Abstract
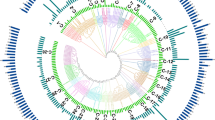
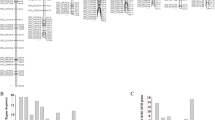
MYB transcription factor represents one of the largest gene families in plant genomes. Sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) is one of the most important fruit crops worldwide, and recently the genome has been sequenced. This provides an opportunity to investigate the organization and evolutionary characteristics of sweet orange MYB genes from whole genome view. In the present study, we identified 100 R2R3-MYB genes in the sweet orange genome. A comprehensive analysis of this gene family was performed, including the phylogeny, gene structure, chromosomal localization and expression pattern analyses. The 100 genes were divided into 29 subfamilies based on the sequence similarity and phylogeny, and the classification was also well supported by the highly conserved exon/intron structures and motif composition. The phylogenomic comparison of MYB gene family among sweet orange and related plant species, Arabidopsis, cacao and papaya suggested the existence of functional divergence during evolution. Expression profiling indicated that sweet orange R2R3-MYB genes exhibited distinct temporal and spatial expression patterns. Our analysis suggested that the sweet orange MYB genes may play important roles in different plant biological processes, some of which may be potentially involved in citrus fruit quality. These results will be useful for future functional analysis of the MYB gene family in sweet orange.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang C, Keddie J, Adam L, Pineda O, Ratcliffe OJ, Samaha RR, Creelman R, Pilgrim M, Broun P, Zhang JZ, Ghandehari D, Sherman BK, Yu G (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290(5499):2105–2110
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15(10):573–581
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4(5):447
Ogata K, Hojo H, Aimoto S, Nakai T, Nakamura H, Sarai A, Ishii S, Nishimura Y (1992) Solution structure of a DNA-binding unit of Myb: a helix-turn-helix-related motif with conserved tryptophans forming a hydrophobic core. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(14):6428–6432
Kanei-Ishii C, Sarai A, Sawazaki T, Nakagoshi H, He DN, Ogata K, Nishimura Y, Ishii S (1990) The tryptophan cluster: a hypothetical structure of the DNA-binding domain of the myb protooncogene product. J Biol Chem 265(32):19990–19995
Kranz HD, Denekamp M, Greco R, Jin H, Leyva A, Meissner RC, Petroni K, Urzainqui A, Bevan M, Martin C (1998) Towards functional characterisation of the members of the R2R3-MYB gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(2):263–276
Martin C, Paz-Ares J (1997) MYB transcription factors in plants. Trends Genet 13(2):67–73
Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H (1987) The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J 6(12):3553–3558
Millar AA, Gubler F (2005) The Arabidopsis GAMYB-like genes, MYB33 and MYB65, are microRNA-regulated genes that redundantly facilitate anther development. Plant Cell 17(3):705–721
Brownfield L, Hafidh S, Borg M, Sidorova A, Mori T, Twell D (2009) A plant germline-specific integrator of sperm specification and cell cycle progression. PLoS Genet 5(3):e1000430
Muller D, Schmitz G, Theres K (2006) Blind homologous R2R3 Myb genes control the pattern of lateral meristem initiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18(3):586–597
Mu RL, Cao YR, Liu YF, Lei G, Zou HF, Liao Y, Wang HW, Zhang WK, Ma B, Du JZ, Yuan M, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2009) An R2R3-type transcription factor gene AtMYB59 regulates root growth and cell cycle progression in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 19(11):1291–1304
Wang X, Niu QW, Teng C, Li C, Mu J, Chua NH, Zuo J (2009) Overexpression of PGA37/MYB118 and MYB115 promotes vegetative-to-embryonic transition in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 19(2):224–235
Zhu J, Verslues PE, Zheng X, Lee B-H, Zhan X, Manabe Y, Sokolchik I, Zhu Y, Dong CH, Zhu JK (2005) HOS10 encodes an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor essential for cold acclimation in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(28):9966–9971
Gao J, Zhang Z, Peng R, Xiong A, Xu J, Zhu B, Yao Q (2010) Forced expression of Mdmyb10, a myb transcription factor gene from apple, enhances tolerance to osmotic stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Rep 38(1):205–211
Yang A, Dai X, Zhang WH (2012) A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 63(7):2541–2556
Qin Y, Wang M, Tian Y, He W, Han L, Xia G (2012) Over-expression of TaMYB33 encoding a novel wheat MYB transcription factor increases salt and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Rep 39(6):7183–7192
Galis I, Simek P, Narisawa T, Sasaki M, Horiguchi T, Fukuda H, Matsuoka K (2006) A novel R2R3 MYB transcription factor NtMYBJS1 is a methyl jasmonate-dependent regulator of phenylpropanoid-conjugate biosynthesis in tobacco. Plant J 46(4):573–592
Song SK, Ryu KH, Kang YH, Song JH, Cho YH, Yoo SD, Schiefelbein J, Lee MM (2011) Cell fate in the Arabidopsis root epidermis is determined by competition between WEREWOLF and CAPRICE. Plant Physiol 157(3):1196–1208
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Huep G, Barsch A, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B (2007) Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J 50(4):660–677
Gonzalez A, Zhao M, Leavitt JM, Lloyd AM (2008) Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J 53(5):814–827
Wei YL, Li JN, Lu J, Tang ZL, Pu DC, Chai YR (2007) Molecular cloning of Brassica napus TRANSPARENT TESTA 2 gene family encoding potential MYB regulatory proteins of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Mol Biol Rep 34(2):105–120
Lin-Wang K, Bolitho K, Grafton K, Kortstee A, Karunairetnam S, McGhie TK, Espley RV, Hellens RP, Allan AC (2010) An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):50
Butelli E, Licciardello C, Zhang Y, Liu J, Mackay S, Bailey P, Reforgiato-Recupero G, Martin C (2012) Retrotransposons control fruit-specific, cold-dependent accumulation of anthocyanins in blood oranges. Plant Cell 24(3):1242–1255
Wilkins O, Nahal H, Foong J, Provart NJ, Campbell MM (2008) Expansion and diversification of the populus R2R3-MYB family of transcription factors. Plant Physiol 149(2):981–993
Matus J, Aquea F, Arce-Johnson P (2008) Analysis of the grape MYB R2R3 subfamily reveals expanded wine quality-related clades and conserved gene structure organization across Vitis and Arabidopsis genomes. BMC Plant Biol 8(1):83
Du H, Feng BR, Yang SS, Huang YB, Tang YX (2012) The R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene family in maize. PLoS ONE 7(6):e37463
Cao ZH, Zhang SZ, Wang RK, Zhang RF, Hao Y-J (2013) Genome wide analysis of the apple MYB transcription factor family allows the identification of MdoMYB121 gene confering abiotic stress tolerance in plants. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69955
Du H, Yang SS, Liang Z, Feng BR, Liu L, Huang YB, Tang YX (2012) Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12(1):106
Katiyar A, Smita S, Lenka SK, Rajwanshi R, Chinnusamy V, Bansal KC (2012) Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics 13(1):544
Tombuloglu H, Kekec G, Sakcali MS, Unver T (2013) Transcriptome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in barley with their boron responsive expression analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 288(3–4):141–155
Zhang L, Zhao G, Jia J, Liu X, Kong X (2011) Molecular characterization of 60 isolated wheat MYB genes and analysis of their expression during abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 63(1):203–214
Xu Q, Chen LL, Ruan X, Chen D, Zhu A, Chen C, Bertrand D, Jiao WB, Hao BH, Lyon MP, Chen J, Gao S, Xing F, Lan H, Chang JW, Ge X, Lei Y, Hu Q, Miao Y, Wang L, Xiao S, Biswas MK, Zeng W, Guo F, Cao H, Yang X, Xu XW, Cheng YJ, Xu J, Liu JH, Luo OJ, Tang Z, Guo WW, Kuang H, Zhang HY, Roose ML, Nagarajan N, Deng XX, Ruan Y (2013) The draft genome of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Nat Genet 45(1):59–66
Finn RD, Mistry J, Tate J, Coggill P, Heger A, Pollington JE, Gavin OL, Gunasekaran P, Ceric G, Forslund K (2010) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 38(suppl 1):D211–D222
Finn RD, Clements J, Eddy SR (2011) HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl 2):W29–W37
de Castro E, Sigrist CJA, Gattiker A, Bulliard V, Langendijk-Genevaux PS, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Hulo N (2006) ScanProsite: detection of PROSITE signature matches and ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 34(suppl 2):W362–W365
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1):D302–D305
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3497–3500
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14(6):1188–1190
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Guo AY, Zhu QH, Chen X, Luo JC (2007) GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi chuan=Hereditas/Zhongguo yi chuan xue hui bian ji 29(8):1023
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37(suppl 2):W202–W208
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93(1):77–78
Wang Y, Tang H, DeBarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee T-H, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H (2012) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40(7):e49
Ming R, Hou S, Feng Y, Yu Q, Dionne-Laporte A, Saw JH, Senin P, Wang W, Ly BV, Lewis KLT, Salzberg SL, Feng L, Jones MR, Skelton RL, Murray JE, Chen C, Qian W, Shen J, Du P, Eustice M, Tong E, Tang H, Lyons E, Paull RE, Michael TP, Wall K, Rice DW, Albert H, Wang M-L, Zhu YJ, Schatz M, Nagarajan N, Acob RA, Guan P, Blas A, Wai CM, Ackerman CM, Ren Y, Liu C, Wang J, Wang J, Na J-K, Shakirov EV, Haas B, Thimmapuram J, Nelson D, Wang X, Bowers JE, Gschwend AR, Delcher AL, Singh R, Suzuki JY, Tripathi S, Neupane K, Wei H, Irikura B, Paidi M, Jiang N, Zhang W, Presting G, Windsor A, Navajas-Pérez R, Torres MJ, Feltus FA, Porter B, Li Y, Burroughs AM, Luo MC, Liu L, Christopher DA, Mount SM, Moore PH, Sugimura T, Jiang J, Schuler MA, Friedman V, Mitchell-Olds T, Shippen DE, dePamphilis CW, Palmer JD, Freeling M, Paterson AH, Gonsalves D, Wang L, Alam M (2008) The draft genome of the transgenic tropical fruit tree papaya (Carica papaya Linnaeus). Nature 452(7190):991–996
Argout X, Salse J, Aury J-M, Guiltinan MJ, Droc G, Gouzy J, Allegre M, Chaparro C, Legavre T, Maximova SN, Abrouk M, Murat F, Fouet O, Poulain J, Ruiz M, Roguet Y, Rodier-Goud M, Barbosa-Neto JF, Sabot F, Kudrna D, Ammiraju JSS, Schuster SC, Carlson JE, Sallet E, Schiex T, Dievart A, Kramer M, Gelley L, Shi Z, Bérard A, Viot C, Boccara M, Risterucci AM, Guignon V, Sabau X, Axtell MJ, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Brown S, Bourge M, Golser W, Song X, Clement D, Rivallan R, Tahi M, Akaza JM, Pitollat B, Gramacho K, D’Hont A, Brunel D, Infante D, Kebe I, Costet P, Wing R, McCombie WR, Guiderdoni E, Quetier F, Panaud O, Wincker P, Bocs S, Lanaud C (2011) The genome of Theobroma cacao. Nat Genet 43(2):101–108
Saeed AI, Bhagabati NK, Braisted JC, Liang W, Sharov V, Howe EA, Li J, Thiagarajan M, White JA, Quackenbush J (2006) TM4 microarray software suite. Methods Enzymol 411:134–193
Liu Q, Xu J, Liu Y, Zhao X, Deng X, Guo L, Gu J (2007) A novel bud mutation that confers abnormal patterns of lycopene accumulation in sweet orange fruit (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck). J Exp Bot 58(15–16):4161–4171
Williams CE, Grotewold E (1997) Differences between plant and animal myb domains are fundamental for DNA binding activity, and chimeric myb domains have novel DNA binding specificities. J Biol Chem 272(1):563–571
Heine G, Hernandez J, Grotewold E (2004) Two cysteines in plant R2R3 MYB domains participate in REDOX-dependent DNA binding. J Biol Chem 279(36):37878–37885
Stephan Guehmann GV, Kalkbrenner Frank, Moelling Karin (1992) Reduction of a conserved cys is essential for myb DNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res 20(9):2279–2286
Rabinowicz PD, Braun EL, Wolfe AD, Bowen B, Grotewold E (1999) Maize R2R3 myb genes: sequence analysis reveals amplification in the higher plants. Genetics 153(1):427–444
Dias A, Braun E, McMullen M, Grotewold E (2003) Recently duplicated maize R2R3 myb genes provide evidence for distinct mechanisms of evolutionary divergence after duplication. Plant Physiol 131(2):610–620
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:10
Zimmermann I, Heim M, Weisshaar B, Uhrig J (2004) Comprehensive identification of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB transcription factors interacting with R/B-like BHLH proteins. Plant J 40(1):22–34
Blanc G, Wolfea KH (2004) Functional divergence of duplicated genes formed by polyploidy during arabidopsis evolution. Plant Cell 16(7):1679–1691
Zhu J, Chen H, Li H, Gao JF, Jiang H, Wang C, Guan YF, Yang ZN (2008) Defective in tapetal development and function 1 is essential for anther development and tapetal function for microspore maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 55(2):266–277
Zhang ZB, Zhu J, Gao JF, Wang C, Li H, Li H, Zhang HQ, Zhang S, Wang DM, Wang QX, Huang H, Xia HJ, Yang ZN (2007) Transcription factor AtMYB103 is required for anther development by regulating tapetum development, callose dissolution and exine formation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52(3):528–538
Xie Z, Li D, Wang L, Sack FD, Grotewold E (2010) Role of the stomatal development regulators FLP/MYB88 in abiotic stress responses. Plant J 64(5):731–739
Lai LB, Nadeau JA, Lucas J, Lee E-K, Nakagawa T, Zhao L, Geisler M, Sack FD (2005) The Arabidopsis R2R3 MYB proteins FOUR LIPS and MYB88 restrict divisions late in the stomatal cell lineage. Plant Cell 17(10):2754–2767
Schmitz G, Tillmann E, Carriero F, Fiore C, Cellini F, Theres K (2002) The tomato blind gene encodes a MYB transcription factor that controls the formation of lateral meristems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(2):1064–1069
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15(1):63–78
Maeda K, Kimura S, Demura T, Takeda J, Ozeki Y (2005) DcMYB1 acts as a transcriptional activator of the carrot phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene (DcPAL1) in response to elicitor treatment, UV-B irradiation and the dilution effect. Plant Mol Biol 59(5):739–752
Zhang L, Zhao G, Jia J, Liu X, Kong X (2012) Molecular characterization of 60 isolated wheat MYB genes and analysis of their expression during abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 63(1):203–214
Moriguchi T, Kita M, Tomono Y, Endo-Inagaki T, Omura M (2001) Gene expression in flavonoid biosynthesis: correlation with flavonoid accumulation in developing citrus fruit. Physiol Plant 111(1):66–74
Nakatsuka T, Saito M, Yamada E, Fujita K, Kakizaki Y, Nishihara M (2012) Isolation and characterization of GtMYBP3 and GtMYBP4, orthologues of R2R3-MYB transcription factors that regulate early flavonoid biosynthesis, in gentian flowers. J Exp Bot 63(18):6505–6517
Lei Y, Liu YZ, Gu QQ, Yang XY, Deng XX, Chen JY (2012) Comparison of cell wall metabolism in the pulp of three cultivars of ‘Nanfeng’ tangerine differing in mastication trait. J Sci Food Agr 92(3):496–502
Karpinska B, Karlsson M, Srivastava M, Stenberg A, Schrader J, Sterky F, Bhalerao R, Wingsle G (2004) MYB transcription factors are differentially expressed and regulated during secondary vascular tissue development in hybrid aspen. Plant Mol Biol 56(2):255–270
Zhong R, Lee C, Zhou J, McCarthy RL, Ye ZH (2008) A battery of transcription factors involved in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20(10):2763–2782
Cultrone A, Cotroneo PS, Recupero GR (2009) Cloning and molecular characterization of R2R3-MYB and bHLH-MYC transcription factors from Citrus sinensis. Tree Genet Genomes 6(1):101–112
Walker AR, Lee E, Bogs J, McDavid DAJ, Thomas MR, Robinson SP (2007) White grapes arose through the mutation of two similar and adjacent regulatory genes. Plant J 49(5):772–785
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49(3):414–427
Chen YH, Yang XY, He K, Liu MH, Li JG, Gao ZF, Lin ZQ, Zhang YF, Wang XX, Qiu XM, Shen YP, Zhang L, Deng XH, Luo JC, Deng XW, Chen ZL, Gu HY, Qu LJ (2006) The myb transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice myb family. Plant Mol Biol 60(1):107–124
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31272148 and 31222047) and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chaoyang Liu and Xia Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Wang, X., Xu, Y. et al. Genome-wide analysis of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) . Mol Biol Rep 41, 6769–6785 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3563-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3563-1