Abstract
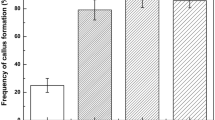
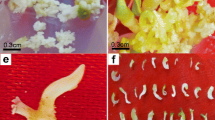
A protocol has been developed for somatic embryogenesis and subsequent plant regeneration in Allium schoenoprasum L. Calli were induced from root sections isolated from axenic seedlings and cultivated on media containing either Murashige and Skoog’s (MS) or Dunstan and Short’s mineral solution supplemented with 5 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in combination with 6-benzylaminopurine (BA), 6-furfurylaminopurine (Kin) or thidiazuron (TDZ) at 1, 5 or 10 μM. The highest frequencies of callus induction were achieved on media with 5 μM 2,4-D in combination with 5 μM TDZ or 10 μM BA (78.9% and 78.4%, respectively). Calli were then transferred to 1 μM 2,4-D, where compact yellow callus turned to segmented yellowish callus with transparent globular somatic embryos at the surface. Calli that were previously grown on media with 5 μM 2,4-D in combination with 10 μM BA or 10 μM TDZ showed the highest frequencies of embryogenic callus formation (45% and 42%) as well as mean number of somatic embryos per regenerating callus. The choice of mineral solution formulation did not significantly affect callus induction or embryogenic callus formation. The embryos could complete development into whole plants on plant growth regulator (PGR)-free medium, but inclusion of Kin (0.5, 2.5 and 5 μM) in this phase improved somatic embryo development and multiplication. Subsequently transferred to 1/2 MS PGR-free medium, all embryos rooted and the survival rate of the plants in a greenhouse was 96%.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BA:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- BDS:
-
Dunstan and Short’s mineral solution
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- Kin:
-
6-Furfurylaminopurine
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog’s mineral solution
- PGR:
-
Plant growth regulator
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
References
Ayabe M, Sumi S (1998) Establishment of a novel tissue culture method, stem-disc culture, and its practical application to micropropagation of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep 17:773–779
Ayabe M, Sumi S (2001) A novel and efficient tissue culture method—“stem-disk dome culture”—for producing virus-free garlic (Allium sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep 20:503–507
Barandiaran X, Martín N, Rodríguez-Conde MF, Di Pietro A, Martín J (1999a) Genetic variability in callus formation and regeneration of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep 18:434–437
Barandiaran X, Martín N, Rodríguez-Conde MF, Di Pietro A, Martín J (1999b) An efficient method for callus culture and shoot regeneration of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Hort Sci 34:348–349
Buiteveld J, Creemers-Molenaar J (1994) Plant regeneration from protoplasts isolated from suspension cultures of leek (Allium ampeloprasum L.). Plant Sci 100:203–210
Buiteveld J, Van der Valk P, Jansen J, Creemers-Molenaar J, Colijn-Hooymans CM (1993) Callus induction and plant regeneration from explants of commercial cultivars of leek (Allium ampeloprasum var. porrum L.). Plant Cell Rep 12:431–434
Debergh P, Standaert-De Metsenaere R (1976) Neoformation of bulbils in Allium porrum L. cultured in vitro. Sci Hort 5:11–12
Dunstan DI, Short KC (1977) Improved growth of tissue cultures of the onion, Allium cepa. Physiol Plant 41:70–72
Dunstan DI, Short KC (1978) Shoot production from onion callus tissue culture. Sci Hortic 9:99–110
Eady CC, Butler RC, Suo Y (1998) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature embryo cultures of onion (Allium cepa). Plant Cell Rep 18:111–116
Fereol L, Chovelon V, Causse S, Michaux-Ferriere N, Kahane R (2002) Evidence of a somatic embryogenesis process for plant regeneration in garlic (Allium sativum L.). Plant Cell Rep 21:197–203
Fereol L, Chovelon V, Causse S, Triarie D, Arnault I, Auger J, Kahane R (2005) Establishment of embryogenic cell suspension cultures of garlic (Allium sativum L.), plant regeneration and biochemical analyses. Plant Cell Rep 24:319–325
Haque MS, Wada T, Hattori K (1997) High frequency shoot regeneration and plantlet formation from root tip of garlic. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 50:83–89
Hong W, Debergh P (1995) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in garden leek. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 43:21–28
Kim JW, Soh WY (1996) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from suspension cultures of Allium fistulosum L. Plant Sci 114:215–220
Luciani G, Marinangeli PA, Curvetto NR (2001) Increasing nitrate/ammonium ratio for improvement of garlic micropropagation. Sci Hort 87:11–20
Luciani GF, Mary AK, Pellegrini C, Curvetto NR (2006) Effects of explants and growth regulators in garlic callus formation and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 87:139–143
Luthar Z, Bohanec B (1999) Induction of direct somatic organogenesis in onion (Allium cepa L.) using a two-step flower or ovary culture. Plant Cell Rep 18:797–802
Martín-Urdíroz N, Garrido-Gala J, Martín J, Barandiaran X (2004) Effect of light on the organogenic ability of garlic using a one-step in vitro system. Plant Cell Rep 22:721–724
Matsuda Y, Adachi T (1996) Plant regeneration via embryogenesis in commercial cultivars of Chinese chive (Allium tuberosum Rottl.). Plant Sci 119:149–156
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Myers JM, Simon PW (1998) Continuous callus production and regeneration of garlic (Allium sativum L.) using root segments from shoot tip-derived plantlets. Plant Cell Rep 17:726–730
Myers JM, Simon PW (1999) Regeneration of garlic callus as affected by clonal variation, plant growth regulators and culture conditions over time. Plant Cell Rep 19:32–36
Robledo-Paz A, Vilalobos-Arambula VM, Jofre-Garfias AE (2000) Efficient plant regeneration of garlic (Allium sativum L.) by root-tip culture. In Vireo Cell Dev Plant 36:416–419
Song P, Peffley EB (1994) Plant regeneration from suspension cultures of Allium fistulosum and an A. fistulosum × A. cepa interspecific hybrid. Plant Sci 98:63–68
Štajner D, Popović BM (2009) Comparative study of antioxidant capacity in organs of different Allium species. Cent Eur J Biol 4:224–228
Štajner D, Čanadanović-Brunet J, Pavlović A (2004) Allium schoenoprasum L., as a natural antioxidant. Phytother Res 18:522–524
Štajner D, Igić R, Popović BM, Dj Malenčić (2008) Comparative study of antioxidant properties of wild growing and cultivated Allium species. Phytother Res 22:113–117
Van der Valk P, Scholten O, Verstappen F, Jansen R, Dons J (1992) High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from zygotic embryo-derived callus cultures of three Allium species. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 30:181–192
Xu Z, Um YC, Kim CH, Lu G, Guo DP, Liu HL, Bah AA, Mao A (2008) Effect of plant growth regulators, temperature and sucrose on shoot proliferation from the stem disc of Chinese jiaotou (Allium chinense) and in vitro bulblet formation. Acta Physiol Plant 30:521–528
Yasseen MY, Barringer SA, Splittstoesser WE (1995) In vitro shoot proliferation and plant regeneration from kurrat (Allium ampeloprasum var. kurrat) seedlings. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 40:195–196
Zhang W, Lin X, Takano H, Takio S, Ono K (2004) Efficient plant regeneration from suspension cells of Allium cepa. Plant Cell Rep 23:371–376
Zheng S, Henken B, Sofiari E, Jacobsen E, Krens FA, Kik C (1998) Factors influencing induction, propagation and regeneration of mature zygotic embryo-derived callus from Allium cepa. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 53:99–105
Zheng S, Henken B, Sofiari E, Keizer P, Jacobsen E, Kik C, Krens FA (1999) Effect of cytokinins and lines on plant regeneration from long-term callus and suspension cultures of Allium cepa L. Euphytica 108:83–90
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, Contract No. 143026B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zdravković-Korać, S., Milojević, J., Tubić, L. et al. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from root sections of Allium schoenoprasum L.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 101, 237–244 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9682-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9682-z