Abstract
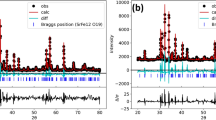
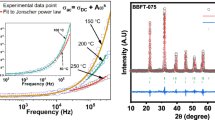
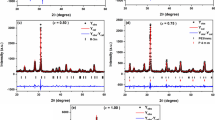
The effect of grain size on crystal structure and the ferroelectric, dielectric, and piezoelectric properties of 0.38Bi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3-0.62PbTiO3 ceramics was studied herein. By controlling the sintering time, 0.38Bi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3-0.62PbTiO3 ceramics with different grain sizes were prepared by the conventional solid-state reaction. It was found that the crystal structure of the ceramics changed slightly with the increase of grain size, from a pure tetragonal perovskite structure to a combination of tetragonal and rhombohedral phases. Both the Curie temperature TC and the depolarization temperature Td of the ceramics decreased with increasing grain size. However, the degree of dielectric relaxation first increased and then decreased, with the relaxation factor γ ranging from 1.35 to 1.87. The remnant polarization Pr and coercive field EC also first increased and then decreased, whereas the strain increased with the increase of grain size. The high field strain coefficient d*33 and piezoelectric coefficient d33 both increased with the increase of grain size. However, in this ceramic system, the electromechanical coupling coefficient kp and mechanical quality factor Qm changed independently of the variation in grain size.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Z. Zhao, V. Buscaglia, M. Viviani et al., Phys. Rev. B 70, 024107 (2004)
S.V. Titov, L.A. Shilkina, V.V. Titov et al., Ferroelectrics 576, 136–147 (2021)
E.V. Barabanova, A.V. Skrylev, G.M. Akbaeva et al., Ferroelectrics 574, 45–52 (2021)
E.V. Barabanova, A.A. Topchiev, O.V. Malyshkina, Phys. Solid State 60, 747–750 (2018)
L. Lv, Y. Wang, L. Gan et al., J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 14883–14889 (2018)
X.F. Zhao, A.K. Soh, Scripta Mater. 178, 313–317 (2020)
T.M. Kamel, G. With, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 851–861 (2008)
H.T. Martirenat, J.C. Burfoot, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 7, 3182–3192 (1974)
X. Tang, H.L. Chan, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 034109 (2005)
Y. Sudo, M. Hagiwara, S. Fujihara, Ceram. Int. 42, 8206–8211 (2016)
Z. Cai, X. Wang, W. Hong et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 5487–5496 (2018)
Y. Yue, X. Xu, M. Zhang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 57548–57559 (2021)
V. Buscaglia, M.T. Buscaglia, M. Viviani et al., J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2889–2898 (2006)
Z. Zhao, V. Buscaglia, M. Viviani, Buscaglia, et al., Phys. Rev. B 70, 024107 (2004)
A. Simon, J. Ravez, M. Maglione, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 16, 963–970 (2004)
K. Uchino, S. Nomura, Ferroelectr. Lett. Sect. 44, 55–61 (1982)
X. Wei, Y. Feng, X. Yao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2031–2033 (2003)
C. Fu, J. Yang, W. Cai, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 22, 47–51 (2011)
C. Fu, F. Pan, W. Cai, Integr. Ferroelectr. 104, 1–7 (2008)
S. Chen, X. Dong, T. Zeng et al., Ferroelectrics 363, 199–208 (2008)
H. Zhang, H. Yan, H. Ning et al., Nanotechnology 20, 385708 (2009)
W. Cai, C. Fu, J. Gao et al., J. Alloy. Compd. 480, 870–873 (2009)
C. Xiao, Z. Chi, F. Li et al., Chinese Phys. 16, 3125 (2007)
S. Ding, T. Song, X. Yang et al., Ferroelectr. 402, 55–59 (2010)
G. Picht, N.H. Khansur, K.G. Webber et al., J. Appl. Phys. 128, 214105 (2020)
X. Liu, S. Xue, F. Wang et al., Acta Mater. 164, 12–24 (2019)
Y. Tan, G. Viola, V. Koval et al., J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 2064–2075 (2019)
G. Viola, K.B. Chong, M. Eriksson et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 182903 (2013)
H. Chen, B. Shen, J. Xu et al., J. Alloy. Compd. 551, 92–97 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Project [Grant No. 51702317], the Youth Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial Science and Technology [Grant No. 20212BAB214019], and the Qingjiang Excellent Young Talents of Jiangxi University of Science and Technology [Grant No. JXUSTQJYX2020004].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors whose names are listed immediately below certify that this manuscript is the authors’ original work and has not been published nor has been submitted simultaneously elsewhere. There is no conflict of interest for this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Pang, D. Effect of grain size on crystal structure and electric properties of Bi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3-PbTiO3 ferroelectric ceramics. J Electroceram 49, 77–84 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-022-00293-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-022-00293-8