Abstract
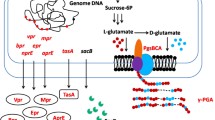
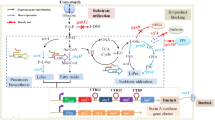
Levan is a functional homopolymer of fructose with considerable applications in food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. To improve the levan production in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the regulatory elements of sacB (encoding levansucrase) expression and levansucrase secretion were optimized. Four heterologous promoters were evaluated for sacB expression, and the Pgrac promoter led to the highest level for both sacB transcription and levansucrase enzyme activity. The levan production in the corresponding recombinant strain ΔLP-pHTPgrac reached 30.5 g/L, which was 114% higher than that of the control strain NK-ΔLP. In a further step, eight signal peptides were investigated (with Pgrac as the promoter for sacB expression) for their effects on the levansucrase secretion and levan production. The signal peptide yncM was identified as the optimal one, with a secretion efficiency of approximately 90%, and the levan production in the corresponding recombinant strain ΔLP-Y reached 37.4 g/L, which was 161% higher when compared with the control strains NK-ΔLP. Finally, fed-batch fermentation was carried out in 5-L bioreactors for levan production using the recombinant strain ΔLP-Y. A final levan concentration of 102 g/L was achieved, which is very close to the ever reported highest levan production level from the literature. To our best knowledge, this is the first report of the improvement of levan production through metabolic optimization for sacB expression and levansucrase secretion. The results from this study provided essential insights for systematically metabolic engineering of microbial cell factories for enhanced biochemical production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fattah AF, Mahmoud DA, Esawy MA (2005) Production of levansucrase from Bacillus subtilis NRC 33a and enzymic synthesis of levan and fructo-oligosaccharides. Curr Microbiol 51(6):402–407
Alamäe T, Visnapuu T, Mardo K, Mäe A, Zamfir AD (2012) Levansucrases of Pseudomonas bacteria: novel approaches for protein expression, assay of enzymes, fructooligosaccharides and heterooligofructans. Carbohydr Polym 38:176–191
Beena K, Udgaonkar JB, Varadarajan R (2004) Effect of signal peptide on the stability and folding kinetics of maltose binding protein. Biochemistry 43(12):3608–3619
Brockmeier U, Caspers M, Freudl R, Jockwer A, Noll T, Eggert T (2006) Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: a powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Biol 362(3):393–402
Caspers M, Brockmeier U, Degering C, Eggert T, Freudl R (2010) Improvement of Sec-dependent secretion of a heterologous model protein in Bacillus subtilis by saturation mutagenesis of the N-domain of the AmyE signal peptide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86(6):1877–1885
Chen Z, Heng C, Li Z, Liang X, Xinchen S (2007) Expression and secretion of a single-chain sweet protein monellin in Bacillus subtilis by sacB promoter and signal peptide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(6):1377–1381
Dahech I, Belghith KS, Hamden K, Feki A, Belghith H, Mejdoub H (2011) Oral administration of levan polysaccharide reduces the alloxan-induced oxidative stress in rats. Int J Biol Macromol 49(5):942–947
Dahech I, Belghith KS, Belghith H, Mejdoub H (2012) Partial purification of a Bacillus licheniformis levansucrase producing levan with antitumor activity. Int J Biol Macromol 51(3):329–335
Dahech I, Harrabi B, Hamden K, Feki A, Mejdoub H, Belghith H, Belghith KS (2013) Antioxidant effect of nondigestible levan and its impact on cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Int J Biol Macromol 58:281–286
de Paula VC, Pinheiro IO, Lopes CE, Calazans GC (2008) Microwave-assisted hydrolysis of Zymomonas mobilis levan envisaging oligofructan production. Bioresour Technol 99(7):2466–2470
Feng J, Gu Y, Wang J, Song C, Yang C, Xie H, Zhang W, Wang S (2013) Curing the plasmid pMC1 from the poly (gamma-glutamic acid) producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LL3 strain using plasmid incompatibility. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171(2):532–542
Feng J, Gao W, Gu Y, Zhang W, Cao M, Song C, Zhang P, Sun M, Yang C, Wang S (2014) Functions of poly-gamma-glutamic acid (γ-PGA) degradation genes in γ-PGA synthesis and cell morphology maintenance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(14):6397–6407
Feng J, Gu Y, Han L, Bi K, Quan Y, Yang C, Zhang W, Cao M, Wang S, Gao W, Sun Y, Song C (2015a) Construction of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain for high purity levan production. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362(11). doi:10.1093/femsle/fnv079
Feng J, Gu Y, Quan Y, Zhang W, Cao M, Gao W, Song C, Yang C, Wang S (2015b) Recruiting a new strategy to improve levan production in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Sci Rep 5:13814. doi:10.1038/srep13814
Jathore NR, Bule MV, Tilay AV, Annapure US (2012) Microbial levan from Pseudomonas fluorescens: characterization and medium optimization for enhanced production. Food Sci Biotechnol 21(4):1045–1053
Kucukasik F, Kazak H, Guney D, Finore I, Poli A, Yenigun O, Nicolaus B, Oner ET (2011) Molasses as fermentation substrate for levan production by Halomonas sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(6):1729–1740
Li W, Yu S, Zhang T, Jiang B, Mu W (2015) Recent novel applications of levansucrases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(17):6959–6969
Liu SL, Du K (2012) Enhanced expression of an endoglucanase in Bacillus subtilis by using the sucrose-inducible sacB promoter and improved properties of the recombinant enzyme. Protein Expr Purif 83(2):164–168
Meijer W, Salas W (2004) Relevance of UP elements for three strong Bacillus subtilis phage phi29 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 32(3):1166–1176
Nakapong S, Pichyangkura R, Ito K, Iizuka M, Pongsawasdi P (2013) High expression level of levansucrase from Bacillus licheniformis RN-01 and synthesis of levan nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 54:30–36
Ng DT, Sarkar CA (2013) Engineering signal peptides for enhanced protein secretion from Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(1):347–356
Öner ET, Hernández L, Combie J (2016) Review of Levan polysaccharide: from a century of past experiences to future prospects. Biotechnol Adv. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.05.002
Phan TT, Nguyen HD, Schumann W (2012) Development of a strong intracellular expression system for Bacillus subtilis by optimizing promoter elements. J Biotechnol 157(1):167–172
Pohl S, Harwood CR (2010) Heterologous protein secretion by Bacillus species: from the cradle to the grave. Adv Appl Microbiol 73:1–25
Radha S, Gunasekaran P (2008) Sustained expression of keratinase gene under PxylA and PamyL promoters in the recombinant Bacillus megaterium MS941. Bioresour Technol 99(13):5528–5537
Reiter L, Kolsto AB, Piehler AP (2011) Reference genes for quantitative, reverse-transcription PCR in Bacillus cereus group strains throughout the bacterial life cycle. J Microbiol Methods 86(2):210–217
Sagiya Y, Yamagata H, Udaka S (1994) Direct high-level secretion into the culture medium of tuna growth hormone in biologically active form by Bacillus brevis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42(2–3):358–363
Senthilkumar V, Rameshkumar N, Busby SJW, Gunasekaran P (2004) Disruption of the Zymomonas mobilis extracellular sucrase gene (sacC) improves levan production. J Appl Microbiol 96(4):671–676
Silbir S, Dagbagli S, Yegin S, Baysal T, Goksungur Y (2014) Levan production by Zymomonas mobilis in batch and continuous fermentation systems. Carbohydr Polym 99:454–461
Sims IM, Frese SA, Walter J, Loach D, Wilson M, Appleyard K, Eason J, Livingston M, Baird M, Cook G, Tannock GW (2011) Structure and functions of exopolysaccharide produced by gut commensal Lactobacillus reuteri 100-23. ISME J 5(7):1115–1124
Song Y, Nikoloff JM, Zhang D (2015) Improving protein production on the level of regulation of both expression and secretion pathways in Bacillus subtilis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(7):963–977
Teixeira JS, Abdi R, Su MS-W, Schwab C, Gänzle MG (2013) Functional characterization of sucrose phosphorylase and scrR, a regulator of sucrose metabolism in Lactobacillus reuteri. Food Microbiol 36(2):432–439
van Dijl JM, Hecker M (2013) Bacillus subtilis: from soil bacterium to supersecreting cell factory. Microb Cell Factories 12:3. doi:10.1186/1475-2859
Wei X, Zhou Y, Chen J, Cai D, Wang D, Qi G, Chen S (2015) Efficient expression of nattokinase in Bacillus licheniformis: host strain construction and signal peptide optimization. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42(2):287–295
Wu FC, Chou SZ, Shih IL (2013) Factors affecting the production and molecular weight of levan of Bacillus subtilis natto in batch and fed-batch culture in fermenter. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 44(6):846–853
Ying Q, Zhang C, Guo F, Wang S, Bie X, Lu F, Lu Z (2012) Secreted expression of a hyperthermophilic alpha-amylase gene from Thermococcus sp. HJ21 in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 22(6):392–398
Zanen G, Houben EN, Meima R, Tjalsma H, Jongbloed JD, Westers H, Oudega B, Luirink J, van Dijl JM, Quax WJ (2005) Signal peptide hydrophobicity is critical for early stages in protein export by Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J 272(18):4617–4630
Zhang XZ, Cui ZL, Hong Q, Li SP (2005) High-level expression and secretion of methyl parathion hydrolase in Bacillus subtilis WB800. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(7):4101–4103
Zhang XZ, Sathitsuksanoh N, Zhu Z, Percival Zhang YH (2011) One-step production of lactate from cellulose as the sole carbon source without any other organic nutrient by recombinant cellulolytic Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 13(4):364–372
Zhang J, Kang Z, Ling Z, Cao W, Liu L, Wang M, Du G, Chen J (2013) High-level extracellular production of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase in Bacillus subtilis with optimized regulatory elements. Bioresour Technol 146:543–548
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Technology Support Program 2015BAD16B04; the Natural Science Foundation of China Grant Nos. 81671842, 31470213 and 31670093; and the Project of Tianjin, China, i.e., 16JCZDJC37600, 15ZCZDNC00450 and 14ZCZDSF00009; and the program of State Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemical Biology 201603007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y., Zheng, J., Feng, J. et al. Improvement of levan production in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens through metabolic optimization of regulatory elements. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 4163–4174 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8171-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8171-2