Abstract
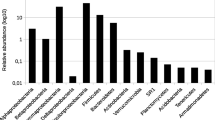
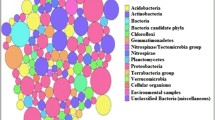
In Morocco, pollution caused by closed mines continues to be a serious threat to the environment, like the generation of acid mine drainage. Mine drainage is produced by environmental and microbial oxidation of sulfur minerals originating from mine wastes. The fundamental role of microbial communities is well known, like implication of Fe-oxidizing and to a lesser extent S-oxidizing microorganism in bioleaching. However, the structure of the microbial communities varies a lot from one site to another, like diversity depends on many factors such as mineralogy, concentration of metals and metalloids or pH, etc. In this study, prokaryotic communities in the pyrrhotite-rich tailings of Kettara mine were characterized using the Illumina sequencing. In-depth phylogenetic analysis revealed a total of 12 phyla of bacteria and 1 phyla of Archaea. The majority of sequences belonged to the phylum of Proteobacteria and Firmicutes with a predominance of Bacillus, Pseudomonas or Corynebacterium genera. Many microbial populations are implicated in the iron, sulfur and arsenic cycles, like Acidiferrobacter, Leptospirillum, or Alicyclobacillus in Fe; Acidiferrobacter and Sulfobacillus in S; and Bacillus or Pseudomonas in As. This is one of the first description of prokaryotic communities in pyrrhotite-rich mine tailings using high-throughput sequencing.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul SM, Jayasinghe SS, Chandana EPS, Jayasumana C et al (2015) Arsenic and human health effects: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40:828–846
Akcil A, Koldas S (2006) Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. J Clean Prod 14:1139–1145
Anandham R, Indiragandhi P, Madhaiyan M, Ryu KY et al (2008) Chemolithoautotrophic oxidation of thiosulfate and phylogenetic distribution of sulfur oxidation gene (soxB) in rhizobacteria isolated from crop plants. Res Microbiol 159:579–589
Auger C, Han S, Appanna VP, Thomas SC, Ulibarri G, Appanna VD (2013) Metabolic reengineering invoked by microbial systems to decontaminate aluminum: implications for bioremediation technologies. Biotechnol Adv 31:266–273
Babi K, Asselin H, Benzaazoua M (2015) Stakeholders’ perceptions of sustainable mining in Morocco: a case study of the abandoned Kettara mine. Extr Ind Soc 1:185–192
Bachate SP, Khapare RM, Kodam KM (2012) Oxidation of arsenite by two β-proteobacteria isolated from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:2135–2145
Bachate SP, Nandre VS, Ghatpande NS, Kodam KM (2013) Simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidation of As(III) by Bacillus firmus TE7 isolated from tannery effluent. Chemosphere 90:2273–2278
Bachy C, Worden AZ (2014) Microbial ecology: finding structure in the rare biosphere. Curr Biol 24:R315–R317
Bahar MM, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2012) Arsenic bioremediation potential of new arsenic oxidizing bacterium Stenotrophomonas sp. MM-7 isolated from soil. Biodegradation 23:803–812
Bahar MM, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2013a) Bioremediation of arsenic-contaminated water: recent advances and future prospects. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1722
Bahar MM, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2013b) Kinetics of arsenite oxidation by Variovorax sp. MM-1 isolated from a soil containing low arsenic and identification of arsenite oxidase gene. J Hazard Mater 262:997–1003
Banerjee S, Majumdar J, Samal AC, Bhattachariya P et al (2013) Biotransformation and bioaccumulation of arsenic by Brevibacillus brevis isolated from arsenic contaminated region of West Bengal. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 3:1–10
Bates ST, Berg-Lyons D, Caporaso JG et al (2011) Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J 5:908–917
Behera BC, Patra M, Dutta SK, Thatoi HN (2014) Isolation and characterisation of sulphur oxidising bacteria from mangrove soil of Mahanadi River Delta and their sulphur oxidising ability. J Appl Environ Microbiol 2:1–5
Bhatnagar L, Henriquet M, Zeikus JG, Aubert JP (1984) Utilization of mercapto-2-ethanol as a medium reductant for determination of the metabolic response of methanogens towards inorganic sulfur compounds. FEMS Microbiol Lett 22:155–158
Blum JS, Bindi AB, Buzelli J, Stolz JF, Oremland RS (1998) Bacillus arsenicoselenatis, sp. nov., and Bacillus selenitireducens, sp. nov.: two haloalkaliphiles from Mono Lake, California that respire oxyanions. Arch Microbiol 171:19–30
Bridge TAM, Johnson DB (1998) Reduction of soluble iron and reductive dissolution of ferric iron-containing minerals by moderately thermophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2181–2186
Campos VL, Escalante G, Yañez J, Zaror CA et al (2009) Isolation of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria from a natural biofilm associated to volcanic rocks of Atacama Desert, Chile. J Basic Microbiol 49:S93–S97
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D et al (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:4516–4522
Chang J-S, Lee J-H, Kim I-S (2011) Bacterial aox genotype from arsenic contaminated mine to adjacent coastal sediment: evidences for potential biogeochemical arsenic oxidation. J Hazard Mater 193:233–242
Chen LX, Li JT, Chen YT, Huang LN et al (2013) Shifts in microbial community composition and function in the acidification of a lead/zinc mine tailings. Environ Microbiol 15:2431–2444
Das S, Jean J-S, Kar S, Chou M-L et al (2014) Screening of plant growth-promoting traits in arsenic-resistant bacteria isolated from agricultural soil and their potential implication for arsenic bioremediation. J Hazard Mater 272:112–120
Diaby N, Dold B, Pfeifer HR, Holliger C, Johnson DB, Hallberg KB (2007) Microbial communities in a porphyry copper tailings impoundment and their impact on the geochemical dynamics of the mine waste. Environ Microbiol 9:298–307
Dopson M, Johnson DB (2012) Biodiversity, metabolism and applications of acidophilic sulfur-metabolizing microorganisms. Environ Microbiol 14:2620–2631
Duan M, Wang Y, Xie X, Su C et al (2013) Arsenite oxidizing bacterium isolated from high arsenic groundwater aquifers from Datong Basin, Northern China. Proc Earth Planet Sci 7:232–235
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C et al (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Fisher J, Hollibaugh JT (2008) Selenate-dependent anaerobic arsenite oxidation by a bacterium from Mono Lake, California. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2588–2594
Friedrich CG, Mitrenga G (1981) Oxidation of thiosulfate by Paracoccus denitrificans and other hydrogen bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 10:209–212
Galand PE, Casamayor EO, Kirchman DL, Lovejoy C (2009) Ecology of the rare microbial biosphere of the Arctic Ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22427–22432
Garcia Balboa C, Bedoya IC, González F, Blázquez ML, Muñoz JA, Ballester A (2010) Bio-reduction of Fe(III) ores using three pure strains of Aeromonas hydrophila, Serratia fonticola and Clostridium celerecrescens and a natural consortium. Biores Technol 101:7864–7871
Hakkou R, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2008a) Acid mine drainage at the abandoned Kettara mine (Morocco): 1. Environmental characterization. Mine Water Environ 27:145–159
Hakkou R, Benzaazoua M, Bussière B (2008b) Acid mine drainage at the abandoned Kettara mine (Morocco): 2. Mine waste geochemical behavior. Mine Water Environ 27:160–170
Hallberg KB (2010) New perspectives in acid mine drainage microbiology. Hydrometallurgy 104:448–453
Hallberg KB, Hedrich S, Johnson DB (2011) Acidiferrobacter thiooxydans, gen. nov. sp. nov.; an acidophilic, thermo-tolerant, facultatively anaerobic iron-and sulfur-oxidizer of the family Ectothiorhodospiraceae. Extremophiles 15:271–279
Han Y, Wang JB, Zhu XY, Guo NN (2012) Stable isotope and REE geological and geochemical characteristics of the calcite in the Fankou Zinc-Lead deposit, Guangdong Province, China. In Adv Mater Res 524:205–212
Huang LN, Zhou WH, Hallberg KB, Wan CY, Li J, Shu WS (2011) Spatial and temporal analysis of the microbial community in the tailings of a Pb-Zn mine generating acidic drainage. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5540–5544
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12:1889–1898
Jiang CY, Liu Y, Liu YY, You XY, Guo X, Liu SJ (2008) Alicyclobacillus ferrooxydans sp. nov., a ferrous-oxidizing bacterium from solfataric soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2898–2903
Johnson DB, Bridge TAM (2002) Reduction of ferric iron by acidophilic heterotrophic bacteria: evidence for constitutive and inducible enzyme systems in Acidiphilium spp. J Appl Microbiol 92:315–321
Johnson DB, Hallberg KB (2008) Carbon, iron and sulfur metabolism in acidophilic micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol 54:201–255
Justice NB, Norman A, Brown CT, Singh A, Thomas BC, Banfield JF (2014) Comparison of environmental and isolate Sulfobacillus genomes reveals diverse carbon, sulfur, nitrogen, and hydrogen metabolisms. BMC Genomics 15:1107
Karavaiko GI, Bogdanova TI, Tourova TP, Kondrat’eva TF et al (2005) Reclassification of ‘Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans subsp thermotolerans’ strain K1 as Alicyclobacillus tolerans sp. nov. and Sulfobacillus disulfidooxidans Dufresne et al 1996 as Alicyclobacillus disulfidooxidans comb. nov., and emended description of the genus Alicyclobacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:941–947
Katayama Y, Hiraishi A, Kuraishi H (1995) Paracoccus thiocyanatus sp. nov., a new species of thiocyanate-utilizing facultative chemolithotroph, and transfer of Thiobacillus versutus to the genus Paracoccus as Paracoccus versutus comb. nov. with emendation of the genus. Microbiology 141:1469–1477
Khalil K, Hanich L, Bannari A, Zouhri L et al (2013) Assessment of soil contamination around an abandoned mine in a semi-arid environment using geochemistry and geostatistics: pre-work of geochemical process modeling with numerical models. J Geochem Explor 125:117–129
Kock D, Schippers A (2008) Quantitative microbial community analysis of three different sulfidic mine tailing dumps generating acid mine drainage. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5211–5219
Korehi H, Blöthe M, Schippers A (2014) Microbial diversity at the moderate acidic stage in three different sulfidic mine tailings dumps generating acid mine drainage. Res Microbiol 165:713–718
Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD (2013) Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:5112–5120
Kumaraswamy R, Sjollema K, Kuenen G, Van Loosdrecht M, Muyzer G (2006) Nitrate-dependent [Fe(II) EDTA]2− oxidation by Paracoccus ferrooxidans sp. nov., isolated from a denitrifying bioreactor. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:276–286
Lghoul M, Teixidó T, Peña JA, Hakkou R, Kchikach A, Guérin R et al (2012) Electrical and seismic tomography used to image the structure of a tailings pond at the abandoned Kettara mine, Morocco. Mine Water Environ 31:53–61
Lghoul M, Maqsoud A, Hakkou R, Kchikach A (2014) Hydrogeochemical behavior around the abandoned Kettara mine site, Morocco. J Geochem Explor 144:456–467
Liao VHC, Chu YJ, Su YC, Hsiao SY, Wei CC, Liu CW et al (2011) Arsenite-oxidizing and arsenate-reducing bacteria associated with arsenic-rich groundwater in Taiwan. J Contam Hydrol 123:20–29
Liu J, Hua ZS, Chen LX, Kuang JL, Li SJ, Shu WS, Huang LN (2014) Correlating microbial diversity patterns with geochemistry in an extreme and heterogeneous environment of mine tailings. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:3677–3686
Luo J, Tian G, Lin W (2013) Enrichment, isolation and identification of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria from sulfide removing bioreactor. J Environ Sci 25:1393–1399
Macur RE, Jackson CR, Botero LM, Mcdermott TR, Inskeep WP (2004) Bacterial populations associated with the oxidation and reduction of arsenic in an unsaturated soil. Environ Sci Technol 38:104–111
Mahmood Q, Zheng P, Hu B, Jilani G, Azim MR, Wu D, Liu D (2009) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas stutzeri QZ1 from an anoxic sulfide-oxidizing bioreactor. Anaerobe 15:108–115
Mandal BK, Suzuki KT (2002) Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58:201–235
Mathieu C, Pieltain F (2003) Analyse chimique des sols. In: Méthode choisis. Ed Lavoisier, Tec and Doc
Mendez MO, Neilson JW, Maier RM (2008) Characterization of a bacterial community in an abandoned semiarid lead-zinc mine tailing site. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3899–3907
Muehe EM, Gerhardt S, Schink B, Kappler A (2009) Ecophysiology and the energetic benefit of mixotrophic Fe(II) oxidation by various strains of nitrate-reducing bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:335–343
Needleman SB, Wunsch CD (1970) A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol 48:443–453
Norris PR, Clark DA, Owen JP, Waterhouse S (1996) Characteristics of Sulfobacillus acidophilus sp. nov. and other moderately thermophilic mineral-sulphide-oxidizing bacteria. Microbiology 142:775–783
Okamura K, Kawai A, Wakao N, Yamada T, Hiraishi A (2015) Acidiphilium iwatense sp. nov., isolated from an acid mine drainage treatment plant, and emendation of the genus Acidiphilium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:42–48
Omori T, Monna LISA, Saiki Y, Kodama T (1992) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Corynebacterium sp. strain SY1. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:911–915
Oremland RS, Stolz JF (2003) The ecology of arsenic. Science 300:939–944
Osborne FH, Ehrlich HL (1976) Oxidation of arsenite by a soil isolate of Alcaligenes. J Appl Microbiol 41:295–305
Paul D, Poddar S, Sar P (2014) Characterization of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria isolated from arsenic-contaminated groundwater of West Bengal. J Environ Sci Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 49:1481–1492
Pina RG, Cervantes C (1996) Microbial interactions with aluminium. BioMetals 9:311–316
R Development Core Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org
Rawlings DE, Johnson DB (2007) The microbiology of biomining: development and optimization of mineral-oxidizing microbial consortia. Microbiology 153:315–324
Sallam A, Steinbüchel A (2009) Clostridium sulfidigenes sp. nov., a mesophilic, proteolytic, thiosulfate-and sulfur-reducing bacterium isolated from pond sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1661–1665
Sanchez Andrea I, Rodriguez N, Amils R, Sanz JL (2011) Microbial diversity in anaerobic sediments at Rio Tinto, a naturally acidic environment with a high heavy metal content. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6085–6093
Santini JM, Sly LI, Schnagl RD, Macy JM (2000) A new chemolithoautotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a gold mine: phylogenetic, physiological, and preliminary biochemical studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:92–97
Sarkar A, Kazy KS, Sar P (2014) Studies on arsenic transforming groundwater bacteria and their role in arsenic release from subsurface sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8645–8662
Schippers A, Sand W (1999) Bacterial leaching of metal sulfides proceeds by two indirect mechanisms via thiosulfate or via polysulfides and sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:319–321
Schippers A, Kock D, Schwartz M, Böttcher ME, Vogel H, Hagger M (2007) Geomicrobiological and geochemical investigation of a pyrrhotite-containing mine waste tailings dam near Selebi-Phikwe in Botswana. J Geochem Explor 92:151–158
Schippers A, Breuker A, Blazejak A, Bosecker K, Kock D, Wright TL (2010) The biogeochemistry and microbiology of sulfidic mine waste and bioleaching dumps and heaps, and novel Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria. Hydrometallurgy 104:342–350
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Schloss PD, Gevers D, Westcott SL (2011) Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS One 6:e27310
Simate GS, Ndlovu S (2014) Acid mine drainage: challenges and opportunities. J Environ Chem Eng 2:1785–1803
Singer PC, Stumm W (1970) Acid mine drainage: the rate-determining step. Science 167:1121–1123
Sorokin DY, Teske A, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1999) Anaerobic oxidation of thiosulphate to tetrathionate by obligately heterotrophic bacteria, belonging to the Pseudomonas stutzeri complex. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30:113–123
Stolz JF, Basu P, Santini JM, Oremland RS (2006) Arsenic and selenium in microbial metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:107–130
Takahashi Y, Suto K, Inoue C (2010) Polysulfide reduction by Clostridium relatives isolated from sulfate-reducing enrichment cultures. J Biosci Bioeng 109:372–380
Tan GL, Shu WS, Hallberg KB, Li F, Lan CY, Zhou WH, Huang LN (2008) Culturable and molecular phylogenetic diversity of microorganisms in an open-dumped, extremely acidic Pb/Zn mine tailings. Extremophiles 12:657–664
Thermo Scientific NITON (2008) Thermo Scientific NITON® XL3t 900 Series Product specifications. http://www.thermo.com/niton (last accessed 3 Nov 2014)
Toughzaoui S, El Amari K, Benkaddour A, Hibti M, Essarraj S (2015) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic studies of the Kettara mine watershed, Morocco. Mine Water Environ 34:308–319
Turner AW (1954) Bacterial oxidation of arsenite. I. Description of bacteria isolated from arsenical cattle-dipping fluids. Aust J Biol Sci 7:452–476
Ventura BA, González F, Ballester A, Blázquez ML, Muñoz JA (2015) Bioreduction of iron compounds by Aeromonas hydrophila. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 103:69–76
Vera M, Schippers A, Sand W (2013) Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation. Part A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7529–7541
Vikromvarasiri N, Boonyawanich S, Pisutpaisal N (2015) Optimizing sulfur oxidizing performance of Paracoccus pantotrophus isolated from leather industry wastewater. Energy Proc 79:629–633
Wang GW, Chen TH, Yue ZB, Zhou YF, Wang J (2014a) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas stutzeri capable of reducing Fe(III) and nitrate from skarn-type copper mine tailings. Geomicrobiol J 31:509–518
Wang P, Sun G, Jia Y, Meharg AA, Zhu Y (2014b) A review on completing arsenic biogeochemical cycle: microbial volatilization of arsines in environment. J Environ Sci 26:371–381
Weber KA, Achenbach LA, Coates JD (2006) Microorganisms pumping iron: anaerobic microbial iron oxidation and reduction. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:752–764
Xiu W, Guo H, Liu Q, Liu Z, Zhang B (2015) Arsenic removal and transformation by Pseudomonas sp. strain GE-1-induced ferrihydrite: co-precipitation versus adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:1–14
Xu XJ, Chen C, Guo HL, Wang AJ, Ren NQ, Lee DJ (2016) Characterization of a newly isolated strain Pseudomonas sp. C27 for sulfide oxidation: reaction kinetics and stoichiometry. Sci Rep 6:21032. doi:10.1038/srep21032
Yamamura S, Amachi S (2014) Microbiology of inorganic arsenic: from metabolism to bioremediation. J Biosci Bioeng 118:1–9
Zeikus JG, Wolfe RS (1972) Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum sp. nov., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol 109:707–713
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the International Research Chairs Initiative funded by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC), Canada, and by the Canada Research Chairs program and the IRD (Institut de Recherche pour le Développement) for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by F. Robb.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruneel, O., Mghazli, N., Hakkou, R. et al. In-depth characterization of bacterial and archaeal communities present in the abandoned Kettara pyrrhotite mine tailings (Morocco). Extremophiles 21, 671–685 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0933-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0933-3