Abstract
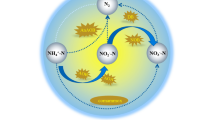
The effects of trace elements on ammonium degradation performance and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) secretion of Acinetobacter harbinensis HITLi7T at low temperature were investigated. Response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to obtain the optimal composition of trace elements and analyze their correlation. In this study, the results indicated that the ammonium removal performance could be enhanced by the presence of 0.1 mg L−1 Fe, Mn, or B in pure cultivation. When the concentrations of Fe and Mn were 0.2 mg L−1, the ammonium removal rates of the novel strain HITLi7T were 0.49 ± 0.01 mg L−1·h−1 and 0.58 ± 0.01 mg L−1·h−1, respectively, while it was the low concentration of 0.05 mg L−1 B that showed the maximum ammonium removal rate (0.56 ± 0.02 mg L−1·h−1) of strain HITLi7T. The regression model was obtained and the optimal formulation of trace elements was: B 0.064 mg L−1, Fe 0.12 mg L−1, and Mn 0.1 mg L−1. Based on these values, the experimental ammonium removal rate could reach 0.59 mg L−1·h−1, which matched well with the predicted response. The study also found that the addition of trace elements, causing high ammonium removal rates, resulted in a high polysaccharide (PS) ratio in the EPS secreted by Acinetobacter harbinensis HITLi7T. Especially under the optimal conditions, the PS ratio reached the highest value of 49.9%.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadi N, Zilouei H (2017) Optimization of organosolv pretreatment of rice straw for enhanced biohydrogen production using Enterobacter aerogenes. Bioresour Technol 227:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.073
Ensign SA, Hyman MR, Arp DJ (1993) In vitro activation of ammonia monooxygenase from Nitrosomonas europaea by copper. J Bacteriol 175:1971–1980
Guerinot ML (1994) Microbial iron transport. Annu Rev Microbiol 48:743–772
Guo Y, Huang T, Wen G, Cao X (2017) The simultaneous removal of ammonium and manganese from groundwater by iron-manganese co-oxide filter film: the role of chemical catalytic oxidation for ammonium removal. Chem Eng J 308:322–329
Huang X, Li W, Zhang D, Qin W (2013) Ammonium removal by a novel oligotrophic Acinetobacter sp. Y16 capable of heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification at low temperature. Bioresour Technol 146:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.046
Im J-K, Cho I-H, Kim S-K, Zoh K-D (2012) Optimization of carbamazepine removal in O3/UV/H2O2 system using a response surface methodology with central composite design. Desalination 285:306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.10.018
Keyer K, Gort AS, Imlay JA (1995) Superoxide and the production of oxidative DNA damage. J Bacteriol 177:6782–6790
Kobayashi M, Matoh T, Azuma JI (1996) Two chains of rhamnogalacturonan II are cross-linked by borate-diol ester bonds in higher plant cell walls. Plant Physiol 110:1017–1020
Krishnan KP, Loka Bharathi PA (2009) Organic carbon and iron modulate nitrification rates in mangrove swamps of Goa, south west coast of India. Estuarine Coast Shelf Sci 84:419–426
Li W, Zhang D, Huang X, Qin W (2014) Acinetobacter harbinensis sp. nov., isolated from river water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1507–1513. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.055251-0
Liu H, Fang HHP (2002) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J Biotechnol 95:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00025-1
Mohamed ZA (2001) Removal of cadmium and manganese by a non-toxic strain of the freshwater cyanobacterium Gloeothece magna. Water Res 35:4405–4409. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00160-9
Nielsen PH (1996) Adsorption of ammonium to activated sludge. Water Res 30:762–764
Novati G, Zannini E (1957) Effects of boron on the morphology of various microorganisms. Nuovi Annali D’igiene e Microbiologia 8:545–547
Oren A, Garrity GM (2014) Notification that new names of prokaryotes, new combinations, and new taxonomic opinions have appeared in volume 64, part 5, of the IJSEM. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2509–2511
Pal A, Paul AK (2008) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: central elements in heavy metal bioremediation. Indian J Microbiol 48:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-008-0006-5
Qin W, Li W, Zhang D, Huang X, Song Y (2016a) Ammonium reduction kinetics in drinking water by newly isolated Acinetobacter sp. HITLi 7 at low temperatures. Desalin Water Treat 57:11275–11282. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1043649
Qin W, Li WG, Zhang DY, Huang XF, Song Y (2016b) Ammonium removal of drinking water at low temperature by activated carbon filter biologically enhanced with heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4650–4659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5561-9
Qin W, Li WG, Gong XJ, Huang XF, Fan WB, Zhang D, Yao P, Wang XJ, Song Y (2017) Seasonal-related effects on ammonium removal in activated carbon filter biologically enhanced by heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria for drinking water treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19569–19582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9522-3
Qu D, Wang C, Wang Y, Zhou R, Ren H (2015) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by a novel groundwater origin cold-adapted bacterium at low temperatures. RSC Adv 5:5149–5157. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA13141J
Reeslev M, Jensen B (1995) Influence of Zn2+ and Fe3+ on polysaccharide production and mycelium/yeast dimorphism of Aureobasidium pullulans in batch cultivations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:910–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191190
Rodriguez-Caballero A, Hallin S, Påhlson C, Odlare M, Dahlquist E (2012) Ammonia oxidizing bacterial community composition and process performance in wastewater treatment plants under low temperature conditions. Water Sci Technol 65:197–204. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.643
Sato C, Schnoor JL, McDonald DB (1986) Characterization of effects of copper, cadmium and nickel on the growth of Nitrosomonas europaea. Environ Toxicol Chem 5:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620050411
Sutherland IW (1990) Biotechnology of microbial exopolysaccharides. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tang YJ, Zhu LL, Liu RS, Li HM, Li DS, Mi ZY (2008) Quantitative response of cell growth and tuber polysaccharides biosynthesis by medicinal mushroom Chinese truffle Tuber sinense to metal ion in culture medium. Bioresour Technol 99:7606–7615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.02.006
Tekerlekopoulou AG, Vayenas DV (2007) Ammonia, iron and manganese removal from potable water using trickling filters. Desalination 210:225–235
Temmink H, Klapwijk A, de Korte KF (2001) Feasibility of the BIOFIX-process for treatment of municipal wastewater. Water Sci Technol 43:241–249
Tsuneda S, Nagano T, Hoshino T, Ejiri Y, Noda N, Hirata A (2003) Characterization of nitrifying granules produced in an aerobic upflow fluidized bed reactor. Water Res 37:4965–4973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.08.017
Wagner FB, Nielsen PB, Boe-Hansen R, Albrechtsen HJ (2016) Copper deficiency can limit nitrification in biological rapid sand filters for drinking water production. Water Res 95:280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.025
Wei X, Vajrala N, Hauser L, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Arp DJ (2006) Iron nutrition and physiological responses to iron stress in Nitrosomonas europaea. Arch Microbiol 186:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0126-4
Whittaker M, Bergmann D, Arciero D, Hooper AB (2000) Electron transfer during the oxidation of ammonia by the chemolithotrophic bacterium Nitrosomonas europaea. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1459:346–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(00)00171-7
Wik T (1999) Adsorption and denitrification in nitrifying trickling filters. Water Res 33:1500–1508
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (1999) What are bacterial extracellular polymeric substances?. Springer, Berlin
Winter TC, Harvey JW, Franke OL, Alley WM (1998) Ground water and surface water: a single resource. U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1139, 79 pp
Yao S, Ni J, Ma T, Li C (2013) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification at low temperature by a newly isolated bacterium, Acinetobacter sp. HA2. Bioresour Technol 139:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.189
Zhang J, Wu P, Hao B, Yu Z (2011) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by the bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri YZN-001. Bioresour Technol 102:9866–9869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.118
Zhang QL, Liu Y, Ai GM, Miao LL, Zheng HY, Liu ZP (2012) The characteristics of a novel heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification bacterium, bacillus methylotrophicus strain L7. Bioresour Technol 108:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.139
Zhao B, He YL, Huang J, Taylor S, Hughes J (2010) Heterotrophic nitrogen removal by Providencia rettgeri strain YL. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:609–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0708-7
Zhao B, An Q, He YL, Guo JS (2012) N2O and N2 production during heterotrophic nitrification by Alcaligenes faecalis strain NR. Bioresour Technol 116:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.113
Zhao B, Tian M, An Q, Ye J, Guo JS (2017) Characteristics of a heterotrophic nitrogen removal bacterium and its potential application on treatment of ammonium-rich wastewater. Bioresour Technol 226:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.120
Zhu L, Ding W, Feng LJ, Kong Y, Xu J, Xu XY (2012) Isolation of aerobic denitrifiers and characterization for their potential application in the bioremediation of oligotrophic ecosystem. Bioresour Technol 108:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.033
Zilouei H, Soares A, Murto M, Guieysse B, Mattiasson B (2006) Influence of temperature on process efficiency and microbial community response during the biological removal of chlorophenols in a packed-bed bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:591–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0296-z
Acknowledgements
The present research was carried out at State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment of the School of Municipal and Environment Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology. The authors are pleased to acknowledge financial support by two grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51578178 and 51608149). The authors gratefully acknowledge our colleagues in this program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Li, W., Huang, X. et al. Effect of trace elements and optimization of their composition for the nitrification of a heterotrophic nitrifying bacterium, Acinetobacter harbinensis HITLi7T, at low temperature. Ann Microbiol 67, 715–725 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-017-1298-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-017-1298-7