Abstract
Background
In all societies, the burden and cost of allergic and chronic respiratory diseases are increasing rapidly. Most economies are struggling to deliver modern health care effectively. There is a need to support the transformation of the health care system into integrated care with organizational health literacy.
Main body
As an example for chronic disease care, MASK (Mobile Airways Sentinel NetworK), a new project of the ARIA (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma) initiative, and POLLAR (Impact of Air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis, EIT Health), in collaboration with professional and patient organizations in the field of allergy and airway diseases, are proposing real-life ICPs centred around the patient with rhinitis, and using mHealth to monitor environmental exposure. Three aspects of care pathways are being developed: (i) Patient participation, health literacy and self-care through technology-assisted “patient activation”, (ii) Implementation of care pathways by pharmacists and (iii) Next-generation guidelines assessing the recommendations of GRADE guidelines in rhinitis and asthma using real-world evidence (RWE) obtained through mobile technology. The EU and global political agendas are of great importance in supporting the digital transformation of health and care, and MASK has been recognized by DG Santé as a Good Practice in the field of digitally-enabled, integrated, person-centred care.
Conclusion
In 20 years, ARIA has considerably evolved from the first multimorbidity guideline in respiratory diseases to the digital transformation of health and care with a strong political involvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In all societies, the burden and cost of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are increasing rapidly as advances in sanitation, public health measures and clinical care result in changes in demography [1]. Most, if not all, economies are struggling to deliver modern health care effectively [2]. Budgets will continue to be challenged with the move towards universal health coverage as demand increases and newer, more expensive technologies become available [3,4,5]. Traditional programmes, heavily reliant on specialist and supporting services, are becoming unaffordable. Innovative solutions are required to alleviate system wide pressures [6, 7]. There is a need to support authorities in the transformation of the health care system into integrated care with organizational health literacy [8].
Integrated care pathways (ICPs) are structured multi-disciplinary care plans detailing the key steps of patient care [9]. They promote the translation of guideline recommendations into local protocols and their application to clinical practice. They may be of particular interest in patients with multimorbidities since guidelines rarely consider them appropriately [10, 11]. An ICP forms all or part of the clinical record, documents the care given, and facilitates the evaluation of outcomes for continuous quality improvement [12]. ICPs should be carried out by a multidisciplinary team including physicians, pharmacists [13, 14] and allied health care professionals [15]. ICPs should integrate recommendations from clinical practice guidelines, but they usually (i) enhance recommendations by combining interventions, integrating quality assurance and (ii) describe co-ordination of care. Self-care and shared decision making are at the forefront of ICPs with the aim of empowering patients and their (professional and lay) care givers.
Rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity can be used as a model for chronic diseases since there is a broad agreement on the ‘gold standard’ of care [16,17,18]. In allergic rhinitis (AR) and asthma, adherence to treatment is a major unresolved problem [19, 20]. The vast majority of physicians prescribe regular treatment but patients (and physicians when they are allergic [21]) do not adhere to the advice. Instead of they self-treat based on personal experience as suggested by real-world data [19, 22]. There is thus a major disconnect between physicians and patients, either because of the clinical approach utilised or due to a lack of patient health literacy, with insufficient shared decision making (SDM). On-demand (prn) approaches are now proposed in both diseases [23,24,25] and represent a major change from previous recommendations. This new approach should be integrated in ICPs, but it needs to be applied to self-management and based on solid evidence.
ICPs have been proposed with a focus on new technologies that, through personally-held data on tablet devices and recording of ‘symptom load’, should enhance self-management and adherence to guidelines and ICPs. The science of supporting self-care and ICPs through mobile devices (mHealth) is in its infancy, but preliminary results are encouraging [26,27,28]. In the context of asthma, a systematic review showed that mobile apps were generally as effective as traditional models of supported self-management, but that they may be preferred in some clinical and demographic contexts as being convenient as well as efficient for the patient and the professional [29]. Standardisation and the establishment of the Privacy Code of Conduct for mHealth apps [25] will be important in ensuring patients on the safeguard of their data and in helping them choose reliable technological tools, which will be essential for ICP implementation.
As an example for chronic disease care, a new development of the ARIA initiative (ARIA phase 4) [30], along with POLLAR (Impact of Air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis), in collaboration with professional and patient organizations in the field of allergy and airway diseases, are proposing real-life ICPs centred around the patient with rhinitis, and using mHealth to monitor environmental exposure.
The current document was finalized and reviewed during a meeting involving ARIA, POLLAR (Impact of Air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis (EIT Health)), the European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing and the Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases (GARD, WHO Alliance). Major allergy societies and patient’s organizations participated in this meeting (Paris, December 3, 2018). The event was carried out with the support of many organizations (Fig. 1).
The gaps in allergic rhinitis and asthma
AR is the most common chronic disease worldwide. Treatment guidelines have improved the knowledge on rhinitis and have had a significant impact on AR management. However, many patients still fail to achieve sufficient symptom control [31] and the costs for society are enormous, in particular due to a major impact on school and work productivity [32] and on allergic or non-allergic multimorbidities [33, 34]. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) has promoted the use of its recommendations [16, 35, 36] to be integrated in ICPs using mobile technology in AR and asthma multimorbidity across the life cycle [37].
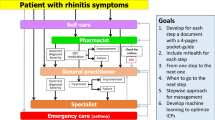
The clinical problem is that a large number of AR patients do not consult physicians because they think their symptoms are ‘normal’ and/or trivial, even though AR negatively impacts social life, school and work productivity [36]. Many AR patients rely on over-the-counter (OTC) drugs and do not see the need to consult with physicians [38,39,40,41]. The vast majority of patients who visit general practitioners (GPs) or specialists have moderate-to-severe rhinitis [42,43,44,45,46]. ICPs should take this reality into account and consider a multi-disciplinary approach as proposed by AIRWAYS ICPs (Fig. 2).

(adapted from [102])
ICPs for rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity
Supported self-management
People with AR and asthma are, by default, making day-to-day decisions about the management of their condition (avoiding triggers, using various treatments and seeking professional advice). Reflecting this broad concept, self-management is defined as “the tasks that individuals must undertake to live well with one or more chronic conditions. These tasks include having the confidence to deal with the medical management, role management and emotional management of their conditions” [47].
The term self-care includes generic “healthy lifestyle behaviours required for human development and functioning” [48]. However, self-care and self-management overlap as, for example, smoking cessation is a generic self-care behaviour and a component of self-management for people with respiratory conditions.
Self-management support is the assistance that professionals (pharmacy, primary care, specialist), patient’s organizations and other sources of information, as well as informal caregivers, give patients in order to make decisions about their condition and to manage disease and health-related tasks [49]. A taxonomy of 14 components of self-management support [50] offers a pick-list of activities that may be considered when planning self-management. These could be practical activities (e.g. teaching inhaler technique, discussing an action plan, helping to quit smoking) and imply SDM [50]. Mobile technology has the potential to contribute to many aspects of the supported self-management of chronic diseases [51].
Supported self-management is a ‘key principle’ for ICPs in long-term conditions [52, 53]. This not only reflects the paradigm shift towards SDM, but also includes pragmatic, economic imperatives, as healthcare systems respond to the increasing NCD burden. The economic impact of effective supported self-management goes beyond healthcare savings. For example, major economic return can be in the workplace where absenteeism and, more importantly, presenteeism are reduced [32] leading to an increased productivity.
Patient activation, defined as the “knowledge, skills and confidence a person has in managing his/her own health and health care” [54], is a goal of many ICP models. “Activation” encompasses the patients’ beliefs about their ability to self-manage (self-efficacy) and the likelihood that they will put these beliefs into action. Levels of activation range from the disengaged patients who let others manage their condition to the fully “activated” patients who embrace SDM and manage their health in partnership with their healthcare advisors, understanding the escalation of treatment options and when to seek pharmacy or medical advice. Higher levels of activation have been associated with better process and health outcomes in adults [55] and there is some evidence that appropriately-targeted self-management support may be more beneficial to disadvantaged groups than to higher literacy/socioeconomic status patients.
Although ARIA appears to meet the patient’s needs, real-life data obtained using the Allergy Diary (MASK-air®) app from around 10,000 people in 23 countries (Argentina, Austria, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Lithuania, Mexico, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK. Brazil is a developing country) have shown that very few patients are being treated according to guidelines and that they often self-medicate [19]. Self-medication is the treatment of common health problems with medicines without medical supervision. It is important to ensure that well-written, short and accurate self-management information is available for people to pick up in pharmacies, or for download. In the case of AR, many patients have prescribed medications at home and, when symptoms occur, they use them. Self-care and SDM centred around the patient should be used more often [56]. ARIA has already followed a change management (CM) strategy embedding the AR-asthma multimorbidity in every day practice [30], but a new CM is now being considered to increase the benefits of self-care and SDM in ICPs using currently-available IT tools. In the case of AR and asthma multimorbidity, aeroallergen exposure and pollution impact disease control and medications. However, there is currently no ICP in airway diseases that takes such environmental parameters into account [57]. These initiatives should prepare and support individuals, teams and organizations in making organizational change centred around the patient.
mHealth, such as apps running on consumer smart devices, is becoming increasingly popular and has the potential to profoundly affect health care and health outcomes [58]. Several apps exist for AR and asthma [59,60,61,62,63]. A review of the Apps in the field of allergic diseases has recently been completed (Matricardi et al. in preparation). One of the reviews—MASK (Mobile Airways Sentinel NetworK), the Phase 3 ARIA initiative [37, 64]—is based on the freely-available MASK app (the Allergy Diary, Android and iOS platforms) for AR and asthma. Importantly, MASK is available in 17 languages and deployed in 23 countries [64]. Data from 26,000 users reporting over 200,000 days of treatment are available. It complies with the recent General Data Protection Regulation (EU) 2016/679 (GDPR) enforced by the EU, May 25, 2018 [65]. The GDPR aims primarily to give control to citizens and residents over their personal data and to simplify the regulatory environment by unifying the regulation within the EU [66, 67]. Importantly, MASK enables the assessment of treatment patterns in real life and provides detailed information on treatment, given that the Allergy Diary is able to distinguish between AR medications [19].
On-line information
Most patients check on-line to help them decide what the problem is and how to address it. This is a crucial self-management area of support and we need to think about how it can be optimized. Because of the multiplicity of sources and the lack of reliability control, it should be recognized that such a task would require an enormous effort. Consequently, it has been abandoned by many other bodies/disease areas. One approach that may be of value in improving reliability would be to focus on sites that provide useful information and generate an accreditation process with international standing.
Pharmacist care
Pharmacists are trusted health care professionals. Most patients with rhinitis are seen by pharmacists who are the initial point of contact of AR management in most countries. Depending on the country, few or most AR medications are available over-the-counter (OTC) [68,69,70,71] and are used by many patients. Therefore, as trusted health care professionals in the community, pharmacists are well placed to play a critical role identifying the symptoms of AR, recommending appropriate OTC treatment [38, 39, 41] and integrating health care teams through ICPs [13, 14]. The specific role of pharmacists in the management of AR within ICPs can been evidenced from several strategies that have been initiated [72] or completed and from studies confirming the important impact of pharmacist interventions on AR outcomes [40, 70, 73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80].
ARIA in the pharmacy 2004 [38] is being revised in order to propose ICPs involving a multi-disciplinary approach. This paper has been built on the evidence and provides tools intended to help pharmacists give optimal advice/interventions/strategies to patients with rhinitis. The ARIA-pharmacy ICP includes a diagnostic questionnaire specifically focusing attention on key symptoms and markers of the disease, a systematic Diagnosis Guide (including a differential diagnosis) and a simple flowchart proposing treatment for rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity. Key prompts for referral within the ICP are included. The use of technology is critical for enhancing the management of AR. The ARIA-pharmacy ICP should be adapted to local health care environments/situations as large regional or national differences in pharmacy-based care exist.
Next-generation guidelines
Practice guidelines contain evidence-based statements about treatment, tests, public health actions and policy decisions intended to assist recipients of care and their care providers in making informed decisions.
ARIA was one of the first chronic respiratory disease guidelines to adopt the GRADE (Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach, an advanced evidence evaluation and development approach for guidelines [16, 81,82,83]. GRADE-based guidelines are available for AR from other organizations and their recommendations are similar [16,17,18]. However, a limitation of GRADE is that evidence often lacks applicability because the populations studied do not reflect most of the patients seen in primary care [84]. The GRADE recommendations are often based on RCT in which patients regularly use their treatment, whereas most AR or asthma patients are non-adherent. GRADE rarely includes recommendations based on implementation research.
The more recently completed work by the GRADE working group on its Evidence to Decision Frameworks requires that guideline developers regularly address implementation and monitoring strategies [85,86,87,88,89]. Searching for and synthesizing evidence of effective implementation strategies enabled the BTS/SIGN asthma guideline to make a recommendation on how supported self-management for asthma could be embedded into routine practice [90]. Strategies include proactively engaging and empowering patients, training and motivating professionals as well as providing an environment that promotes self-management and monitors implementation [91]. In AR, cluster-randomized controlled trials have confirmed the overall value of guidelines [92, 93]. However, there has been only one direct testing of individual guideline recommendations in real–life studies in an effort to achieve optimization [94].
Next-generation ARIA-GRADE guidelines should consider testing the recommendations based on the GRADE approach with real-world evidence (RWE) using data obtained by mHealth tools such as MASK in order to confirm the efficiency or to refine current GRADE-based recommendations. The first results of MASK confirm the feasibility of the project [19]. Adherence to treatment is very low as < 5% of users record symptoms and medications for a period of 2 weeks. This indicates that it is important to further test whether on-demand is equally or even more efficient than regular-continuous treatment and that guidelines should consider both regular and on-demand treatment [19, 95].
Guideline recommendations often address isolated questions or focus on a single disease or problem. They should be considered in the context of the many decisions that are made. ICPs try to address the multiple options and iterative changes in a patient’s status and problems. Guideline recommendations should support these iterative changes.
The key challenge for conventional treatment guidelines is that available evidence, both from randomized trials and non-randomized studies, does not usually address the complex pathways, but only affects isolated decision points within a pathway. For example, when an oral H1-antihistamine is not achieving symptom control, we propose to replace it by an intra-nasal corticosteroid. However, this is often not the way that studies are designed and not how patients use these medications. Assuming that properly developed pathways require evidence, our guidelines must start identifying the best available evidence to support decision points. When the evidence is indirect, which is frequently the case, connecting the relevant decision points and considering all of that evidence together results in low certainty on the overall structure and timing of an ICP.
The next-generation guidelines, if complemented by the intelligent use of tools such as MASK, which records patients’ symptoms and provides advice at given time points to follow ICPs, could exemplify unique new tools to both implement and evaluate recommendations in the context of pathways. Studies should be carried out in which patients are randomized to ICPs or to follow ARIA recommendations that are not presented as pathways. Such studies will provide both information on the use of the recommendations and on the usefulness of the pathways. Through implementation of recommendations, we will be able to increase our certainty in the evidence by evaluating the entire pathway and measuring outcomes in direct population-based studies that record what patients do as opposed to what clinicians prescribe (and patients do not do).
Study proposals of ARIA phase 4 and POLLAR
ARIA Phase 4 is the change management strategy for AR and asthma [96]. POLLAR is an EIT-Health (European Institute for Innovation and technology) project which aims to better understand, prevent and manage the impact of air pollution and allergen exposure on airway diseases [57]. POLLAR will use the MASK App, which is a Good Practice [64]. One of the POLLAR work-packages is the development of ICPs integrating aerobiology and air pollution. This will be developed using a step-wise approach centred around the patient. The four-step project is a WHO Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases (GARD) demonstration project.
Step 1: First meeting (December 3, 2018, Paris): Development of next-generation ICPs with a focus on self-management, pharmacy care and next-generation guidelines
The Paris meeting addressed a number of areas as delineated below (Fig. 3).
Step 2: 2019–2021: Further development and implementation of next-generation ICPs
-
1.
Develop a strategic and practical approach to improving patient autonomy and self-management programmes.
-
2.
Deploy to other chronic respiratory diseases (asthma, COPD and rhinosinusitis [97]) and NCDs developing a multimorbidity App based on MASK expertise and experience.
-
3.
Develop documents for specific age groups: pre-school and school children, older adults.
-
4.
Establish a best practice across several regions in the EU linking the study to policy makers aiming to improve air quality and outcomes in their population.
Step 3: Second meeting (December 2019): Embedding environmental data in next-generation ICPs
Using the results obtained by POLLAR for air pollution, a second meeting will be held to integrate aerobiology and air pollution data in mobile technology and to propose ICPs for the prevention of severe exacerbations and asthma during peaks of allergens and/or pollution. This meeting will also consider the deployment to other chronic diseases (Fig. 4) and the impact of biodiversity in chronic diseases [98].
Embedding next-generation care pathways in the EU and global political agendas for allergic and chronic respiratory diseases
The Polish Presidency of the EU Council (2011) targeted CRDs in children to promote their early recognition, prevention and management to ultimately impact active and healthy ageing (AHA) [99]. The developmental determinants of CRDs in ageing were reinforced during the Cyprus Presidency of the EU Council “Healthy ageing across the lifecycle” (2012) [100] and an EU-NIH meeting held in Montpellier (2013) [101].
The objective of AIRWAYS-ICPs [102] was to launch a collaboration to develop multi-sectoral ICPs for CRDs in European countries and regions. AIRWAYS-ICPs was initiated in 2014 by the European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing (EIP on AHA, DG Santé and DG CONNECT) [103] as a GARD (Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases) demonstration project [104]. In collaboration with GARD, the Directorate General of Health of Portugal, the EIP on AHA and the Région Occitanie (France), a high-level meeting was organized July 1, 2015 with all major European scientific societies and patient’s organizations in Lisbon to review the implementation results of AIRWAYS ICPs [105].
Euforea (European Forum for Research and Education in Allergy and Airway Diseases) [56] proposed an annual stepwise strategy at the EU or ministerial levels. A European Symposium on Precision Medicine in Allergy and Airways Diseases was held at the EU Parliament October 14, 2015 [106]. Another EU Parliament meeting was held in Brussels March 29, 2017 on the Prevention and Self-Management of CRDs using novel mobile health tools [37, 56, 97].
POLLAR (Impact of air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis, EIT Health) is focusing on the impact of allergens and air pollution on airway diseases and aims to propose novel ICPs integrating pollution, sleep and patients’ literacy and to assess the societal implications of the interaction [57].
Euforea organized an EU Summit in Vilnius, Lithuania (March 2018) in collaboration with the Ministers of Health of Lithuania, Moldova, Georgia and Ukraine. The aim was to discuss and start the implementation of the POLLAR concepts, and to deploy it to EU neighboring countries. The Vilnius Declaration on Chronic Respiratory Diseases proposed multisectoral ICPs embedding guided self-management, mHealth and air pollution in CRDs [107].
The joint meeting discussed in this report (December 3, 2018) proposed next-generation care pathways based on the Vilnius Declaration.
MASK has been selected by the European Commission’s Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety (DG SANTE) and the newly-established Commission Expert Group “Steering Group on Health Promotion, Disease Prevention and Management of Non-Communicable Diseases” as a Good Practice (GP) in the field of digitally-enabled, integrated, person-centred care.
On May 3, 2019, a Euforea-led meeting took place in the Parliament of Malta to review the results of the December 3 meeting and to propose practical strategies at the EU and global levels with GARD.
This new next-generation care pathway is completely aligned with the recommendations issued by the Thematic Network SHAFE—Smart Healthy Age-Friendly Environments (approved by the European Commission—DG SANTE and DG CONNECT)—on its Joint Statement delivered 12th November 2018. The Statement underlined the need to patient empowerment and active involvement in its healthcare process and also urged the use of lifestyle medicine that provides effective impact on the patient’s wellbeing.
Conclusions
There is a need to support the digital transformation of health and care with integrated care. An innovative patient-centered approach is proposed by the ARIA expert group for rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity to be scaled up to chronic diseases.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AIRWAYS ICPs:
-
integrated care pathways for airway diseases
- AR:
-
allergic rhinitis
- ARIA:
-
Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma
- BTS/SIGN:
-
British Thoracic Society/Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
- CRD:
-
chronic respiratory diseases
- EIP on AHA:
-
European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing
- EIT-Health:
-
European Institute for Innovation and technology-Health
- Euforea:
-
European Forum for Research and Education in Allergy and Airway Diseases
- GARD:
-
Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases
- GDPR:
-
General Data Privacy Regulation
- GLASS-ARIA:
-
Global Allergy Simple Solution
- GP:
-
general practitioner
- GRADE:
-
Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation
- ICP:
-
integrated care pathways
- MASK:
-
Mobile Airways Sentinel Network
- MHealth:
-
mobile health
- OTC:
-
over-the-counter
- PG:
-
pocket guides
- POLLAR:
-
Impact of Air POLLution in Asthma and Rhinitis
- RWE:
-
Real World Evidence
- SDM:
-
shared decision making
- WAO :
-
World Allergy Organization
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Bousquet J, Anto JM, Sterk PJ, Adcock IM, Chung KF, Roca J, et al. Systems medicine and integrated care to combat chronic noncommunicable diseases. Genome Med. 2011;3(7):43.
Stenberg K, Lauer JA, Gkountouras G, Fitzpatrick C, Stanciole A. Econometric estimation of WHO-CHOICE country-specific costs for inpatient and outpatient health service delivery. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2018;16:11.
Crespi-Lofton J, Skelton JB. The growing role of biologics and biosimilars in the United States: Perspectives from the APhA Biologics and Biosimilars Stakeholder Conference. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2017;57(5):e15–27.
Gronde TV, Uyl-de Groot CA, Pieters T. Addressing the challenge of high-priced prescription drugs in the era of precision medicine: a systematic review of drug life cycles, therapeutic drug markets and regulatory frameworks. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(8):e0182613.
Global Burden of Disease Health Financing Collaborator N. Future and potential spending on health 2015–2040: development assistance for health, and government, prepaid private, and out-of-pocket health spending in 184 countries. Lancet. 2017;389(10083):2005–30.
Russell J, Greenhalgh T. Affordability as a discursive accomplishment in a changing National Health Service. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(12):2463–71.
Hunter DJ, Erskine J, Small A, McGovern T, Hicks C, Whitty P, et al. Doing transformational change in the English NHS in the context of “big bang” redisorganisation. J Health Organ Manag. 2015;29(1):10–24.
Farmanova E, Bonneville L, Bouchard L. Organizational health literacy: review of theories, frameworks, guides, and implementation issues. Inquiry. 2018;55:46958018757848.
Campbell H, Hotchkiss R, Bradshaw N, Porteous M. Integrated care pathways. BMJ. 1998;316(7125):133–7.
Hujala A, Taskinen H, Rissanen S. In: Richardson E, van Ginneken E, editors. How to support integration to promote care for people with multimorbidity in Europe? European Observatory Policy Briefs. Copenhagen (Denmark); 2017.
Palmer K, Marengoni A, Forjaz MJ, Jureviciene E, Laatikainen T, Mammarella F, et al. Multimorbidity care model: recommendations from the consensus meeting of the Joint Action on Chronic Diseases and Promoting Healthy Ageing across the Life Cycle (JA-CHRODIS). Health Policy. 2018;122(1):4–11.
Overill S. A practical guide to care pathways. J Integr Care. 1998;2:93–8.
Chisholm-Burns MA, Kim Lee J, Spivey CA, Slack M, Herrier RN, Hall-Lipsy E, et al. US pharmacists’ effect as team members on patient care: systematic review and meta-analyses. Med Care. 2010;48(10):923–33.
Lee JK, Slack MK, Martin J, Ehrman C, Chisholm-Burns M. Geriatric patient care by U.S. pharmacists in healthcare teams: systematic review and meta-analyses. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61(7):1119–27.
Skypala IJ, de Jong NW, Angier E, Gardner J, Kull I, Ryan D, et al. Promoting and achieving excellence in the delivery of Integrated Allergy Care: the European Academy of Allergy & Clinical Immunology competencies for allied health professionals working in allergy. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:31.
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(3):466–76.
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) Guidelines—2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140(4):950–8.
Dykewicz MS, Wallace DV, Baroody F, Bernstein J, Craig T, Finegold I, et al. Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: an evidence-based focused 2017 guideline update. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;119(6):489–511.
Bousquet J, Devillier P, Arnavielhe S, Bedbrook A, Alexis-Alexandre G, van Eerd M, et al. Treatment of allergic rhinitis using mobile technology with real-world data: The MASK observational pilot study. Allergy. 2018;73(9):1763–74.
Gray WN, Netz M, McConville A, Fedele D, Wagoner ST, Schaefer MR. Medication adherence in pediatric asthma: a systematic review of the literature. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2018;53(5):668–84.
Bousquet J, Murray R, Price D, Somekh D, Munter L, Phillips J, et al. The allergic allergist behaves like a patient. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018;121(6):741–2.
Bedard A, Basagana X, Anto JM, Garcia-Aymerich J, Devillier P, Arnavielhe S, et al. Mobile technology offers novel insights on control and treatment of allergic rhinitis. The MASK study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144(1):135–143.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.01.053.
Bateman ED, Reddel HK, O’Byrne PM, Barnes PJ, Zhong N, Keen C, et al. As-needed budesonide–formoterol versus maintenance budesonide in mild asthma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(20):1877–87.
O’Byrne PM, FitzGerald JM, Bateman ED, Barnes PJ, Zhong N, Keen C, et al. Inhaled combined budesonide–formoterol as needed in mild asthma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(20):1865–76.
Camargos P, Affonso A, Calazans G, Ramalho L, Ribeiro ML, Jentzsch N, et al. On-demand intermittent beclomethasone is effective for mild asthma in Brazil. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:7.
Levine DMSS, Squires A, Nicholson J, Jay M. Technology-assisted weight loss interventions in primary care: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med. 2015;30(1):107–17.
Van der Roest HGWJ, Pastink C, Dröes RM, Orrell M. Assistive technology for memory support in dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6:CD009627. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd009627.
Bhattarai PPJ. The role of digital health technologies in management of pain in older people: an integrative review. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2017;68:14–24.
Hui CY, Walton R, McKinstry B, Jackson T, Parker R, Pinnock H. The use of mobile applications to support self-management for people with asthma: a systematic review of controlled studies to identify features associated with clinical effectiveness and adherence. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2017;24(3):619–32.
Bousquet J, Hellings P, Agache I, Amat F, Annesi-Maesano I, Ansotegui I, et al. ARIA Phase 4 (2018): Change management in allergic rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity using mobile technology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2018 (in press).
De Greve G, Hellings PW, Fokkens WJ, Pugin B, Steelant B, Seys SF. Endotype-driven treatment in chronic upper airway diseases. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017;7:22.
Vandenplas O, Vinnikov D, Blanc PD, Agache I, Bachert C, Bewick M, et al. Impact of rhinitis on work productivity: a systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6(4):1274–86.
Amaral R, Fonseca JA, Jacinto T, Pereira AM, Malinovschi A, Janson C, et al. Having concomitant asthma phenotypes is common and independently relates to poor lung function in NHANES 2007–2012. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:13.
Cingi C, Gevaert P, Mosges R, Rondon C, Hox V, Rudenko M, et al. Multi-morbidities of allergic rhinitis in adults: European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Task Force Report. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017;7:17.
Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108(5 Suppl):S147–334.
Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008;63(Suppl 86):8–160.
Bousquet J, Hellings PW, Agache I, Bedbrook A, Bachert C, Bergmann KC, et al. ARIA 2016: Care pathways implementing emerging technologies for predictive medicine in rhinitis and asthma across the life cycle. Clin Transl Allergy. 2016;6:47.
ARIA in the pharmacy: management of allergic rhinitis symptoms in the pharmacy. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. Allergy. 2004;59(4):373-87.
Carr WW, Yawn BP. Management of allergic rhinitis in the era of effective over-the-counter treatments. Postgrad Med. 2017;129(6):572–80.
Lombardi C, Musicco E, Rastrelli F, Bettoncelli G, Passalacqua G, Canonica GW. The patient with rhinitis in the pharmacy. A cross-sectional study in real life. Asthma Res Pract. 2015;1(1):4.
Fromer LM, Blaiss MS, Jacob-Nara JA, Long RM, Mannion KM, Lauersen LA. Current Allergic Rhinitis Experiences Survey (CARES): consumers’ awareness, attitudes and practices. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2014;35(4):307–15.
Bousquet J, Neukirch F, Bousquet PJ, Gehano P, Klossek JM, Le Gal M, et al. Severity and impairment of allergic rhinitis in patients consulting in primary care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(1):158–62.
Bousquet J, Annesi-Maesano I, Carat F, Leger D, Rugina M, Pribil C, et al. Characteristics of intermittent and persistent allergic rhinitis: DREAMS study group. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35(6):728–32.
Bousquet PJ, Devillier P, Tadmouri A, Mesbah K, Demoly P, Bousquet J. Clinical relevance of cluster analysis in phenotyping allergic rhinitis in a real-life study. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015;166(3):231–40.
del Cuvillo A, Montoro J, Bartra J, Valero A, Ferrer M, Jauregui I, et al. Validation of ARIA duration and severity classifications in Spanish allergic rhinitis patients—the ADRIAL cohort study. Rhinology. 2010;48(2):201–5.
Jauregui I, Davila I, Sastre J, Bartra J, del Cuvillo A, Ferrer M, et al. Validation of ARIA (Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma) classification in a pediatric population: the PEDRIAL study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011;22(4):388–92.
Adams K, Greiner A, JM JC. The 1st Annual Crossing the Quality Chasm Summit—a Focus on Communities Chapter 5. 2004. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK215507.
Richard A, Shea K. Delineation of self-care and associated concepts. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2011;43:255–64.
Silva DD. Helping people help themselves: a review of the evidence considering whether it is worthwhile to support self-management. The Health Foundation 2011. http://www.healthorguk/sites/health/files/HelpingPeopleHelpThemselvespdf. 2011.
Pearce G, Parke H, Pinnock H, Epiphaniou E, Bourne C, Sheikh A, et al. The PRISMS taxonomy of self-management support: derivation of a novel taxonomy and initial testing of utility. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2016;21:73–82.
Pinnock H, Effing T, Bourbeau J, van-der-Palen J. Self-management of respiratory disease. Respipedia, the respiratory wiki. 2017. http://respipedia.ers-education.org/article/article/?idTopic=217. Accessed 29 Aug 2017.
Singh D, Ham C. A review of UK and international frameworks. http://www.improvingchroniccareorg/downloads/review_of_international_framework.
Bodenheimer T, Lorig K, Holman H, Grumbach K. Patient self-management of chronic disease in primary care. JAMA. 2002;288(19):2469–75.
Hibbard J, Gilburt H. Supporting people to manage their health: an introduction to patient activation. King’s Fund 2014. 2014. https://www.kingsfund.org.uk/sites/files/kf/field/field_publication_file/supporting-people-manage-health-patient-activation-may14.pdf.
Mosen D, Schmittdiel J, Hibbard J, Sobel D, Remmers G, Bellows J. Is patient activation associated with outcomes of care for adults with chronic conditions? J Ambul Care Manag. 2007;30:21–9.
Hellings PW, Borrelli D, Pietikainen S, Agache I, Akdis C, Bachert C, et al. European Summit on the Prevention and Self-Management of Chronic Respiratory Diseases: report of the European Union Parliament Summit (29 March 2017). Clin Transl Allergy. 2017;7:49.
Bousquet J, Anto JM, Annesi-Maesano I, Dedeu T, Dupas E, Pepin JL, et al. POLLAR: Impact of air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis; a European Institute of Innovation and Technology Health (EIT Health) project. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:36.
Bousquet J, Chavannes NH, Guldemond N, Haahtela T, Hellings PW, Sheikh A. Realising the potential of mHealth to improve asthma and allergy care: how to shape the future. Eur Respir J. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00447-2017.
Costa C, Menesatti P, Brighetti MA, Travaglini A, Rimatori V, Di Rienzo Businco A, et al. Pilot study on the short-term prediction of symptoms in children with hay fever monitored with e-Health technology. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;46(6):216–25.
Pizzulli A, Perna S, Florack J, Pizzulli A, Giordani P, Tripodi S, et al. The impact of telemonitoring on adherence to nasal corticosteroid treatment in children with seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014;44(10):1246–54.
Bianchi A, Tsilochristou O, Gabrielli F, Tripodi S, Matricardi PM. The smartphone: a novel diagnostic tool in pollen allergy? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2016;26(3):204–7.
Huang X, Matricardi PM. Allergy and Asthma Care in the Mobile Phone Era. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016.
Bastl K, Berger U, Kmenta M. Evaluation of pollen apps forecasts: the need for quality control in an eHealth service. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19(5):e152.
Bousquet J, Arnavielhe S, Bedbrook A, Bewick M, Laune D, Mathieu-Dupas E, et al. MASK 2017: ARIA digitally-enabled, integrated, person-centred care for rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity using real-world-evidence. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:45.
Samreth D, Arnavielhe S, Ingenrieth F, Bedbrook A, Onorato GL, Murray R, et al. Geolocation with respect to personal privacy for the Allergy Diary app—a MASK study. World Allergy Organ J. 2018;11(1):15.
Recital 26-EU GDPR. EU general data protection regulation 2016/679. http://www.privacy-regulation.eu/en/recital-26-GDPR.htm. Accessed 18 Aug 2019
Article 4 EU GDPR. « Definitions » . EU general data protection regulation 2016/679 (GDPR). http://www.privacy-regulation.eu/en/article-4-definitions-GDPR.htm. Accessed 18 Aug 2019
Sullivan PW, Nair KV, Patel BV. The effect of the Rx-to-OTC switch of loratadine and changes in prescription drug benefits on utilization and cost of therapy. Am J Manag Care. 2005;11(6):374–82.
Rachelefsky G, Farrar JR. Are you comfortable with over-the-counter intranasal steroids for children? A call to action. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2(3):271–4.
Carney AS, Price DB, Smith PK, Harvey R, Kritikos V, Bosnic-Anticevich SZ, et al. Seasonal patterns of oral antihistamine and intranasal corticosteroid purchases from Australian community pharmacies: a retrospective observational study. Pragmat Obs Res. 2017;8:157–65.
OTC fluticasone furoate nasal spray (Flonase Sensimist) for allergic rhinitis. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2017;59(1519):e70-e1.
Porteous T, Wyke S, Smith S, Bond C, Francis J, Lee AJ, et al. ‘Help for Hay Fever’, a goal-focused intervention for people with intermittent allergic rhinitis, delivered in Scottish community pharmacies: study protocol for a pilot cluster randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14:217.
Walls RS, Heddle RJ, Tang ML, Basger BJ, Solley GO, Yeo GT. Optimising the management of allergic rhinitis: an Australian perspective. Med J Aust. 2005;182(1):28–33.
Smith L, Brown L, Saini B, Seeto C. Strategies for the management of intermittent allergic rhinitis: an Australian study. Health Expect. 2014;17(2):154–63.
O’Connor J, Seeto C, Saini B, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Krass I, Armour C, et al. Healthcare professional versus patient goal setting in intermittent allergic rhinitis. Patient Educ Couns. 2008;70(1):111–7.
Smith L, Nguyen T, Seeto C, Saini B, Brown L. The role of non-clinicians in a goal setting model for the management of allergic rhinitis in community pharmacy settings. Patient Educ Couns. 2011;85(2):e26–32.
Lourenco O, Calado S, Sa-Sousa A, Fonseca J. Evaluation of allergic rhinitis and asthma control in a Portuguese community pharmacy setting. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2014;20(5):513–22.
Kuipers E, Wensing M, de Smet P, Teichert M. Self-management research of asthma and good drug use (SMARAGD study): a pilot trial. Int J Clin Pharm. 2017;39(4):888–96.
Canonica GW, Triggiani M, Senna G. 360 degree perspective on allergic rhinitis management in Italy: a survey of GPs, pharmacists and patients. Clin Mol Allergy. 2015;13:25.
Smith P, Price D, Harvey R, Carney AS, Kritikos V, Bosnic-Anticevich SZ, et al. Medication-related costs of rhinitis in Australia: a NostraData cross-sectional study of pharmacy purchases. J Asthma Allergy. 2017;10:153–61.
Brozek JL, Akl EA, Alonso-Coello P, Lang D, Jaeschke R, Williams JW, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in clinical practice guidelines. Part 1 of 3. An overview of the GRADE approach and grading quality of evidence about interventions. Allergy. 2009;64(5):669–77.
Brozek JL, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Rasi G, van Wijk RG, et al. Methodology for development of the Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma guideline 2008 update. Allergy. 2008;63(1):38–46.
Padjas A, Kehar R, Aleem S, Mejza F, Bousquet J, Schunemann HJ, et al. Methodological rigor and reporting of clinical practice guidelines in patients with allergic rhinitis: QuGAR study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(3):777–83.
Costa DJ, Amouyal M, Lambert P, Ryan D, Schunemann HJ, Daures JP, et al. How representative are clinical study patients with allergic rhinitis in primary care? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(4):920–6.
Parmelli E, Amato L, Oxman AD, Alonso-Coello P, Brunetti M, Moberg J, et al. Grade evidence to decision (EtD) framework for coverage decisions. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2017;33(2):176–82.
Schunemann HJ, Mustafa R, Brozek J, Santesso N, Alonso-Coello P, Guyatt G, et al. GRADE Guidelines: 16. GRADE evidence to decision frameworks for tests in clinical practice and public health. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;76:89–98.
Alonso-Coello P, Oxman AD, Moberg J, Brignardello-Petersen R, Akl EA, Davoli M, et al. GRADE Evidence to Decision (EtD) frameworks: a systematic and transparent approach to making well informed healthcare choices. 2: Clinical practice guidelines. BMJ. 2016;353:i2089.
Schunemann HJ, Hill SR, Kakad M, Vist GE, Bellamy R, Stockman L, et al. Transparent development of the WHO rapid advice guidelines. PLoS Med. 2007;4(5):e119.
Neumann I, Brignardello-Petersen R, Wiercioch W, Carrasco-Labra A, Cuello C, Akl E, et al. The GRADE evidence-to-decision framework: a report of its testing and application in 15 international guideline panels. Implement Sci. 2016;11:93.
update. BTSSIGNBGotMoAS. http://www.sign.ac.uk/sign-153-british-guideline-on-the-management-of-asthma.html. 2016.
Pinnock HEE, Pearce G, Parke HL, Greenhalgh T, Sheikh A, Griffiths CJ, Taylor SJC. Implementing supported self-management for asthma: a systematic review of implementation studies. BMC Med. 2015;13:127.
Bousquet J, Lund VJ, Van Cauwenberge P, Bremard-Oury C, Mounedji N, Stevens MT, et al. Implementation of guidelines for seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled trial. Allergy. 2003;58(8):733–41.
Bousquet J, Bodez T, Gehano P, Klossek JM, Liard F, Neukirch F, et al. Implementation of guidelines for allergic rhinitis in specialist practices. A randomized pragmatic controlled trial. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009;150(1):75–82.
Bousquet J, Schünemann H, Togias A, Bachert C, Erhola M, Hellings P, et al. Next-generation ARIA guidelines for allergic rhinitis based on GRADE and real-world evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 (in press).
Bachert C, Bousquet J, Hellings P. Rapid onset of action and reduced nasal hyperreactivity: new targets in allergic rhinitis management. Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;8:25.
Bousquet J, Hellings PW, Agache I, Amat F, Annesi-Maesano I, Ansotegui IJ, et al. ARIA Phase 4 (2018): Change management in allergic rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity using mobile technology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.08.049.
Seys SF, Bousquet J, Bachert C, Fokkens WJ, Agache I, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, et al. mySinusitisCoach: patient empowerment in chronic rhinosinusitis using mobile technology. Rhinology. 2018;56(3):209–15.
Flandroy L, Poutahidis T, Berg G, Clarke G, Dao MC, Decaestecker E, et al. The impact of human activities and lifestyles on the interlinked microbiota and health of humans and of ecosystems. Sci Total Environ. 2018;627:1018–38.
Samolinski B, Fronczak A, Wlodarczyk A, Bousquet J. Council of the European Union conclusions on chronic respiratory diseases in children. Lancet. 2012;379(9822):e45–6.
Bousquet J, Tanasescu CC, Camuzat T, Anto JM, Blasi F, Neou A, et al. Impact of early diagnosis and control of chronic respiratory diseases on active and healthy ageing. A debate at the European Union Parliament. Allergy. 2013;68(5):555–61.
Bousquet J, Anto JM, Berkouk K, Gergen P, Antunes JP, Auge P, et al. Developmental determinants in non-communicable chronic diseases and ageing. Thorax. 2015;70(6):595–7.
Bousquet J, Addis A, Adcock I, Agache I, Agusti A, Alonso A, et al. Integrated care pathways for airway diseases (AIRWAYS-ICPs). Eur Respir J. 2014;44(2):304–23.
Bousquet J, Michel J, Standberg T, Crooks G, Iakovidis I, Gomez M. The European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing: the European Geriatric Medicine introduces the EIP on AHA Column. Eur Geriatr Med. 2014;5(6):361–2.
Bousquet J, Dahl R, Khaltaev N. Global alliance against chronic respiratory diseases. Allergy. 2007;62(3):216–23.
Bousquet J, Barbara C, Bateman E, Bel E, Bewick M, Chavannes NH, et al. AIRWAYS-ICPs (European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing) from concept to implementation. Eur Respir J. 2016;47(4):1028–33.
Muraro A, Fokkens WJ, Pietikainen S, Borrelli D, Agache I, Bousquet J, et al. European Symposium on Precision Medicine in Allergy and Airways Diseases: report of the European Union Parliament Symposium (October 14, 2015). Allergy. 2016;71(5):583–7.
Valiulis A, Bousquet J, Veryga A, Suprun U, Sergeenko D, Cebotari S, et al. Vilnius Declaration on chronic respiratory diseases: multisectoral care pathways embedding guided self-management, mHealth and air pollution in chronic respiratory diseases. Clin Transl Allergy. 2019;9:7.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Togias’ co-authorship of this publication does not constitute endorsement by the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases or by any other United States government agency.
MASK Study group
See Additional file 1.
Funding
Partly funded by POLLAR (Impact of Air POLLution on Asthma and Rhinitis, EIT Health), and ARIA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
All authors are MASK members and have contributed to the design of the project. Many authors also included users and disseminated the project in their own country. Moreover, JB, HJ, AT, ME, TZ, IA, IJA, JMA, CB, SBA, IB, GB, EC, AAC, WC, WJF, JF, MI, LK, VK, LTT, DLL, DL, OML, EM, JM, YO, NP, NPT, HP, CR, BS, STS, IT, AV, AAM, MTV, SW, SW, XB, AB, SB, NB, GWC, VC, AMC, LC, AMCS, DC, EC, ME, GM, JM, EM, LM, GO, JLP, FP, DS, RvdK, AZ participated in the meeting held in Paris, December 3, 2018. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors gave their agreement for the publication of the paper.
Competing interests
Dr. Ansotegui reports personal fees from Mundipharma, Roxall, Sanofi, MSD, Faes Farma, Hikma, UCB, Astra Zeneca, outside the submitted work. Dr. Bosnic-Anticevich reports grants from TEVA, personal fees from TEVA, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Mylan, outside the submitted work. Dr. Bousquet reports personal fees and others from Chiesi, Cipla, Hikma, Menarini, Mundipharma, Mylan, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Takeda, Teva, Uriach, others from Kyomed, outside the submitted work. Dr. Boulet reports and Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest—last 3 years. Research grants for participation to multicentre studies, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, GlaxoSmithKline, Hoffman La Roche, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Sanofi, Takeda. Support for research projects introduced by the investigator AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Takeda. Consulting and advisory boards Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Methapharm. Royalties Co-author of “Up-To-Date” (occupational asthma). Nonprofit grants for production of educational materials AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Frosst, Novartis. Conference fees AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis. Support for participation in conferences and meetings Novartis, Takeda. Other participations Past president and Member of the Canadian Thoracic Society Respiratory Guidelines Committee; Chair of the Board of Directors of the Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Chair of Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Guidelines Dissemination and Implementation Committee; Laval University Chair on Knowledge Transfer, Prevention and Education in Respiratory and Cardiovascular Health; Member of scientific committees for the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society and the World Allergy Organization; 1st Vice-President of the Global Asthma Organization “InterAsma”. Dr. Casale reports grants and non-financial support from Stallergenes, outside the submitted work. Dr. Cruz reports grants and personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline, personal fees from Boehrinher Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Merk, Sharp & Dohme, MEDA Pharma, EUROFARMA, Sanofi Aventis, outside the submitted work. Dr. Ebisawa reports personal fees from DBV Technologies, Mylan EPD maruho, Shionogi & CO., Ltd., Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Thermofisher Diagnostics, Pfizer, Beyer, Nippon Chemifar, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., MSD, outside the submitted work. Dr. Ivancevich reports personal fees from Euro Farma Argentina, Faes Farma, non-financial support from Laboratorios Casasco, outside the submitted work. Dr. Haahtela reports personal fees from Mundipharma, Novartis, and Orion Pharma, outside the submitted work. Dr. Klimek reports grants and personal fees from ALK Abelló, Denmark, Novartis, Switzerland, Allergopharma, Germany, Bionorica, Germany, GSK, Great Britain, Lofarma, Italy, personal fees from MEDA, Sweden, Boehringer Ingelheim, Germany, grants from Biomay, Austria, HAL, Netherlands, LETI, Spain, Roxall, Germany, Bencard, Great Britain, outside the submitted work. V.KV has received payment for consultancy from GSK and for lectures from StallergensGreer, Berlin-CHemie and sponsorship from MYLAN for in the following professional training: ARIA masterclass in allergic rhinitis participation. Dr. Larenas Linnemann reports personal fees from GSK, Astrazeneca, MEDA, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Grunenthal, UCB, Amstrong, Siegfried, DBV Technologies, MSD, Pfizer., grants from Sanofi, Astrazeneca, Novartis, UCB, GSK, TEVA, Chiesi, Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. Dr. Mösges reports personal fees from ALK, grants from ASIT biotech, Leti, BitopAG, Hulka, Ursapharm, Optima; personal fees from allergopharma, Nuvo, Meda, Friulchem, Hexal, Servier, Bayer, Johnson & Johnson, Klosterfrau, GSK, MSD, FAES, Stada, UCB, Allergy Therapeutics; grants and personal fees from Bencard, Stallergenes; grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Lofarma; non-financial support from Roxall, Atmos, Bionorica, Otonomy, Ferrero; personal fees and non-financial support from Novartis; Dr. Okamoto reports personal fees from Eizai Co., Ltd., Shionogi Co., Ltd., Torii Co., Ltd., GSK, MSD, Kyowa Co., Ltd., grants and personal fees from Kyorin Co., Ltd., Tiho Co., Ltd., grants from Yakuruto Co., Ltd., Yamada Bee Farm, outside the submitted work. Dr. Papadopoulos reports grants from Gerolymatos, personal fees from Hal Allergy B.V., Novartis Pharma AG, Menarini, Hal Allergy B.V., outside the submitted work. Dr. Pépin reports grants from AIR LIQUIDE FOUNDATION, AGIR à dom, ASTRA ZENECA, FISHER & PAYKEL, MUTUALIA, PHILIPS, RESMED, VITALAIRE, other from AGIR à dom, ASTRA ZENECA, BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM, JAZZ PHARMACEUTICAL, NIGHT BALANCE, PHILIPS, RESMED, SEFAM, outside the submitted work. Dr. Pfaar reports grants and personal fees from ALK-Abelló, Allergopharma Stallergenes Greer, HAL Allergy Holding B.V./HAL Allergie GmbH, Bencard Allergie GmbH/Allergy Therapeutics, Lofarma, grants from Biomay, ASIT Biotech Tools S.A, Laboratorios LETI/LETI Pharma, Anergis S.A., grants from Nuvo, Circassia, Glaxo Smith Kline, personal fees from Novartis Pharma, MEDA Pharma, Mobile Chamber Experts (a GA2LEN Partner), Pohl-Boskamp, Indoor Biotechnologies, grants from, outside the submitted work. Dr. Todo-Bom reports grants and personal fees from Novartis, Mundipharma, GSK Teva Pharma, personal fees from AstraZeneca, grants from Leti, outside the submitted work. Dr. Tsiligianni reports advisory boards from Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis and a grant from GSK, outside the submitted work. Dr. Wallace reports and Indicates that she is the co-chair of the Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters, a task force composed of 12 members of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology and the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. Dr. Waserman reports other from CSL Behring, Shire, AstraZeneca,Teva, Meda, Merck, outside the submitted work. Dr. Zuberbier reports and Organizational affiliations: Commitee member: WHO-Initiative “Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma” (ARIA). Member of the Board: German Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology (DGAKI). Head: European Centre for Allergy Research Foundation (ECARF). Secretary General: Global Allergy and Asthma European Network (GA2LEN). Member: Committee on Allergy Diagnosis and Molecular Allergology, World Allergy Organization (WAO).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional file
Additional file 1.
The MASK Study Group.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Bousquet, J.J., Schünemann, H.J., Togias, A. et al. Next-generation ARIA care pathways for rhinitis and asthma: a model for multimorbid chronic diseases. Clin Transl Allergy 9, 44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13601-019-0279-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13601-019-0279-2