Abstract
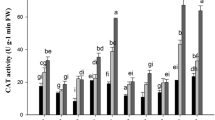
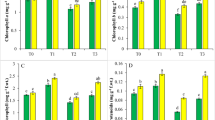
We present here a comprehensive study depicting the differences in biochemical responses to increasing CdCl2 concentrations (0.1, 0.25, 0.5 and 1.5 mM) in the two indica rice varieties, IR-29 (salt-sensitive) and Nonabokra (salt-tolerant), in order to contribute to our understanding of genotypic variation of cadmium tolerance. The oxidative damages in both the varieties enhanced with the increase in CdCl2 concentrations, the susceptibility of IR-29 being more pronounced than Nonabokra. The detrimental effects in IR-29 were reflected in greater chlorophyll loss, higher H2O2 and malondialdehyde content even at lower concentrations and drastically higher lipoxygenase activity, protein oxidation and putrescine accumulation, especially at higher CdCl2 levels. The antioxidants like anthocyanin and carotenoids, antioxidative enzymes like guaiacol peroxidase (GPX) and ascorbate peroxidase (APX), osmolytes like proline, reducing sugars, spermidine and spermine, increased in both the varieties with CdCl2 levels. While anthocyanin, reducing sugars and spermine showed greater increment in IR-29, the GPX/APX activity was more enhanced in Nonabokra; the increase in carotenoids, proline and spermidine being similar in both the varieties. However, reverse trends were noted for cysteine level and CAT activity; IR-29 showed marked decrease in cysteine content and CAT activity with increased cadmium exposure, whereas in Nonabokra, both the parameters increased, particularly at higher cadmium levels. Thus, the detoxification mechanism in the more-susceptible IR-29 was probably rendered by anthocyanin, reducing sugars and spermine in particular, as well as by GPX/APX, rather than cysteine and CAT, which showed cadmium sensitivity. Thus, the CdCl2 stress-dependent comparative biochemical analyses displayed major differences in the two rice varieties in terms of tolerance to Cd toxicity. Our data provides evidence that Nonabokra, which is a well-known variety tolerant to sodium chloride toxicity, also shows promising tolerance to cadmium toxicity, and hints at their possible utilization in Cd remediation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- Cys:
-
Cysteine
- GPX:
-
Guaiacol peroxidase
- LOX:
-
Lipoxygenase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- PAs:
-
Polyamines
- Pro:
-
Proline
- Put:
-
Putrescine
- Spd:
-
Spermidine
- Spm:
-
Spermine
References
Agrawal M, Singh DS (2003) Physiological and biochemical responses of two cultivars of wheat to elevated levels of CO2 and SO2, singly and in combination. Environ Pollut 121:189–197
Alia P, Saradhi PP (1991) Proline accumulation under heavy meal stress. J Plant Physiol 138:554–558
Aravind P, Prasad MNV (2003) Zinc alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Ceratophyllum demersum L.: a free floating freshwater macrophyte. Plant Physiol Biochem 41:391–397
Astolfi S, Zuchi S, Passera C (2004) Effects of cadmium on the metabolic activity of Avena sativa plants grown in soil or hydroponic culture. Biol Plant 48:413–418
Basu S, Roychoudhury A, Saha PP, Sengupta DN (2010a) Differential antioxidative responses of indica rice cultivars to drought stress. Plant Growth Regul 60:51–59
Basu S, Roychoudhury A, Saha PP, Sengupta DN (2010b) Comparative analysis of some biochemical responses of three indica rice varieties during polyethylene glycol-mediated water stress exhibits distinct varietal differences. Acta Physiol Plant 32:551–563
Besford RT, Richardson CM, Campos JL, Tiburcio AF (1993) Effect of polyamines on stabilization of molecular complexes of thylakoid membranes of osmotically stressed oat leaves. Planta 189:201–206
Bishnoi NR, Sheoran IS, Singh R (1993) Influence of cadmium and nickel on photosynthesis and water relations in wheat leaves of different insertion level. Photosynthetica 28:473–479
Cardoso PF, Molina SMG, Pereira GJG, Vitoria AP, Azevedo RA (2002) Response of rice inbred lines to cadmium exposure. J Plant Nutr 25:927–944
Chaoui A, Mazhoudi S, Ghorbal E, El Ferjani E (1997) Cadmium and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 127:139–147
Cho U-H, Seo N-H (2005) Oxidative stress in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to cadmium is due to hydrogen peroxide accumulation. Plant Sci 168:113–120
Chen SL, Kao CH (1995) Cd induced changes in proline level and peroxidase activity in roots of rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 17:67–71
Dixit V, Pandey V, Shymar R (2001) Differential antioxidative responses to cadmium in roots and leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv Azard). J Exp Bot 52:1101–1109
Dubey RS, Singh AK (1999) Salinity induced accumulation of soluble sugars and alters the activity of sugar metabolizing enzymes in rice plants. Biol Plant 42:233–239
Ferreira RR, Fornazier RF, Vitoria AP, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2002) Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities in soybean under cadmium stress. J Plant Nutr 25:327–342
Fojtova M, Kovarik A (2000) Genotoxic effect of cadmium is associated with apoptotic changes in tobacco cells. Plant Cell Environ 23:531–537
Fornazier RF, Ferreira RR, Vitoria AP, Molina SMG, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2002) Effects of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme activities in sugar cane. Biol Plant 41:91–97
Fusco N, Micheletto L, Corso GD, Borgato L, Furini A (2005) Identification of cadmium-regulated genes by cDNA-AFLP in the heavy metal accumulator Brassica juncea L. J Exp Bot 56:3017–3027
Gallego SM, Benavides MP, Tomaro ML (1996) Effects of heavy metal ion in excess on sunflower leaves: evidences for involvement of oxidative stress. Plant Sci 121:151–159
Garnier L, Simon-Plas F, Thuleau P, Agnel JP, Blein JP, Ranjeva R, Montillet JL (2006) Cadmium affects tobacco cells by a series of three waves of reactive oxygen species that contribute to cytotoxicity. Plant Cell Environ 29:1956–1969
Groppa MD, Ianuzzo MP, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2007a) Polyamine metabolism in sunflower plants under long-term cadmium or copper stress. Amino Acids 32:265–275
Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2001) Polyamines as protectors against cadmium or copper-induced oxidative damage in sunflower leaf discs. Plant Sci 161:481–488
Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2007b) Polyamines and heavy metal stress: the antioxidant behavior of spermine in cadmium- and copper-treated wheat leaves. BioMetals 20:185–195
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2003a) Accumulation of ammonium ion in cadmium tolerant and sensitive cultivars of Oryza sativa. Plant Growth Regul 39:271–276
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2003b) Role of abscisic acid in cadmium tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 26:867–874
Hsu YT, Kao CH (2005) Abscisic acid accumulation and cadmium tolerance in rice seedlings. Physiol Plant 124:71–80
Huttermann A, Arduini I, Godbold DL (1999) Metal pollution and forest decline. In: Prasad MNV, Hagemeyer J (eds) Heavy metal stress in plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 253–272
Kuo MC, Kao CH (2004) Antioxidant enzyme activities are upregulated in response to cadmium in sensitive, but not in tolerant, rice (Oryza sativa L,) seedlings. Bot Bull Acad Sin 45:291–299
Kneer R, Jenk MH (1992) Phytochelatins protect plant enzymes from heavy metal poisoning. Phytochemistry 31:2663–2667
Laspina NV, Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2005) Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. Plant Sci 169:323–330
Lomozik L, Gasowska A, Bregier-Jarzebowska R, Jastrzab R (2005) Coordination chemistry of polyamines and their interactions in ternary systems including metal ions, nucleosides and nucleotides. Coord Chem Rev 249:2335–2350
Lovaas E (1997) Antioxidant and metal-chelating effects of polyamines. In: Sies H (ed) Advances in Pharmacology, vol 38: Antioxidants in Disease Mechanisms and Therapy. Academic Press, pp, pp 119–149
Metwally A, Safronova VI, Belimov AA, Dietz KJ (2005) Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. J Exp Bot 56:167–178
Moons A, Bauw G, Prinsen E, Van Montagu M, Van der Straeten D (1995) Molecular and physiological responses to abscisic acid and salts in roots of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant indica rice varieties. Plant Physiol 107:177–186
Nada E, Ferjani BA, Ali R, Bechir BR, Imed M, Makki B (2007) Cadmium-induced growth inhibition and alteration of biochemical parameters in almond seedlings grown in solution culture. Acta Physiol Plant 29:57–62
Parkhi V, Rai M, Tan J, Oliva N, Rehana S, Bandyopadhyay A, Torrizo L, Ghole V, Datta K, Datta SK (2005) Molecular characterization of marker-free transgenic lines of indica rice that accumulate carotenoids in seed endosperm. Mol Gen Genomics 274:325–336
Reinheckel T, Noack H, Lorenz S, Wiswedel I, Augustin W (1998) Comparison of protein oxidation and aldehyde formation during oxidative stress in isolated mitochondria. Free Radical Res 29:297–305
Rellan-Alvarez R, Ortega-Villasante C, Alvarez-Fernandez A, del Campo FF, Hernandez LE (2006) Stress response of Zea mays to cadmium and mercury. Plant Soil 279:41–50
Rodríguez-Serrano M, Romero-Puertas MC, Pazmiño DM, Testillano PS, Risueño MC, Del Río LA, Sandalio LM (2009) Cellular response of pea plants to cadmium toxicity: cross talk between reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and calcium. Plant Physiol 150:229–243
Romero-Puertas MC, Palma JM, Gomez M, del Rio LA, Sandalio LM (2002) Cadmium causes the oxidative modification of proteins in pea plants. Plant Cell Environ 25:677–686
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sarkar SN, Sengupta DN (2008) Comparative physiological and molecular responses of a common aromatic indica rice cultivar to high salinity with non-aromatic indica rice cultivars. Plant Cell Rep 27:1395–1410
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta DN (2009) Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on some physiological responses in a popular aromatic indica rice compared with those from two traditional non-aromatic indica rice cultivars. Acta Physiol Plant 31:915–926
Roychoudhury A, Basu S, Sengupta DN (2011) Amelioration of salinity stress by exogenously applied spermidine or spermine in three varieties of indica rice differing in their level of salt tolerance. J Plant Physiol 168:317–328
RoyChoudhury A, Roy C, Sengupta DN (2007) Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing the heterologous lea gene Rab16A from rice during high salt and water deficit display enhanced tolerance to salinity stress. Plant Cell Rep 26:1839–1859
Salt DE, Smith RD, Raskin I (1998) Phytoremediation. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:643–668
Sandalio LM, Dalurzo HC, Gomez M, Romero-Puertas MC, Del Rio LA (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J Exp Bot 52:2115–2126
Sanita di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Env Exp Bot 41:105–130
Schützendübel A, Nikolova P, Rudolf C, Polle A (2002) Cadmium and H2O2-induced oxidative stress in Populus X canescens roots. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:577–584
Schützendübel A, Polle A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J Exp Bot 53:1351–1365
Schützendübel A, Schwanz P, Teichmann T, Gross K, Langenfeld-Heyser R, Godbold DL, Polle A (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in antioxidative systems, H2O2 content and differentiation in pine (Pinus sylvestris) roots. Plant Physiol 127:887–892
Shah K, Kumar RG, Verma S, Dubey RS (2001) Effect of cadmium on lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion generation and activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Sci 161:1135–1144
Shaw BP (1995) Changes in the levels of photosynthetic pigments in Phaseolus aureus Roxb. exposed to Hg and Cd at two stages of developments: a comparative study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 55:574–580
Skorzynska-Polit E, Drążkiewicz M, Krupa Z (2003/4) The activity of the antioxidative system in cadmium-treated Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol Plant 47:71–78
Sobkowiak R, Rymer K, Rucinska R, Deckert J (2004) Cadmium-induced changes in antioxidant enzymes in suspension culture of soybean cells. Acta Biochim Pol 51:219–222
Sobrino-Plata J, Ortega-Villasante C, Flores-Caceres ML, Escobar C, Campo FFD, Hernandez LE (2009) Differential alterations of antioxidant defenses as bioindicators of mercury and cadmium toxicity in alfalfa. Chemosphere 77:946–954
Streb P, Michael-Knauf A, Feierabend J (1993) Preferential photoinactivation of catalase and photoinhibition of photosystem II are common early symptoms under various osmotic and chemical stress conditions. Physiol Plant 88:590–598
Stroinski A, Bandurska A (1996) Cadmium influence on antioxidants levels in potato tuber. In: Grzesiak S and Miszalski Z (eds) Proceedings of the conference: Ekofizjologiczne aspekty reakcji roglin na dziatanie abiotycznych czynnikow stresowych, pp 191–198 (English abstract), Krakow
Stroinski A, Kozlowska M (1997) Cadmium-induced oxidative stress in potato tuber. Acta Soc Bot Pol 66:189–195
Talarico L (2002) Fine structure and X-ray microanalysis of a red macrophyte cultured under cadmium stress. Environ Pollut 120:813–821
Terry AP, Stone W (2002) Biosorption of cadmium and copper contaminated water by Scenedesmus abundans. Chemosphere 47:249–255
Verma S, Dubey RS (2001) Effect of cadmium on soluble sugars and enzymes of their metabolism in rice. Biol Plant 44:117–123
Vitoria AP, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2001) Antioxidant enzymes responses to cadmium in radish tissues. Phytochemistry 57:701–710
Wu FB, Chen F, Wei F, Zhang GP (2004) Effect of cadmium on free amino acid, glutathione and ascorbic acid concentrations in two barley genotypes (Hordeum vulgare L.) differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 57:447–454
Yamamoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Devi RS, Rikiishi S, Matsumoto H (2002) Aluminum toxicity is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and the production of reactive oxygen species in plant cells. Plant Physiol 128:63–72
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, New Delhi as well as Bose Institute Research Fellowship is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Klobus.
A. Roychoudhury and S. Basu have equal contributions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roychoudhury, A., Basu, S. & Sengupta, D.N. Antioxidants and stress-related metabolites in the seedlings of two indica rice varieties exposed to cadmium chloride toxicity. Acta Physiol Plant 34, 835–847 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0881-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0881-y