Abstract
Rationale
Combinations of mu and kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) agonists have been proposed as analgesic formulations with reduced abuse potential. The feasibility of this approach has been increased by the development of KOR agonists with biased signaling profiles that produce KOR-typical antinociception with fewer KOR-typical side effects.
Objective
The present study determined if the biased KOR agonists, nalfurafine and triazole 1.1, could reduce choice for oxycodone in rhesus monkeys as effectively as the typical KOR agonist, salvinorin A.
Methods
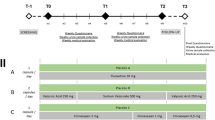
Adult male rhesus monkeys (N = 5) responded under a concurrent schedule of food delivery and intravenous cocaine injections (0.018 mg/kg/injection). Once trained, cocaine (0.018 mg/kg/injection) or oxycodone (0.0056 mg/kg/injection) was tested alone or in combination with contingent injections of salvinorin A (0.1–3.2 µg/kg/injection), nalfurafine (0.0032–0.1 µg/kg/injection), triazole 1.1 (3.2–100.0 µg/kg/injection), or vehicle. In each condition, the cocaine or oxycodone dose, as well as the food amount, was held constant across choice components, while the dose of the KOR agonist was increased across choice components.
Results
Cocaine and oxycodone were chosen over food on more than 80% of trials when administered alone or contingently with vehicle. When KOR agonists were administered contingently with either cocaine or oxycodone, drug choice decreased in a dose-dependent manner. Salvinorin A and triazole 1.1 decreased drug-reinforcer choice without altering total trials completed (i.e., choice allocation shifted to food), while nalfurafine dose dependently decreased total trials completed.
Conclusions
These results demonstrate that salvinorin A and triazole 1.1, but not nalfurafine, selectively reduce cocaine and oxycodone self-administration independent of nonspecific effects on behavior, suggesting that G-protein bias does not appear to be a moderating factor in this outcome. Triazole 1.1 represents an important prototypical compound for developing novel KOR agonists as deterrents for prescription opioid abuse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azrin NH, Holz WC (1966) Punishment. In: Honig WK (ed) Operant behavior: areas of research and application. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 380–447
Banks ML, Negus SS (2017) Insights from preclinical choice models on treating drug addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38:181–194
Beck TC, Hapstack MA, Beck KR, Dix TA (2019) Therapeutic potential of kappa opioid agonist. Pharmaceuticals 12:95
Bedini A, Di Cesare Mannelli L, Micheli L, Baiula M, Vaca G, De Marco R, Gentilucci L, Ghelardini C, Spampinato S (2020) Functional selectivity and antinociceptive effects of a novel KOPr agonist. Front Pharmacol 11: 188 10.3389
Bolanos CA, Garmsen GM, Clair MA, McDougall SA (1996) Effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist U-50,488 on morphine-induced place preference conditioning in the developing rat. Eur J Pharmacol 317:1–8
Brust TF, Morgenweck J, Kim SA, Rose JH, Locke JL, Schmid CL, Zhou L, Stahl EL, Cameron MD, Scarry SM, Aube J, Jones SR, Martin TJ, Bohn LM (2016) Biased agonists of the kappa opioid receptor suppress pain and itch without causing sedation or dysphoria. Sci Signal 9: ra117
Chan HCS, McCarthy D, Li J, Palczewski K, Yuan S (2017) Designing safer analgesics via mu-opioid receptor pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38:1016–1037
Cunningham CW, Rothman RB, Prisinzano TE (2011) Neuropharmacology of the naturally occurring kappa-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A. Pharmacol Rev 63:316–347
Dunn AD, Reed B, Erazo J, Ben-Ezra A, Kreek MJ (2019) Signaling properties of structurally diverse kappa opioid receptor ligands: toward in vitro models of in vivo responses. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:3590–3600
Freeman KB, Naylor JE, Prisinzano TE, Woolverton WL (2014) Assessment of the kappa opioid agonist, salvinorin A, as a punisher of drug self-administration in monkeys. Psychopharmacology 231:2751–2758
Glick SD, Maisonneuve IM, Raucci J, Archer S (1995) Kappa opioid inhibition of morphine and cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res 681:147–152
Hasebe K, Kawai K, Suzuki T, Kawamura K, Tanaka T, Narita M et al (2004) Possible pharmacotherapy of the opioid kappa receptor agonist for drug dependence. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:404–413
Huskinson SL, Platt DM, Brasfield M, Follett ME, Prisinzano TE, Blough BE, Freeman KB (2020) Quantification of observable behaviors induced by typical and atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists in male rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 237:2075–2087
Huskinson SL, Platt DM, Zamarripa CA, Dunaway K, Brasfield M, Prisinzano TE, Blough BE, Freeman KB (2022) The G-protein biased kappa opioid agonists, triazole 1.1 and nalfurafine, produce non-uniform behavioral effects in male rhesus monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 217:173394
Inan S, Huerta AT, Jensen LE, Dun NJ, Cowan A (2019) Nalbuphine, a kappa opioid receptor agonist and mu opioid receptor antagonist attenuates pruritus, decreases IL-31, and increases IL-10 in mice with contact dermatitis. Eur J Pharmacol 864:172702
Inui S (2015) Nalfurafine hydrochloride to treat pruritus: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 8:249–255
Jones MR, Kaye AD, Kaye AJ, Urman RD (2016) The emerging therapeutic roles of kappa-opioid agonists. J Opioid Manag 12:101–107
Kaski SW, White AN, Gross JD, Trexler KR, Wix K, Harland AA et al (2019) Preclinical testing of nalfurafine as an opioid-sparing adjuvant that potentiates analgesia by the mu opioid receptor-targeting agonist morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 371:487–499
Ko MC, Husbands SM (2009) Effects of atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists on intrathecal morphine-induced itch and analgesia in primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:193–200
Kamimura K, Yokoo T, Kamimura H, Sakamaki A, Abe S, Tsuchiya A, Takamura M, Kawai H, Yamagiwa S, Terai S (2017) Long-term efficacy and safety of nalfurafine hydrochloride on pruritus in chronic liver disease patients: patient-reported outcome based analyses. PLoS ONE 12:e017899
Liu JJ, Chiu YT, DiMattio KM, Chen C, Huang P, Gentile TA, Muschamp JW, Cowan A, Mann M, Liu-Chen LY (2019) Phosphoproteomic approach for agonist-specific signaling in mouse brains: mTOR pathway is involved in κ opioid aversion. Neuropsychopharmacology 44:939–949
MacLean KA, Johnson MW, Reissig CJ, Prisinzano TE, Griffiths RR (2013) Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects. Psychopharmacology 226:381–392
Mores KL, Cummins BR, Cassell RJ, van Rijn RM (2019) A review of the therapeutic potential of recently developed g protein-biased kappa agonists. Front Pharmacol 10:407
Nakao K, Mochizuki H (2009) Nalfurafine hydrochloride: a new drug for the treatment of uremic pruritus in hemodialysis patients. Drugs Today (barc) 45:323–329
Negus SS, Bilsky EJ, Do Carmo GP, Stevenson GW (2010) Rationale and methods for assessment of pain-depressed behavior in preclinical assays of pain and analgesia. Methods Mol Biol 617:79–91
Negus SS, Schrode K, Stevenson GW (2008) Micro/kappa opioid interactions in rhesus monkeys: implications for analgesia and abuse liability. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16:386–399
Paton KF, Kumar N, Crowley RS, Harper JL, Prisinzano TE, Kivell BM (2017) The analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Salvinorin A analogue β-tetrahydropyran salvinorin B in mice. Eur J Pain 21:1039–1050
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Ranganathan M, Schnakenberg A, Skosnik PD, Cohen BM, Pittman B, Sewell RA et al (2012) Dose-related behavioral, subjective, endocrine, and psychophysiological effects of the kappa opioid agonist salvinorin A in humans. Biol Psychiatry 72:871–879
Rankovic Z, Brust TF, Bohn LM (2016) Biased agonism: an emerging paradigm in GPCR drug discovery. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26:241–250
Schattauer SS, Kuhar JR, Song A, Chavkin C (2017) Nalfurafine is a G-protein biased agonist having significantly greater bias at the human than rodent form of the kappa opioid receptor. Cell Signal 32:59–65
Townsend EA (2021) Effects of kappa opioid receptor agonists on fentanyl vs. food choice in male and female rats: contingent vs. non-contingent administration. Psychopharmacology 238:1017–1028
Townsend EA, Naylor JE, Negus SS, Edwards SR, Qureshi HN, McLendon HW, McCurdy CR, Kapanda CN, do Carmo JM, da Silva FS, Hall JE, Sufka KJ, Freeman KB (2017) Effects of nalfurafine on the reinforcing, thermal antinociceptive, and respiratory-depressant effects of oxycodone: modeling an abuse-deterrent opioid analgesic in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 234: 2597-2605
Tsuji M, Takeda H, Matsumiya T, Nagase H, Narita M, Suzuki T (2001) The novel kappa-opioid receptor agonist TRK-820 suppresses the rewarding and locomotor-enhancing effects of morphine in mice. Life Sci 68:1717–1725
Urban JD, Clarke WP, von Zastrow M, Nichols DE, Kobilka B, Weinstein H, Javitch JA, Roth BL, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM, Miller KJ, Spedding M, Mailman RB (2007) Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320(1–13):10
Zamarripa CA, Naylor JE, Huskinson SL, Townsend EA, Prisinzano TE, Freeman KB (2020a) Kappa opioid agonists reduce oxycodone self-administration in male rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 237:1471–1480
Zamarripa CA, Pareek T, Schrock HM, Prisinzano TE, Blough BE, Sufka KJ, Freeman KB (2021) The kappa-opioid receptor agonist, triazole 1.1, reduces oxycodone self-administration and enhances oxycodone-induced thermal antinociception in male rats. Psychopharmacology 238:3463–3476
Zamarripa CA, Patel TR, Williams BC, Pareek T, Schrock HM, Prisinzano TE, Freeman KB (2020b) The kappa-opioid receptor agonist, nalfurafine, blocks acquisition of oxycodone self-administration and oxycodone’s conditioned rewarding effects in male rats. Behav Pharmacol 31:792–797
Zhang Y, Kreek MJ (2020) Nalfurafine modulates the reinforcing effects of oxycodone in male and female adolescent C57BL/6J mice. Neuropharmacology 176:108244
Zhou L, Lovell KM, Frankowski KJ, Slauson SR, Phillips AM, Streicher JM, Stahl E, Schmid CL, Hodder P, Madoux F, Cameron MD, Prisinzano TE, Aube J, Bohn LM (2013) Development of functionally selective, small molecule agonists at kappa opioid receptors. J Biol Chem 288:36703–36716
Zhou Y, Freeman K, Setola V, Cao D, Kaski S, Kreek MJ, Liu-Chen LY (2022) Preclinical studies on nalfurafine (TRK-820), a clinically used KOR agonist. Handb Exp Pharmacol 271:137–162
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Josh Woods, Jessica Howard, Zachary Smith, Kandace Farmer, and Kristen Dunaway for their technical assistance. The authors would also like to thank Drs. Steve Negus and Matthew Banks for consultation on the programming code used for the choice procedure.
Funding
This research and manuscript preparation were supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse grants DA039167 to K.B.F., DA048586 to C.A.Z., DA018151 to T.E.P., DA045011 to S.L.H, and DA043204 to J.K.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zamarripa, C.A., Huskinson, S.L., Townsend, E.A. et al. Contingent administration of typical and biased kappa opioid agonists reduces cocaine and oxycodone choice in a drug vs. food choice procedure in male rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 241, 305–314 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06486-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06486-5