Abstract
Purpose
To assess the capability of inflow inversion recovery (IFIR) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), compared with contrast-enhanced MRA (CE-MRA) as reference standard, in evaluating renal artery stenosis (RAS).
Methods
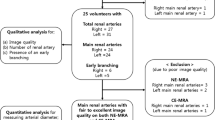
Seventy-two subjects were examined by IFIR MRA with respiratory-gated, prior to CE-MRA with a 1.5-T scanner. Two readers evaluated the quality of IFIR MRA images and renal artery depiction on artery-by-artery basis. The agreement of two methods to assess RAS was analyzed using the Kappa test. The relationship between image quality of IFIR MRA and respiratory rate was analyzed by ANOVA test.
Results
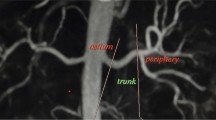
The visibility of renal artery branch vessels was significantly higher using IFIR MRA than CE-MRA (p < 0.05). A good agreement of two methods in evaluating stenosis grade, and a near-perfect inter-observer agreement for IFIR MRA (Kappa value 0.98) and CE-MRA (Kappa value 0.93), were demonstrated. As RAS ≥50%, the sensitivity and specificity of IFIR MRA were 92 and 98% in reader 1, 93 and 98% in reader 2, respectively. The image quality was significantly better in patients with stable respiration (p < 0.01).
Conclusions
IFIR MRA in patients with stable respiration has higher visibility of renal artery branch vessels than CE-MRA, and a good agreement with CE-MRA in evaluating stenosis grade. It could be used to evaluate RAS for screening, and monitoring treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hajjar I, Kotchen JM, Kotchen TA (2006) Hypertension: trends in prevalence, incidence, and control. Annu Rev Public Health 27:465–490
Safian RD, Textor SC (2001) Renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 344(6):431–442
AbuRahma AF, Yacoub M (2013) Renal imaging: duplex ultrasound, computed tomography angiography, magnetic resonance angiography, and angiography. Semin Vasc Surg 26(4):134–143
Eklof H, Ahlstrom H, Magnusson A, et al. (2006) A prospective comparison of duplex ultrasonography, captopril renography, MRA, and CTA in assessing renal artery stenosis. Acta Radiol 47(8):764–774
Glockner JF, Takahashi N, Kawashima A, et al. (2010) Non-contrast renal artery MRA using an inflow inversion recovery steady state free precession technique (Inhance): comparison with 3D contrast-enhanced MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(6):1411–1418
Prince MR, Zhang H, Morris MA, et al. (2008) Incidence of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis at two large medical centers. Radiology 248(3):807–816
Broome DR (2008) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: a summary of the medical literature reporting. Eur J Radiol. 66(2):230–234
Weinreb JC, Kuo PH (2009) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 17(1):159–167
Morita S, Masukawa A, Suzuki K, et al. (2011) Unenhanced MR angiography: techniques and clinical applications in patients with chronic kidney disease. Radiographics 31(2):E13–E33
Miyazaki M, Lee VS (2008) Nonenhanced MR angiography. Radiology 248(1):20–43
Wilson GJ, Maki JH (2009) Non-contrast-enhanced MR imaging of renal artery stenosis at 1.5 tesla. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 17(1):13–27
Wyttenbach R, Braghetti A, Wyss M, et al. (2007) Renal artery assessment with nonenhanced steady-state free precession versus contrast-enhanced MR angiography. Radiology 245(1):186–195
Parienty I, Rostoker G, Jouniaux F, et al. (2011) Renal artery stenosis evaluation in chronic kidney disease patients: nonenhanced time-spatial labeling inversion-pulse three-dimensional MR angiography with regulated breathing versus DSA. Radiology 259(2):592–601
Bley TA, François CJ, Schiebler ML, et al. (2016) Non-contrast-enhanced MRA of renal artery stenosis validation against DSA in a porcine model. Eur Radiol 26(2):547–555
Gaudiano C, Busato F, Ferramosca E, et al. (2014) 3D FIESTA pulse sequence for assessing renal artery stenosis is it a reliable application in unenhanced magnetic resonance angiography. Eur Radiol 24(12):3042–3050
Fain SB, King BF, Breen JF, et al. (2001) High-spatial-resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the renal arteries: a prospective comparison with digital subtraction angiography. Radiology 218(2):481–490
Tan KT, van Beek EJ, Brown PW, et al. (2002) Magnetic resonance angiography for the diagnosis of renal artery stenosis: a meta-analysis. Clin Radiol 57(7):617–624
Kramer U, Wiskirchen J, Fenchel MC, et al. (2008) Isotropic high-spatial resolution contrast-enhanced 3.0-T MR angiography in patients suspected of having renal artery stenosis. Radiology 247(1):228–240
McGregor R, Vymazal J, Martinez-Lopez M, et al. (2008) A multi-center, comparative, phase 3 study to determine the efficacy of gadofosveset-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for evaluation of renal artery disease. Eur J Radiol 65(2):316–325
Soulez G, Pasowicz M, Benea G, et al. (2008) Renal artery stenosis evaluation: diagnostic performance of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR angiography-comparison with DSA. Radiology 247(1):273–285
François CJ, Lum DP, Johnson KM, et al. (2011) Renal arteries: isotropic, high-spatial-resolution, unenhanced MR angiography with three-dimensional radial phase contrast. Radiology 258(1):254–260
Shin T, Worters PW, Hu BS, et al. (2013) Non-contrast-enhanced renal and abdominal MR angiography using velocity-selective inversion preparation. Magn Reson Med. 69(5):1268–1275
Utsunomiya D, Miyazaki M, Nomitsu Y, et al. (2008) Clinical role of non-contrast magnetic resonance angiography for evaluation of renal artery stenosis. Circ J. 72(10):1627–1630
Khoo MM, Deeab D, Gedroyc WM, et al. (2011) Renal artery stenosis: comparative assessment by unenhanced renal artery MRA versus contrast-enhanced MRA. Eur Radiol 21(7):1470–1476
Miyazaki M, Akahane M (2012) Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: established techniques. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(1):1–19
Serai S, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ (2012) Non-contrast MRA using an inflow-enhanced, inversion recovery SSFP technique in pediatric abdominal imaging. Pediatr Radiol 42(3):364–368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Lin, X., Huang, J. et al. The capability of inflow inversion recovery magnetic resonance compared to contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance in renal artery angiography. Abdom Radiol 42, 2479–2487 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1161-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1161-0