Abstract
Purpose
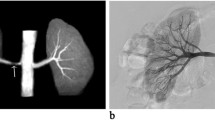
In this study, we compared non-contrast MR angiography (NC-MRA) with conventional 3D contrast-enhanced MRA (CE-MRA) in patients suspected to have renal artery stenosis (RAS).
Methods
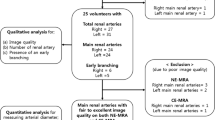
From March 2014 to March 2020, patients who were evaluated for RAS and had a glomerular filtration rate > 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 underwent MR imaging on a 3T MR Scanner (Signa Hdxt General Electrics, Milwaukee, USA) using a Torso PA coil. The NC-MRA sequence was performed using a 3D fat-suppressed inflow inversion recovery balanced steady state free precession (SSFP) sequence (Inhance 3D Inflow IR, GE Medical) whereas the CE-MRA sequence was a 3D fast spoiled gradient echo (FSPGR). Overall quality of images was rated 1 to 4. Stenosis was reported as grade 1 (Normal), 2 (< 50% narrowing), 3 (> 50% narrowing) and 4 (Total occlusion). Grade 3 and 4 were considered haemodynamically significant.
Results
During the study period, 201 patients were enrolled (400 renal arteries). For hemodynamically significant (grade 3/4) stenosis, NC-MRA correctly diagnosed 72 patients (95 arteries) while in 2 patients (2 arteries), NC-MRA underdiagnosed the stenosis as grade 2 (these were found to have grade 3 stenosis on CE-MRA). The kappa value of agreement between NC-MRA and CE-MRA for detection of RAS showing excellent agreement (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In one of the largest series of patients so far, we found that NC-MRA is a viable alternative to CE-MRA for detection of RAS, highly correlating with CE-MRA for grade of stenosis and with additional advantage of lack of gadolinium based contrast agents toxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dworkin LD, Cooper CJ (2009) Clinical practice. Renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med 361(20):1972-1978. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp0809200
Rooke TW, Hirsch AT, Misra S, et al. (2013) Management of patients with peripheral artery disease (compilation of 2005 and 2011 ACCF/AHA Guideline Recommendations): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 61(14):1555-1570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.01.004
Tendera M, Aboyans V, Bartelink ML, et al. (2011) ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases: Document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries: the Task Force on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Artery Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 32(22):2851-2906. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr211
Riccabona M, Avni FE, Damasio MB, et al. (2012) ESPR Uroradiology Task Force and ESUR Paediatric Working Group--Imaging recommendations in paediatric uroradiology, part V: childhood cystic kidney disease, childhood renal transplantation and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in children. Pediatr Radiol 42(10):1275-1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2436-9
Oelerich M, Lentschig MG, Zunker P, Reimer P, Rummeny EJ, Schuierer G (1998) Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusion: comparison of 3D time-of-flight and 3D phase-contrast MR angiography. Neuroradiology 40(9):567-573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050645
Sebastià C, Sotomayor AD, Paño B, et al. (2016) Accuracy of unenhanced magnetic resonance angiography for the assessment of renal artery stenosis. Eur J Radiol Open 3:200-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejro.2016.07.003
Spuentrup E, Manning WJ, Börnert P, Kissinger KV, Botnar RM, Stuber M (2002) Renal arteries: navigator-gated balanced fast field-echo projection MR angiography with aortic spin labeling: initial experience. Radiology 225(2):589-596. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2252011366
Wyttenbach R, Braghetti A, Wyss M, et al. (2007) Renal artery assessment with nonenhanced steady-state free precession versus contrast-enhanced MR angiography. Radiology 245(1):186-195. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2443061769
Maki JH, Wilson GJ, Eubank WB, Glickerman DJ, Millan JA, Hoogeveen RM (2007) Navigator-gated MR angiography of the renal arteries: a potential screening tool for renal artery stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188(6):W540-W546. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.06.1138
Utsunomiya D, Miyazaki M, Nomitsu Y, et al. (2008) Clinical role of non-contrast magnetic resonance angiography for evaluation of renal artery stenosis. Circ J 72(10):1627-1630. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-08-0005
Shonai T, Takahashi T, Ikeguchi H, Miyazaki M, Amano K, Yui M (2009) Improved arterial visibility using short-tau inversion-recovery (STIR) fat suppression in non-contrast-enhanced time-spatial labeling inversion pulse (Time-SLIP) renal MR angiography (MRA). J Magn Reson Imaging 29(6):1471-1477. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21792
Morita S, Masukawa A, Suzuki K, Hirata M, Kojima S, Ueno E (2011) Unenhanced MR angiography: techniques and clinical applications in patients with chronic kidney disease. Radiographics 31(2):E13-E33. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.312105075
Miyazaki M, Lee VS (2008) Nonenhanced MR angiography. Radiology 248(1):20-43. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2481071497
[14] Parienty I, Rostoker G, Jouniaux F, Piotin M, Admiraal-behloul F, Miyazaki M (2011) Renal artery stenosis evaluation in chronic kidney disease patients: nonenhanced time-spatial labeling inversion-pulse three-dimensional MR angiography with regulated breathing versus DSA. Radiology 259(2):592-601. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.11101422
Mohrs OK, Petersen SE, Schulze T, et al. (2010) High-resolution 3D unenhanced ECG-gated respiratory-navigated MR angiography of the renal arteries: comparison with contrast-enhanced MR angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195(6):1423-1428. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.10.4365
Maki JH, Wilson GJ, Eubank WB, Glickerman DJ, Pipavath S, Hoogeveen RM (2007) Steady-state free precession MRA of the renal arteries: breath-hold and navigator-gated techniques vs. CE-MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(4):966-973. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21134
Fabrega-foster KE, Agarwal S, Rastegar N, Haverstock D, Agris JM, Kamel IR (2018) Efficacy and safety of gadobutrol-enhanced MRA of the renal arteries: Results from GRAMS (Gadobutrol-enhanced renal artery MRA study), a prospective, intraindividual multicenter phase 3 blinded study. J Magn Reson Imaging 47(2):572-581. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25774
Angeretti MG, Lumia D, Canì A, et al. (2013) Non-enhanced MR angiography of renal arteries: comparison with contrast-enhanced MR angiography. Acta Radiol 54(7):749-756. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185113482690
Bley TA, François CJ, Schiebler ML, et al. (2016) Non-contrast-enhanced MRA of renal artery stenosis: validation against DSA in a porcine model. Eur Radiol 26(2):547-555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3833-x
Braidy C, Daou I, Diop AD, et al. (2012) Unenhanced MR angiography of renal arteries: 51 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(5):W629-W637. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.12.8513
Park SY, Kim CK, Kim E, Park BK (2015) Noncontrast-enhanced magnetic resonance renal angiography using a repetitive artery and venous labelling technique at 3 T: comparison with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography in subjects with normal renal function. Eur Radiol 25(2):533-540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3416-2
Shimada T, Amanuma M, Takahashi A, Tsushima Y (2012) Non-Contrast Renal MR Angiography: Value of Subtraction of Tagging and Non-Tagging Technique. Ann Vasc Dis 5(2):161-165. https://doi.org/10.3400/avd.oa.11.00065
Takahashi J, Ohmoto-sekine Y, Yoshida T, Miyazaki M (2020) Comparison of axial and coronal acquisitions by non-contrast-enhanced renal 3D MR angiography using flow-in time-spatial labeling inversion pulse. MAGMA 33(1):95-102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-019-00796-6
Albert TS, Akahane M, Parienty I, et al. (2015) An international multicenter comparison of time-SLIP unenhanced MR angiography and contrast-enhanced CT angiography for assessing renal artery stenosis: the renal artery contrast-free trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204(1):182-188. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.13.12022
Paris CL, White CJ, Collins TJ, et al. (2011) Catheter-based therapy of common femoral artery atherosclerotic disease. Vasc Med 16(2):109-112. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X11404280
Glockner JF, Takahashi N, Kawashima A, et al. (2010) Non-contrast renal artery MRA using an inflow inversion recovery steady state free precession technique (Inhance): comparison with 3D contrast-enhanced MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(6):1411-1418. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22194
Scarabino T, Carriero A, Magarelli N, et al. (1998) MR angiography in carotid stenosis: a comparison of three techniques. Eur J Radiol 28(2):117-125. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0720-048x(97)00121-6
Zhang W, Lin J, Wang S, et al. (2014) Unenhanced respiratory-gated magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of renal artery in hypertensive patients using true fast imaging with steady-state precession technique compared with contrast-enhanced MRA. J Comput Assist Tomogr 38(5):700-704. https://doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0000000000000094
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
All study participants gave written informed consent for participation in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lal, H., Singh, R.K.R., Yadav, P. et al. Non-contrast MR angiography versus contrast enhanced MR angiography for detection of renal artery stenosis: a comparative analysis in 400 renal arteries. Abdom Radiol 46, 2064–2071 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02836-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02836-5