Abstract
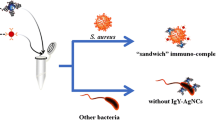
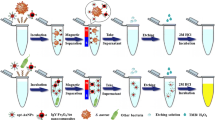
A novel sandwich strategy based on the dual recognition by teicoplanin (Teic) and IgG was developed for the rapid separation and identification of Staphylococcus aureus. This dual-recognition strategy was established using Teic-functionalized bovine serum albumin-PEGylated magnetic nanoparticles (Teic-BSA-PEG-MNPs) as the broad-spectrum capture probes for efficient isolation of gram-positive bacteria and IgG-functionalized quantum dots (QDs) as the signal probes for specific and sensitive detection of target bacteria in spiked foods. As a broad-spectrum antibiotic, Teic was introduced to replace antibodies to recognize S. aureus owing to the strong binding between Teic and bacterial cell wall. The construction of BSA-PEG provides an excellent molecular backbone carrier for high Teic loading capacity, allowing for multivalent interactions toward S. aureus. The application of Teic-BSA-PEG-MNPs allowed for satisfactory concentration and capture of S. aureus with a capture efficiency of as high as 75.62% in beef sample within 45 min, even at high bacterial concentrations of 3 × 106 CFU/mL. By integrating the enrichment of the Teic-BSA-PEG-MNPs nanoplatform and the sensitive fluorescence detection of the IgG-functionalized QDs, the detection of S. aureus was linear within the range of 3 × 101 to 3 × 106 CFU/mL, with a sensitivity of 30 CFU/mL. The low cost and sensitivity of this strategy show that it has a considerable potential application in food safety monitoring.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
My manuscript has no associated data.
References
Allen NE, Nicas TI (2003) Mechanism of action of oritavancin and related glycopeptide antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:511–532. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2003.tb00628.x
Argudín MÁ, Mendoza MC, Rodicio MR (2010) Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins 2(7):1751–1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2071751
Armenia I, Marcone GL, Berini F, Orlandi VT, Pirrone C, Martegani E, Gornati R, Bernardini G, Marinelli F (2018) Magnetic nanoconjugated teicoplanin: a novel tool for bacterial infection site targeting. Front Microbiol 9:2270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02270
Banada PP, Huff K, Bae E, Rajwa B, Aroonnual A, Bayraktar B, Adil A, Robinson JP, Hirleman ED, Bhunia AK (2009) Label-free detection of multiple bacterial pathogens using light-scattering sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24(6):1685–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.08.053
Binda E, Marinelli F, Marcone GL (2014) Old and new glycopeptide antibiotics: action and resistance. Antibiotics 3(4):572–594. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics3040572
Cenci-Goga BT, Karama M, Rossitto PV, Morgante RA, Cullor JS (2003) Enterotoxin production by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mastitic cows. J Food Prot 66(9):1693–1696. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-66.9.1693
Chang AY, Lu MS (2013) A CMOS magnetic microbead-based capacitive biosensor array with on-chip electromagnetic manipulation. Biosens Bioelectron 45:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.01.033
Edgar R, McKinstry M, Hwang J, Oppenheim AB, Fekete RA, Giulian G, Merril C, Nagashima K, Adhya S (2006) High-sensitivity bacterial detection using biotin-tagged phage and quantum-dot nanocomplexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(13):4841–4845. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601211103
Goodridge L, Chen J, Griffiths M (1999) The use of a fluorescent bacteriophage assay for detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in inoculated ground beef and raw milk. Int J Food Microbiol 47(1–2):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1605(99)00010-0
Grispoldi L, Massetti L, Sechi P, Iulietto MF, Ceccarelli M, Karama M, Popescu PA, Pandolfi F, Cenci-Goga BT (2019) Short communication: Characterization of enterotoxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mastitic cows. J Dairy Sci 102(2):1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-15373
Gao XL, Shao MF, Xu YS, Luo Y, Zhang K, Ouyang F, Li J (2016) Non-selective separation of bacterial cells with magnetic nanoparticles facilitated by varying surface charge. Front Microbiol 7:1891. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01891
Ghasemi R, Mirahmadi-Zare SZ, Nasr-Esfahani MH, Allafchian A, Behmanesh M (2019) Optical biosensing of Streptococcus agalactiae based on core/shell magnetic nanoparticle-quantum dot. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(25):6733–6743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02046-z
Golob M, Pate M, Kušar D, Dermota U, Avberšek J, Papić B, Zdovc I (2019) Antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes in Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis from humans and retail red meat. Biomed Res Int 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2815279
Hébert L, Courtin P, Torelli R, Sanguinetti M, Chapot-Chartier MP, Auffray Y, Benachour A (2007) Enterococcus faecalis constitutes an unusual bacterial model in lysozyme resistance. Infect Immun 75(11):5390–5398. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00571-07
Huycke MM, Sahm DF, Gilmore MS (1998) Multiple-drug resistant enterococci: the nature of the problem and an agenda for the future. Emerg Infect Dis 4(2):239–49. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0402.980211
Kaniusaite M, Tailhades J, Kittilä T, Fage CD, Goode RJ, Schittenhelm RB, Cryle MJ (2021) Understanding the early stages of peptide formation during the biosynthesis of teicoplanin and related glycopeptide antibiotics. FEBS J 288(2):507–529. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15350
Kadariya J, Smith TC, Thapaliya D (2014) Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: an ongoing challenge in public health. BioMed Res Int 2014:827965. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/827965
Lee JG, Sagui C, Roland C (2004) First principles investigation of vancomycin and teicoplanin binding to bacterial cell wall termini. J Am Chem Soc 126(27):8384–8385. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja048645c
Li F, Yang G, Aguilar ZP, Xiong Y, Xu H (2018) Affordable and simple method for separating and detecting ovarian cancer circulating tumor cells using BSA coated magnetic nanoprobes modified with folic acid. Sens Actuators B Chem 262:611–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.038
Lichtenberg JY, Ling Y, Kim S (2019) Non-specific adsorption reduction methods in biosensing. Sensors 19(11):2488. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112488
Majdinasab M, Hayat A, Marty JL (2018) Aptamer-based assays and aptasensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria in food samples. Trends Analyt Chem 107:60–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.07.016
Mao G, Cai Q, Wang F, Luo C, Ji X, He Z (2017) One-Step Synthesis of Rox-DNA Functionalized CdZnTeS Quantum Dots for the Visual Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide and Blood Glucose. Anal Chem 89(21):11628–11635. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b03053
Mao Y, Huang X, Xiong S, Xu H, Aguilar ZP, Xiong Y (2016) Large-volume immunomagnetic separation combined with multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria ivanovii in lettuce. Food Control 59:601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.06.048
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4(6):435–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1390
Meng X, Yang G, Li F, Liang T, Lai W, Xu H (2017a) Sensitive Detection of Staphylococcus aureus with Vancomycin-Conjugated Magnetic Beads as Enrichment Carriers Combined with Flow Cytometry. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(25):21464–21472. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b05479
Meng X, Li F, Li F, Xiong Y, Xu H (2017b) Vancomycin modified PEGylated-magnetic nanoparticles combined with PCR for efficient enrichment and detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sens Actuators B Chem 247:546–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.079
Otsuka H, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K (2003) PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55(3):403–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00226-0
Pleskova S, Mikheeva E, Gornostaeva E (2018) Using of quantum dots in biology and medicine. Adv Exp Med Biol 1048:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72041-8_19
Reynolds PE (1989) Structure, biochemistry and mechanism of action of glycopeptide antibiotics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 8(11):943–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01967563
Schelin J, Susilo YB, Johler S (2017) Expression of staphylococcal enterotoxins under stress encountered during food production and preservation. Toxins 9(12):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9120401
Su X, Wang M, Wu Y, He Y, Fu Z (2017) Specific chemiluminescent protocol for dual-site recognition of Streptococcus mutans utilizing strong affinity between teicoplanin and Gram-positive bacteria. Talanta 179:350–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.11.004
Treviño J, Bayón C, Ardá A, Marinelli F, Gandolfi R, Molinari F, Jimenez-Barbero J, Hernáiz MJ (2014) New insights into glycopeptide antibiotic binding to cell wall precursors using SPR and NMR spectroscopy. Chem 20:7363–7372. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201303310
Wang D, Lian F, Yao S, Liu Y, Wang J, Song X, Ge L, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhao C, Xu K (2020) Simultaneous Detection of Three Foodborne Pathogens Based on Immunomagnetic Nanoparticles and Fluorescent Quantum Dots. ACS Omega 5(36):23070–23080. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02833
Wang Y, Salazar JK (2016) Culture-independent rapid detection methods for bacterial pathogens and toxins in food matrices. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 15(1):183–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12175
Wu X, Lai T, Jiang J, Ma Y, Tao G, Liu F, Li N (2019) An on-site bacterial detection strategy based on broad-spectrum antibacterial ε-polylysine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles combined with a portable fluorometer. Mikrochim Acta 186(8):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3632-1
Wu Y, Jiang S, Fu Z (2020) Employment of teicoplanin-coated magnetic particles for quantifying gram-positive bacteria via catalase-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction of H2O2. Talanta 211:120728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120728
Xiong J, Wang W, Fu Z (2017) Fluorimetric sandwich affinity assay for Staphylococcus aureus based on dual-peptide recognition on magnetic nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 184(10):4197–4202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2396-8
Yi Z, Wang S, Meng X, Wu A, Li Q, Song Y, Zhao R, Qiao J (2019) Lysin cell-binding domain-functionalized magnetic beads for detection of Staphylococcus aureus via inhibition of fluorescence of Amplex Red/hydrogen peroxide assay by intracellular catalase. Anal Bioanal Chem 411(27):7177–7185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02099-0
Yan C, Zhang Y, Yang H, Yu J, Wei H (2017) Combining phagomagnetic separation with immunoassay for specific, fast and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Talanta 170:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.007
Yang G, Meng X, Wang Y, Yan M, Aguilar ZP, Xu H (2019) 2-Step lectin-magnetic separation (LMS) strategy combined with AuNPs-based colorimetric system for S. aureus detection in blood. Sens Actuators B Chem 279:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.112
Zhao X, Lin CW, Wang J, Oh DH (2014) Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(3):297–312. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1310.10013
Zhao Y, Ye M, Chao Q, Jia N, Ge Y, Shen H (2009) Simultaneous detection of multifood-borne pathogenic bacteria based on functionalized quantum dots coupled with immunomagnetic separation in food samples. J Agric Food Chem 57(2):517–524. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf802817y
Zhong Z, Gao X, Gao R, Jia L (2018) Selective capture and sensitive fluorometric determination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by using aptamer modified magnetic nanoparticles. Mikrochim Acta 185(8):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2914-3
Zhu M, Liu W, Liu H, Liao Y, Wei J, Zhou X, Xing D (2015) Construction of Fe3O4/Vancomycin/PEG Magnetic Nanocarrier for Highly Efficient Pathogen Enrichment and Gene Sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(23):12873–12881. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02374
Funding
The work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1602500), Research Foundation from Academic and Technical Leaders of Major Disciplines in Jiangxi Province, China (20194BCJ22004), and Research Foundation from State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University, China (SKLF-ZZA-201912).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jin Huang and Guanhua Chen are co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Chen, G., Sun, Y. et al. A Dual-Recognition Strategy for Staphylococcus aureus Detection Using Teicoplanin-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles and IgG-Functionalized Quantum Dots. Food Anal. Methods 15, 1968–1978 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02256-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02256-9