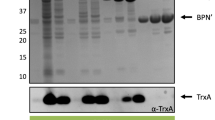
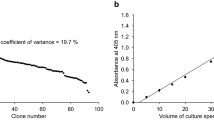
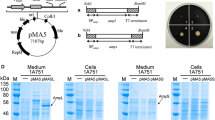
Abstract
Due to the lack of an outer membrane, Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., Bacillus species) are considered as promising host organisms for the secretory production of biotechnologically relevant heterologous proteins. However, the yields of the desired target proteins were often reported to be disappointingly low. Here, we used saturation mutagenesis of the positively charged N-domain (positions 2–7) of the signal peptide of the Bacillus subtilis α-amylase (AmyE) as a novel approach for the improvement of the secretion of a heterologous model protein, cutinase from Fusarium solani pisi, by the general secretory pathway of B. subtilis. Automated high-throughput screening of the resulting signal peptide libraries allowed for the identification of four single point mutations that resulted in significantly increased cutinase amounts, three of which surprisingly reduced the net charge of the N-domain from +3 to +2. Characterization of the effects of the identified mutations on protein synthesis and export kinetics by pulse-chase analyses indicates that an optimal balance between biosynthesis and the flow of the target protein through all stages of the B. subtilis secretion pathway is of crucial importance with respect to yield and quality of secreted heterologous proteins.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airaksinen A, Hovi T (1998) Modified base compositions at degenerate positions of a mutagenic oligonucleotide enhance randomness in site-saturation mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 26:576–581
Akita M, Sasaki S, Matsuyama SI, Mizushima S (1990) SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 265:8164–8169
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: signalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Borchert TV, Nagarajan V (1991) Effect of signal sequence alterations on export of levansucrase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 173:276–282
Brockmeier U, Caspers M, Freudl R, Jockwer A, Noll T, Eggert T (2006) Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: a powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Biol 362:393–402
Carvalho CML, Aires-Barros MR, Cabral JM (1999) Cutinase: from molecular level to bioprocess development. Biotechnol Bioeng 66:17–34
Chen M, Nagarajan V (1994) Effect of alteration of charged residues at the N-termini of signal peptides on protein export in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 176:5796–5801
Darmon E, Noone D, Masson A, Bron S, Kuipers OP, Devine KM, van Dijl JM (2002) A novel class of heat and secretion stress-responsive genes is controlled by the autoregulated CssRS two-component system of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 184:5661–5671
Eggert T, Brockmeier U, Dröge MJ, Quax WJ, Jaeger KE (2003) Extracellular lipases from Bacillus subtilis: regulation of gene expression and enzyme activity by amino acid supply and external pH. FEMS Microbiol Lett 225:319–324
Faß SH, Engels JW (1996) Influence of specific signal peptide mutations on the expression and secretion of the alpha-amylase inhibitor tendamistat in Streptomyces lividans. J Biol Chem 271:15244–15252
Harwood CR, Cranenburgh R (2008) Bacillus protein secretion: an unfolding story. Trends Microbiol 16:73–79
Hemilä H, Pakkanen R, Heikinheimo R, Palva ET, Palva I (1992) Expression of the Erwinia carotovora polygalacturonase-encoding gene in Bacillus subtilis: role of the signal peptide fusions on production of a heterologous protein. Gene 116:27–33
Jaeger KE, Eggert T, Eippner A, Reetz MT (2001) Directed evolution and the creation of enantioselective biocatalysts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:519–530
Kebir MO, Kendall DA (2002) SecA specificity for different signal peptides. Biochemistry 41:5573–5580
Kontinen VP, Sarvas M (1993) The PrsA lipoprotein is essential for protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis and sets a limit for high-level secretion. Mol Microbiol 8:727–737
Kunst F, Rapoport G (1995) Salt stress is an environmental signal affecting degradative enzyme synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 177:2403–2407
Lehnhardt S, Pollitt S, Inouye M (1987) The differential effect on two hybrid proteins of deletion mutations within the hydrophobic region of the Escherichia coli OmpA signal peptide. J Biol Chem 262:1716–1719
Lehnhardt S, Pollit NS, Goldstein J, Inouye M (1988) Modulation of the effects of mutations in the basic region of the OmpA signal peptide by the mature portion of the protein. J Biol Chem 263:10300–10303
Leloup L, Driessen AJM, Freudl R, Chambert R, Petit-Glatron MF (1999) Differential dependence of levansucrase and α-amylase secretion on SecA (Div) during the exponential phase of growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 181:1820–1826
Martinez C, De Geus P, Lauwereys M, Matthyssens G, Cambillau C (1992) Fusarium solani cutinase is a lipolytic enzyme with a catalytic serine accessible to solvent. Nature 356:615–618
Mathiesen G, Sveen A, Piard JC, Axelsson L, Eijsink VG (2008) Heterologous protein secretion by Lactobacillus plantarum using homologous signal peptides. J Appl Microbiol 105:215–226
Mathiesen G, Sveen A, Brurberg MB, Fredriksen L, Axelsson L, Eijsink VGH (2009) Genome-wide analysis of signal peptide functionality in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFSI. BMC Genomics 10:425
Monroy-Lagos O, Soberon X, Gaytan P, Osuna J (2006) Improvement of an unusual twin-arginine transporter leader peptide by a codon-based randomization approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3797–3801
Nakamura K, Itoh Y, Yamane K (1988) Enhanced secretion of ß-lactamase on structural modification of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase signal peptide. J Biochem (Tokyo) 104:265–269
Nakamura K, Fujita Y, Itoh Y, Yamane K (1989) Modification of length, hydrophobic properties and electric charge of Bacillus subtilis α-amylase signal peptide and their different effects on the production of secretory proteins in B. subtilis and Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 216:1–9
Natale P, Brüser T, Driessen AJM (2008) Sec- and Tat-mediated protein secretion across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane—distinct translocases and mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:1735–1756
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak S, von Heijne G (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng 10:1–6
Peterson JH, Woolhead CA, Bernstein HD (2003) Basic amino acids in a distinct subset of signal peptides promote interaction with the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem 278:46155–46162
Saunders CW, Pedroni JA, Monahan PM (1991) Optimization of the signal sequence cleavage site for secretion from Bacillus subtilis of a 34-amino acid fragment of human parathyroid hormone. Gene 102:277–282
Schallmey M, Singh A, Ward OP (2004) Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can J Microbiol 50:1–17
van Dijl JM, de Jong A, Smith H, Bron S, Venema G (1991) Non-functional expression of Escherichia coli signal peptidase I in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol 137:2073–2083
van Wely KHM, Swaving J, Freudl R, Driessen AJM (2001) Translocation of proteins across the cell envelope of Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:437–454
Vasantha N, Balakrishnan R, Kaur S, Jayaraman K (1980) Biosynthesis of polymyxin by Bacillus polymyxa. I. The status of the biosynthetic multienzyme complex during active antibiotic synthesis and sporulation. Arch Biochem Biophys 200:40–44
von Heijne G (1990) The signal peptide. J Membr Biol 115:195–201
Watanabe K, Tsuchida Y, Okibe N, Teramoto H, Suzuki N, Inui M, Yukawa H (2009) Scanning the Corynebacterium glutamicum R genome for high-efficiency secretion signal sequences. Microbiology (UK) 155:741–750
Winkler UK, Stuckmann M (1979) Glycogen, hyaluronate, and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol 138:663–670
Zanen G, Houben EN, Meima R, Tjalsma H, Jongbloed JD, Westers H, Oudega B, Luirink J, van Dijl JM, Quax WJ (2005) Signal peptide hydrophobicity is critical for early stages in protein export by Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J 272:4617–4630
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to H. Sahm, K.-E. Jaeger, and M. Bott for their support. M.C. was in part funded by the Graduiertenkolleg GRK 57/3-03 “Molekulare Physiologie: Stoff- und Energieumwandlung”. U.B was a recipient of a scholarship from the European Graduate College 795 entitled “Regulatory Circuits in Cellular Systems: Fundamentals and Biotechnological Applications” funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Michael Caspers and Ulf Brockmeier contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caspers, M., Brockmeier, U., Degering, C. et al. Improvement of Sec-dependent secretion of a heterologous model protein in Bacillus subtilis by saturation mutagenesis of the N-domain of the AmyE signal peptide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1877–1885 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2405-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2405-x