, Rhimi M, Fruchet B et al. Mucosal-associated invariant T cells promote inflammation and intestinal dysbiosis leading to metabolic dysfunction during obesity. Nat Commun. 2020;11.
Carolan E, Tobin LM, Mangan BA, Corrigan M, Gaoatswe G, Byrne G, et al. Altered distribution and increased IL-17 production by Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells in adult and childhood obesity. J Immunol. 2015;194:5775–80.
Bergin R, Kinlen D, Kedia-Mehta N, Hayes E, Cassidy FC, Cody D, et al. Mucosal-associated invariant T cells are associated with insulin resistance in childhood obesity, and disrupt insulin signalling via IL-17. Diabetologia. 2022;65:1012–7.
Guo S, Mao X, Liu J. Multi-faceted roles of C1q/TNF-related proteins family in atherosclerosis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1253433.
Arking A, Sarver DC, Magge SN, Wong GW, Wolf RM. Novel adipokines CTRP1, CTRP9, and FGF21 in Pediatric Type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional analysis. Horm Res Paediatr. 2022;95:43–50.
Wolf RM, Jaffe AE, Rodriguez S, Lei X, Sarver DC, Straub AT, et al. Altered adipokines in obese adolescents: a cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis across the spectrum of glycemia. Am J Physiol - Endocrinol Metab. 2021;320:E1044–52.
Erbaş İM, Paketçi A, Turan S, Şişman AR, Demir K, Böber E, et al. Low complement C1q/TNF-related Protein-13 levels are Associated with childhood obesity but not binge eating disorder. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2022;14:179–87.
Shanaki M, Fadaei R, Moradi N, Emamgholipour S, Poustchi H. The circulating CTRP13 in type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic. Fat Liver Patients. 2016;1–11.
Rosa JS, Mitsuhashi M, Oliver SR, Ogura M, Flores RL, Pontello AM, et al. Ex vivo TCR-induced leukocyte gene expression of inflammatory mediators is increased in type 1 diabetic patients but not in overweight children. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2014;32:13–23.
Redondo M, Rodriguez L, Haymond M, Hampe C, Smith E, Balasubramanyam A, et al. Serum adiposity-induced biomarkers in obese and lean children with recently diagnosed autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;15:543–9.
Pawelczak M, Rosenthal J, Milla S, Liu YH, Shah B. Evaluation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis Factor-α in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2014;27:356–9.
El-Ayash H, Puyau M, Bacha F, Hyperglycemia. A determinant of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in youth with obesity across the spectrum of glycemic regulation. Pediatr Obes. 2023;18:1–8.
Achenbach P, Hippich M, Zapardiel-Gonzalo J, Karges B, Holl RW, Petrera A, et al. A classification and regression tree analysis identifies subgroups of childhood type 1 diabetes. eBioMedicine. 2022;82:104118.
Wankhade UD, Lee JH, Dagur PK, Yadav H, Shen M, Chen W, et al. TGF-β receptor 1 regulates progenitors that promote browning of white fat. Mol Metab. 2018;16:160–71.
Lee MJ. Transforming growth factor beta superfamily regulation of adipose tissue biology in obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864:1160–71.
Noori S, Mirzababaei A, Shiraseb F, Bagheri R, Clark CCT, Wong A et al. The Association of Inflammatory Markers, IL-1 α and TGF- β, with Dietary Insulin Load and Dietary Insulin Index in Overweight and Obese Women with Healthy and Unhealthy Metabolic Phenotypes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022.
Kinik ST, Özbek N, Yuce M, Yazici AC, Verdi H, Ataç FB. PAI-1 gene 4G/5G polymorphism, cytokine levels and their relations with metabolic parameters in obese children. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:352–6.
Kanra AR, Tulgar-Kinik S, Verdi H, Belgin Ataç F, Yazici AC, Özbek N. Transforming growth factor-beta1 (509 C/T, 915 G/C, 869 T/C) polymorphisms are not related to obesity in Turkish children. Turk J Pediatr. 2011;53:645–50.
Fain JN, Tichansky DS, Madan AK. Transforming growth factor β1 release by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity. Metabolism. 2005;54:1546–51.
Mattos RT, Medeiros NI, Menezes CA, Fares RCG, Franco EP, Dutra WO, et al. Chronic low-grade inflammation in childhood obesity is associated with decreased il-10 expression by monocyte subsets. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:1–14.
Makowski LM, Leffers M, Waltenberger J, Pardali E. Transforming growth factor-β1 signalling triggers vascular endothelial growth factor resistance and monocyte dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:5316–25.
Correia-Costa L, Morato M, Sousa T, Cosme D, Guimarães JT, Guerra A, et al. Urinary fibrogenic cytokines ET-1 and TGF-β1 are associated with urinary angiotensinogen levels in obese children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2016;31:455–64.
Mirea AM, Tack CJ, Chavakis T, Joosten LAB, Toonen EJM. IL-1 family cytokine pathways underlying NAFLD: towards New Treatment Strategies. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24:458–71.
Pihlajamäki J, Kuulasmaa T, Kaminska D, Simonen M, Kärjä V, Grönlund S, et al. Serum interleukin 1 receptor antagonist as an independent marker of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in humans. J Hepatol. 2012;56:663–70.
Lischka J, Schanzer A, Hojreh A, Ba-Ssalamah A, de Gier C, Valent I, et al. Circulating microRNAs 34a, 122, and 192 are linked to obesity-associated inflammation and metabolic disease in pediatric patients. Int J Obes. 2021;45:1763–72.
Perito ER, Ajmera V, Bass NM, Rosenthal P, Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB, et al. Association between cytokines and liver histology in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Commun. 2017;1:609–22.
Fain JN. Release of inflammatory mediators by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity and primarily by the nonfat cells: A review. Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010.
Tragomalou A, Paltoglou G, Manou M, Kostopoulos IV, Loukopoulou S, Binou M, et al. Non-traditional Cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents with obesity and metabolic syndrome May Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients. 2023;15:4342.
Mandato C, Lucariello S, Licenziati MR, Franzese A, Spagnuolo MI, Ficarella R, et al. Metabolic, hormonal, oxidative, and inflammatory factors in pediatric obesity-related liver disease. J Pediatr. 2005;147:62–6.
de Assunção SNF, Sorte NCAB, Alves CDAD, Mendes PSA, Alves CRB, Silva LR. Inflammatory cytokines and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in obese children and adolescents. Nutr Hosp. 2018;35:78–83.
Das SK, Balakrishnan V. Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2011;26:202–9.
Crudele A, Dato S, Re O, Lo, Maugeri A, Sanna P, Giallongo S, et al. Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is affected by Genetic Variants Involved in Lifespan/Healthspan. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021;73:161–8.
El Amrousy D, El-Afify D. Osteocalcin and osteoprotegerin levels and their relationship with adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cytokine. 2020;135:155215.
Zolfaghari H, Askari G, Siassi F, Feizi A, Sotoudeh G. Intake of nutrients, fiber, and sugar in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in comparison to healthy individuals. Int J Prev Med. 2016;2016August.
Skaaby T, Husemoen LLN, Borglykke A, Jørgensen T, Thuesen BH, Pisinger C, et al. Vitamin D status, liver enzymes, and incident liver disease and mortality: a general population study. Endocrine. 2014;47:213–20.
Roth CL, Elfers CT, Figlewicz DP, Melhorn SJ, Morton GJ, Hoofnagle A, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in obese rats exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and increases hepatic resistin and toll-like receptor activation. Hepatology. 2012;55:1103–11.
Loureiro C, Martínez-Aguayo A, Campino C, Carvajal C, Fardella C, García H. Hepatic steatosis as diabetes type 2 predictor. Nutr Hosp. 2014;29:350–8.
Nier A, Brandt A, Conzelmann IB, Özel Y, Bergheim I. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in overweight children: role of fructose intake and dietary pattern. Nutrients. 2018;10:1329.
Ceccarelli S, Panera N, Mina M, Gnani D, Crudele CDSA, Rychlicki C, et al. LPS-induced TNF-alpha factor mediates pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic pattern in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Oncotarget. 2015;6:34–52.
Hernández MJG, Klünder M, Nieto NG, Alvarenga JCL, Gil JV, Huerta SF, et al. Pediatric Visceral Adiposity Index Adaptation correlates with Homa-IR, Matsuda, and transaminases. Endocr Pract. 2018;24:294–301.
Jonas W, Schürmann A. Genetic and epigenetic factors determining NAFLD risk. Mol Metab. 2021;50:101111.
Dongiovanni P, Crudele A, Panera N, Romito I, Meroni M, De Stefanis C, et al. β-Klotho gene variation is associated with liver damage in children with NAFLD. J Hepatol. 2020;72:411–9.
Cabrera D, Cabello-Verrugio C, Solís N, Martín DS, Cofré C, Pizarro M, et al. Somatotropic axis dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: beneficial hepatic and systemic effects of hormone supplementation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:1339.
Mosca A, Della Volpe L, Alisi A, Panera N, Maggiore G, Vania A. The role of the GH/IGF1 Axis on the development of MAFLD in Pediatric patients with obesity. Metabolites. 2022;12:1221.
Kim JS, Lê KA, Mahurkar S, Davis JN, Goran MI. Influence of elevated liver fat on circulating adipocytokines and insulin resistance in obese hispanic adolescents. Pediatr Obes. 2012;7:158–64.
Shi JQ, Shen WX, Wang XZ, Huang K, Zou CC. Relationship between immune parameters and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Indian Pediatr. 2017;54:825–9.
Abdallah A, El Mashad G. Interleukin 10, thyroid status and ferritin are non-invasive prognostic biomarkers for diagnosis of fatty liver disease in children. J Int Res Med. 2015;8:85–93.
Kim HM, Lee BR, Lee ES, Kwon MH, Huh JH, Kwon BE, et al. INKT cells prevent obesity-induced hepatic steatosis in mice in a C-C chemokine receptor 7-dependent manner. Int J Obes. 2018;42:270–9.
Mosca A, Crudele A, Smeriglio A, Braghini MR, Panera N, Comparcola D, et al. Antioxidant activity of Hydroxytyrosol and vitamin E reduces systemic inflammation in children with paediatric NAFLD. Dig Liver Dis. 2021;53:1154–8.
Loomba R, Friedman SL, Shulman GI. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. 2021;184:2537–64.
Zhang C, Yang M, Ericsson AC. The potential gut microbiota-mediated treatment options for Liver Cancer. Front Oncol. 2020;10:1–8.
Cairoli V, De Matteo E, Rios D, Lezama C, Galoppo M, Casciato P, et al. Hepatic lymphocytes involved in the pathogenesis of pediatric and adult non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2021;11:1–10.
Akbulut UE, Emeksiz HC, Citli S, Cebi AH, Korkmaz HAA, Baki G. IL-17A, MCP-1, CCR-2, and ABCA1 polymorphisms in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2019;95:350–7.
Barretto JR, Boa-Sorte N, Vinhaes CL, Malta-Santos H, Rebouças-Silva J, Ramos CF, et al. Heightened plasma levels of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and increased degree of systemic biochemical perturbation characterizes hepatic steatosis in overweight pediatric patients: a cross-sectional study. Nutrients. 2020;12:1650.
Galuppo B, Agazzi C, Pierpont B, Chick J, Li Z, Caprio S, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in youth with overweight or obesity. Nutr Diabetes. 2022;12:15–8.
Ibrahim SH, Hirsova P, Gores GJ. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis pathogenesis: sublethal hepatocyte injury as a driver of liver inflammation. Gut. 2018;67:963–72.
Alisi A, Nobili V, Ceccarelli S, Panera N, De Stefanis C, De Vito R, et al. Plasma high mobility group box 1 protein reflects fibrosis in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2014;14:763–71.
Mittal M, Jain V. Management of obesity and its complications in children and adolescents. Indian J Pediatr. 2021;88:1222–34.
Della L, Codella R. Cytokine and growth factor reviews Exercise tolls the bell for key mediators of low-grade inflammation in dysmetabolic conditions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021;62:83–93.
Rosa JS, Heydari S, Oliver SR, Flores RL, Pontello AM, Ibardolaza M, et al. Inflammatory cytokine profiles during exercise in obese, diabetic, and healthy children. JCRPE J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2011;3:115–21.
Rosa JS, Oliver SR, Flores RL, Ngo J, Milne GL, Zaldivar FP, et al. Altered inflammatory, oxidative, and metabolic responses to exercise in pediatric obesity and type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2011;12:464–72.
Kim JS, Lee YH, Kim JC, Ko YH, Yoon CS, Yi HK. Effect of exercise training of different intensities on anti-inflammatory reaction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biol Sport. 2014;31:73–9.
Simpson RJ, Kunz H, Agha N, Graff R. Exercise and the regulation of Immune functions. Mol Cell Regul Adapt Exerc. 2015.
Nash D, Hughes MG, Butcher L, Aicheler R, Smith P, Cullen T, et al. IL-6 signaling in acute exercise and chronic training: potential consequences for health and athletic performance. Scand J Med Sci Sport. 2022;33:4–19.
Steensberg A, Fischer CP, Keller C, Møller K, Pedersen BK. IL-6 enhances plasma IL-1ra, IL-10, and cortisol in humans. Am J Physiol - Endocrinol Metab. 2003;285:433–7.
Aminianfar FAMFA, Shirzad KDN, Larijani CCTCB. The effect of Mediterranean diet on inflammatory biomarkers and components of metabolic syndrome in adolescent girls. J Endocrinol Invest. 2023;46:1995–2004.
Valle-Martos R, Jiménez-Reina L, Cañete R, Martos R, Valle M, Cañete MD. Changes in liver enzymes are associated with changes in insulin resistance, inflammatory biomarkers and leptin in prepubertal children with obesity. Ital J Pediatr. 2023;49:1–10.
Ye C, Brand D, Zheng SG, Targeting. IL-2: an unexpected effect in treating immunological diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018;3:2.
Rosenzwajg M, Salet R, Lorenzon R, Tchitchek N, Roux A, Bernard C, et al. Low-dose IL-2 in children with recently diagnosed type 1 diabetes: a phase I/II randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study. Diabetologia. 2020;63:1808–21.
Peterson LB, Bell CJM, Howlett SK, Pekalski ML, Brady K, Hinton H, et al. A long-lived IL-2 mutein that selectively activates and expands regulatory T cells as a therapy for autoimmune disease. J Autoimmun. 2018;95:1–14.
Reinehr T, Karges B, Meissner T, Wiegand S, Stoffel-Wagner B, Holl RW, et al. Inflammatory markers in obese adolescents with type 2 diabetes and their relationship to hepatokines and adipokines. J Pediatr. 2016;173:131–5.
Fordjour L, Cai C, Bronshtein V, Bronshtein M, Aranda JV, Beharry KD. Growth factors in the fetus and pre-adolescent offspring of hyperglycemic rats. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2021;18.
Mizgier M, Jarząbek-Bielecka G, Wendland N, Jodłowska-Siewert E, Nowicki M, Brożek A, et al. Relation between inflammation, oxidative stress, and macronutrient intakes in normal and excessive body weight adolescent girls with clinical features of polycystic ovary syndrome. Nutrients. 2021;13:896.
Khashchenko E, Vysokikh M, Uvarova E, Krechetova L, Vtorushina V, Ivanets T, et al. Activation of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome in combination with metabolic disorders and excessive body weight. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1399.
Paltoglou G, Schoina M, Valsamakis G, Salakos N, Avloniti A, Chatzinikolaou A, et al. Interrelations among the adipocytokines leptin and adiponectin, oxidative stress and aseptic inflammation markers in pre- and early-pubertal normal-weight and obese boys. Endocrine. 2017;55:925–33.
Shokri E, Heidarianpour A, Razavi Z. Positive effect of combined exercise on adipokines levels and pubertal signs in overweight and obese girls with central precocious puberty. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20:152.
Jiang Y, Yang L, Chen H, Chen J, Yang L, Wang Z, et al. Network pharmacology combined with lipidomics to reveal the regulatory effects and mechanisms of Kangzao granules in the hypothalamus of rats with central precocious puberty. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024;242:116059.
Lischka J, Schanzer A, de Gier C, Greber-Platzer S, Zeyda M. Macrophage-associated markers of metaflammation are linked to metabolic dysfunction in pediatric obesity. Cytokine. 2023;171:156372.
Yuan X, Chen R, McCormick KL, Zhang Y, Lin X, Yang X. The role of the gut microbiota on the metabolic status of obese children. Microb Cell Fact. 2021;20:20.
Sanches MD, Goldberg TBL, Rizzo A, da CB VN, Mosca LN, Romagnoli GG, et al. Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in obese adolescents with antibody against to adenovirus 36. Sci Rep. 2023;13:9918.
Bugajska J, Berska J, Wójcik M, Sztefko K. Amino acid profile in overweight and obese prepubertal children– can simple biochemical tests help in the early prevention of associated comorbidities? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1274011.
Visuthranukul C, Kwanbunbumpen T, Chongpison Y, Chamni S, Panichsillaphakit E, Uaariyapanichkul J, et al. The impact of Dietary Fiber as a prebiotic on inflammation in children with obesity. Foods. 2022;11:2856.
Taghizadeh N, Mohammadi S, Yousefi Z, Golpour P, Taheri A, Maleki MH, et al. Assessment of global histone acetylation in pediatric and adolescent obesity: correlations with SIRT1 expression and metabolic-inflammatory profiles. PLoS ONE. 2023;18:e0293217.
Thürmann L, Bauer M, Ferland M, Messingschlager M, Schikowski T, Von Berg A, et al. Undiagnosed Pediatric elevated blood pressure is characterized by induction of Proinflammatory and Cytotoxic mediators. Hypertension. 2023;80:2425–36.
Yang Y, Li J, Zhou Z, Wu S, Zhao J, Jia W, et al. Gut microbiota perturbation in early life could Influence Pediatric blood pressure regulation in a sex-dependent manner in juvenile rats. Nutrients. 2023;15:2661.
Prunicki M, Cauwenberghs N, Ataam JA, Movassagh H, Kim JB, Kuznetsova T, et al. Immune biomarkers link air pollution exposure to blood pressure in adolescents. Environ Heal Glob Access Sci Source. 2020;19:1–17.
Stinson SE, Jonsson AE, Andersen MK, Lund MAV, Holm LA, Fonvig CE, et al. High plasma levels of Soluble Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein Receptor-1 are Associated with inflammation and cardiometabolic risk profiles in Pediatric overweight and obesity. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023;12:e8145.
Maggio ABR, Farpour-Lambert NJ, Aggoun Y, Galan K, Montecucco F, Mach F, et al. Serum cardiovascular risk biomarkers in pre-pubertal obese children. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48:e12995.
Thorsteinsdottir H, Salvador CL, Mjøen G, Lie A, Sugulle M, Tøndel C, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 in children with chronic kidney Disease and after renal transplantation. Dis Markers. 2020;2020:8.
Kamianowska M, Kamianowska A, Wasilewska A. Urinary levels of kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) in children and adolescents with hyperuricemia. Adv Med Sci. 2023;68:79–85.
Mager DR, Iñiguez IR, Gilmour S, Yap J. The effect of a low fructose and low glycemic index/load (FRAGILE) dietary intervention on indices of liver function, cardiometabolic risk factors, and body composition in children and adolescents with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2015;39:73–84.
Acknowledgements
West China Hospital and Sichuan University financially supported this study. BioRender.com was used to create the figures.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070671, 32270690), the COVID-19 research projects of West China Hospital Sichuan University (Grant no. HX-2019-nCoV-057), and the regional innovation cooperation between Sichuan and Guangxi Provinces (2020YFQ0019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the work’s conception, drafting, illustration, and final revision. Each author reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors say they have no commercial or financial ties that could be seen as a conflict of interest in our study. Because of this, there were no conflicts of interest in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, A., Singla, R.K., Batool, Z. et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines are the game-changers in childhood obesity-associated metabolic disorders (diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases). Rev Endocr Metab Disord (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-024-09884-y
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-024-09884-y