Abstract
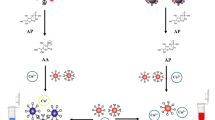
A novel colorimetric immunoassay for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) based on a combination of immunomagnetic separation and signal amplification via etching-enhanced peroxidase-like catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was developed. Nanoconjugates composed of gold and iron oxide nanoparticles were synthesized and further modified with antiS. aureus immunoglobulin Y (IgY), which was used for the selective enrichment and rapid separation of target bacteria in complex matrices. AuNPs functionalized with antiS. aureus aptamer were used as an artificial enzyme which has peroxidase-like catalysis activity. Catalytic activity of AuNPs is inhibited by modifying aptamer. However, catalysis of modified AuNPs remarkably enhanced by hydrogen peroxide etching. Based on collecting unbound modified AuNPs in the supernatant and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine-hydrogen peroxide reporting system, the yellow color of solution decreases linearly with increasing the concentration of S. aureus ranging from 10 to 106 cfu/mL. The limit of detection is 10 cfu/mL, and total detection time is 65 min. The recoveries of the S. aureus spiked in food samples are 88.2–119.8%.

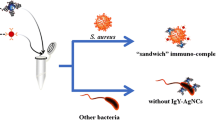
Schematic illustration of colorimetric method for detection of S. aureus based on the IgY-Fe3O4/Au nanocomposites as capture probes and apt-AuNPs as artificial enzyme with etching-enhanced peroxidase-like catalytic activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kadariya J, Smith TC, Thapaliya D (2014) Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: an ongoing challenge in public health. Biomed Res Int 2014:1–9
Chakraborty SP, Mahapatra SK, Sahu SK, Chattopadhyay S, Pramanik P, Roy S (2011) Nitric oxide mediated Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis and protective role of nanoconjugated vancomycin. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 1(2):102–109
Park B, Choi SJ (2017) Sensitive immunoassay-based detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus using capture and labeling particles in a stationary liquid phase lab-on-a-chip. Biosens Bioelectron 90:269–275
Malorny B, Lofstrom C, Wagner M, Kramer N, Hoorfar J (2008) Enumeration of salmonella bacteria in food and feed samples by real-time PCR for quantitative microbial risk assessment. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(5):1299–1304
Seo SM, Cho IH, Jeon JW, Cho HK, Oh EG, Yu HS, Shin SB, Lee HJ, Paek SH (2010) An ELISA-on-a-chip biosensor system coupled with immunomagnetic separation for the detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus within a single working day. J Food Protect 73(8):1466–1473
Roth-Konforti M, Green O, Hupfeld M, Fieseler L, Heinrich N, Ihssen J, Vorberg R, Wick L, Spitz U, Shabat D (2019) Ultrasensitive detection of Salmonella and Listeria monocytogenes by small-molecule chemiluminescence probes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 58(30):10361–10367
Kumar S, Nehra M, Mehta J, Dilbaghi N, Marrazza G, Kaushik A (2019) Point-of-care strategies for detection of waterborne pathogens. Sensors 19(20):4476
Xiong J, Wang W, Zhou Y, Kong W, Wang Z, Fu Z (2016) Ultra-sensitive chemiluminescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on competitive binding of Staphylococcus protein A-modified magnetic beads to immunoglobulin G. Microchim Acta 183(4):1507–1512
Park HY, Schadt MJ, Wang L, Lim IIS, Njoki PN, Kim SH, Jang MY, Luo J, Zhong CJ (2007) Fabrication of magnetic core @ shell Fe oxide @ Au nanoparticles for interfacial bioactivity and bio-separation. Langmuir 23(17):9050–9056
Zhao XL, Cai YQ, Wang T, Shi YL, Jiang GB (2008) Preparation of alkanethiolate-functionalized core/shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles and its interaction with several typical target molecules. Anal Chem 80(23):9091–9096
Xu ZC, Hou YL, Sun SH (2007) Magnetic core/shell Fe3O4/au and Fe3O4/Au/Ag nanoparticles with tunable plasmonic properties. J Am Chem Soc 129(28):8698–8699
Liu YS, Zhao C, Song XL, Xu K, Wang J, Li J (2017) Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta 184(12):4785–4792
Li X, Zhao C, Liu Y, Li Y, Lian F, Wang D, Zhang Y, Wang J, Song X, Li J, Yang Y, Xu K (2019) Fluorescence signal amplification assay for the detection of B. melitensis 16M, based on peptide-mediated magnetic separation technology and a AuNP-mediated bio-barcode assembled by quantum dot technology. Analyst 144(8):2704–2715
Hamula CLA, Zhang HQ, Li F, Wang ZX, Le XC, Li XF (2011) Selection and analytical applications of aptamers binding microbial pathogens. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 30(10):1587–1597
Yuan JL, Tao Z, Yu Y, Ma XY, Xia Y, Wang L, Wang ZP (2014) A visual detection method for Salmonella typhimurium based on aptamer recognition and nanogold labeling. Food Control 37:188–192
Hansen JA, Wang J, Kawde AN, Xiang Y, Gothelf KV, Collins G (2006) Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J Am Chem Soc 128(7):2228–2229
Li JJ, Xu M, Huang HP, Zhou JJ, Abdel-Halim ES, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ (2011) Aptamer-quantum dots conjugates-based ultrasensitive competitive electrochemical cytosensor for the detection of tumor cell. Talanta 85(4):2113–2120
Liu YS, Wang J, Song XL, Xu K, Chen HS, Zhao C, Li J (2018) Colorimetric immunoassay for Listeria monocytogenes by using core gold nanoparticles, silver nanoclusters as oxidase mimetics, and aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(8):360
Qu WS, Liu YY, Liu DB, Wang Z, Jiang XY (2011) Copper-mediated amplification allows readout of immunoassays by the naked eye. Angew Chem Int Edit 50(15):3442–3445
Khoris IM, Takemura K, Lee J, Hara T, Abe F, Suzuki T, Park EY (2019) Enhanced colorimetric detection of norovirus using in-situ growth of Ag shell on Au NPs. Biosens Bioelectron 126:425–432
Zhang R, Lu N, Zhang J, Yan R, Li J, Wang L, Wang N, Lv M, Zhang M (2020) Ultrasensitive aptamer-based protein assays based on one-dimensional core-shell nanozymes. Biosens Bioelectron 150:111881
Weerathunge P, Ramanathan R, Shukla R, Sharma TK, Bansal V (2014) Aptamer-controlled reversible inhibition of gold nanozyme activity for pesticide sensing. Anal Chem 86(24):11937–11941
Yu H, Chen M, Rice PM, Wang SX, White RL, Sun S (2005) Dumbbell-like bifunctional Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Nano Lett 5(2):379–382
Bing W, Sun HJ, Wang FM, Song YQ, Ren JS (2018) Hydrogen-producing hyperthermophilic bacteria synthesized size-controllable fine gold nanoparticles with excellence for eradicating biofilm and antibacterial applications. J Mater Chem B 6(28):4602–4609
Zheng N, Stucky GD (2006) A general synthetic strategy for oxide-supported metal nanoparticle catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 128(44):14278–14280
Valden M, Lai X, Goodman DW (1998) Onset of catalytic activity of gold clusters on titania with the appearance of nonmetallic properties. Science 281(5383):1647–1650
Sun SM, Zhao R, Feng SM, Xie YL (2018) Colorimetric zearalenone assay based on the use of an aptamer and of gold nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity. Microchim Acta 185(12):535
Chen M, Kang H, Gong Y, Guo J, Liu R (2015) Bacterial cellulose supported gold nanoparticles with excellent catalytic properties. Acs Appl Mater Inter 7(39):21717–21726
Funding
The authors thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81872668), Health commission of Jilin Province (2018Q033) and Norman Bethune Health Science Center of Jilin University (2018A05), Jilin Province Development and Reform Commission (Grant No. 2019C049-3), Jilin Province Science and Technology Development Plan Item (Grant No.: 20200602010ZP and 20200403035SF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6309 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, S., Li, J., Pang, B. et al. Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on etching-enhanced peroxidase-like catalytic activity of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 187, 504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04473-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04473-7