Abstract
Background
Lepidoptera encompasses more than 160,000 described species that have been classified into 45–48 superfamilies. The previously determined Lepidoptera mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) are limited to six superfamilies of the lineage Ditrysia. Compared with the ancestral insect gene order, these mitogenomes all contain a tRNA rearrangement. To gain new insights into Lepidoptera mitogenome evolution, we sequenced the mitogenomes of two ghost moths that belong to the non-ditrysian lineage Hepialoidea and conducted a comparative mitogenomic analysis across Lepidoptera.
Results
The mitogenomes of Thitarodes renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis are 16,173 bp and 15,816 bp long with an A + T content of 81.28 % and 82.34 %, respectively. Both mitogenomes include 13 protein-coding genes, 22 transfer RNA genes, 2 ribosomal RNA genes, and the A + T-rich region. Different tandem repeats in the A + T-rich region mainly account for the size difference between the two mitogenomes. All the protein-coding genes start with typical mitochondrial initiation codons, except for cox1 (CGA) and nad1 (TTG) in both mitogenomes. The anticodon of trnS(AGN) in T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis is UCU instead of the mostly used GCU in other sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes. The 1,584-bp sequence from rrnS to nad2 was also determined for an unspecified ghost moth (Thitarodes sp.), which has no repetitive sequence in the A + T-rich region. All three Thitarodes species possess the ancestral gene order with trnI-trnQ-trnM located between the A + T-rich region and nad2, which is different from the gene order trnM-trnI-trnQ in all previously sequenced Lepidoptera species. The formerly identified conserved elements of Lepidoptera mitogenomes (i.e. the motif ‘ATAGA’ and poly-T stretch in the A + T-rich region and the long intergenic spacer upstream of nad2) are absent in the Thitarodes mitogenomes.
Conclusion
The mitogenomes of T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis exhibit unusual features compared with the previously determined Lepidoptera mitogenomes. Their ancestral gene order indicates that the tRNA rearrangement event(s) likely occurred after Hepialoidea diverged from other lepidopteran lineages. Characterization of the two ghost moth mitogenomes has enriched our knowledge of Lepidoptera mitogenomes and contributed to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying mitogenome evolution, especially gene rearrangements.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Insect mitogenomes are usually small closed-circular molecules (15–20 kb) containing 13 protein-coding genes (PCGs), 2 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes, 22 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, and a large non-coding element termed the A + T-rich or control region [1, 2]. Because of their unique features, including coding content conservation, maternal inheritance, and rapid evolution, mitogenome sequences have been widely used as molecular markers for diverse evolutionary studies [1, 3]. The order of the genes in the Drosophila yakuba mitogenome, the first insect mitogenome to have its sequence determined, is shared by the majority of insect species, and this is therefore considered to be the ancestral order for the entire class Insecta [1, 4–6]. Various gene rearrangements have been reported in other insect mitogenomes and the most common type of rearrangements involves tRNA genes [7]. All tRNA gene rearrangements can be classified as translocation, local inversion, or remote inversion (translocation and inversion) [8, 9]. These rearrangements represent a molecular mitochondrial signature at the order or lower taxonomic levels [8, 10, 11]. Therefore, in addition to sequence data, the mitochondrial gene order can provide important evidence to establish evolutionary relationships [1, 5, 12]. With the increasing availability of sequence data, the mitogenome has become a model for investigating the mode and mechanism of genome evolution [13].
Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths), one of the two largest insect orders, has more than 160,000 described species that have been classified into 45–48 superfamilies [14, 15]. Based on the information available in the GenBank database up to 2011, more than 41 complete or nearly complete mitogenome sequences have been determined for the Lepidoptera species. All these species are limited to six superfamilies, Tortricoidea, Bombycoidea, Noctuoidea, Pyraloidea, Geometroidea, and Papilionoidea, which belong to the lepidopteran lineage Ditrysia. Taxonomic sampling is still poor mainly because of the absence of information about the non-ditrysian lineages. A better understanding of the Lepidoptera mitogenomes requires an expansion of taxon samplings, especially of the non-ditrysian lineages (e.g. Exoporia). All the Lepidoptera mitogenomes available in GenBank are characterized by the gene order trnM trnI trnQ, revealing a translocation of trnM compared with the ancestral gene order trnI trnQ trnM. It is not known whether this rearrangement is common for the whole order Lepidoptera or whether it occurred after the split of Lepidoptera. Mitogenome sequencing of non-ditrysian lineages of Lepidoptera will help address this interesting question and shed light on the underlying mechanisms of mitogenome evolution.
The ghost moth genus Thitarodes Viette (previously called Hepialus[16–19]) belongs to the family Hepialidae (Lepidoptera: Exoporia: Hepialoidea) and Hepialoidea is the most successful among the non-ditrysian lineages in terms of extant diversity [15, 16]. Thitarodes are the only known hosts for the ascomycete Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Berk.), commonly known as the Chinese caterpillar fungus, which is a prized traditional Chinese medicine that is believed to boost immunity and increase stamina [20]. Members of the Thitarodes occupy diverse habitats on the alpine meadows in the Himalayas and on the Tibetan Plateau [21, 22]. Among them, T. renzhiensis is distributed on the Renzhi and Baima Snow mountains, at altitudes of 3880–4750 m, in northwest Yunnan Province, China [23]. Thitarodes yunnanensis is found only on Laojun Mountain, at elevations of 3680–3750 m, in northwest Yunnan Province, China [24]. There are distinct differences in the male genital structure between these two species. Compared with T. yunnanensis, there is a heavily sclerotized curved spine on the end of the valve in T. renzhiensis[23, 24].
In the present study, we sequenced the entire mitogenomes of the ghost moths, T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis. To confirm our findings, the 1,584-bp sequence from rrnS to nad2 was also determined for a third species in Thitarodes. We compared the sequences with other insect mitogenomes, particularly with those of previously determined Lepidoptera species.
Results and discussion
Genome structure, organization, and composition
The complete mitogenomes of T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis are circular molecules with 16,173 bp and 15,816 bp, respectively. The two mitogenome sequences have been deposited in GenBank (T. renzhiensis [GenBank: HM744694] and T. yunnanensis [GenBank: HM744695]). Because of expansion of the A + T-rich region, the mitogenome sequence of T. renzhiensis is longer than any other complete Lepidoptera mitogenome sequenced to date. The 1,584-bp mtDNA sequence comprising partial rrnS, the A + T-rich region, trnI, trnQ, trnM, and partial nad2, was also determined for Thitarodes sp. [GenBank: HQ883371].
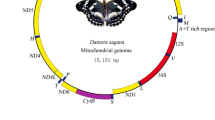
The T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis mitogenomes both include the entire set of 37 genes (13 PCGs, 22 tRNA genes, and 2 rRNA genes; see Table 1) and the A + T-rich region that is usually present in animal mitogenomes [1]. The order of the genes in the sequences of the three Thitarodes species was identical to that of the inferred ancestral insects, but different from the gene order in all other Lepidoptera mitogenomes sequenced to date because of the rearrangement of three tRNA genes between the A + T-region and nad2 (Figure 1).
Schematic representation of mitochondrial gene arrangements and the A + T-rich regions in three Thitarodes species. All the currently determined Thitarodes species have the ancestral gene order. Previously sequenced lepidopteran species have the trnM (M) translocated upstream of trnI (I), trnQ (Q), and an intergenic spacer (IS). There are 4.9 repeat units (I–IV with 107 bp per unit) in T. yunnanensis and 8.5 repeat units (i–viii with 113 bp per unit) in T. renzhiensis. Similar repetitive sequence is absent in Thitarodes sp.
In addition to the A + T-rich region, a total of 49-bp and 81-bp noncoding sequences are present in the mitogenomes of T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis, respectively. In the T. yunnanensis mitogenome, trnI and trnQ are separated by a 27-bp intergenic spacer (ATTTT)3CTTTTTCAACTA whereas there is no such intergenic spacer in T. renzhiensis. There is a 15-bp intergenic spacer between trnS(UCN) and nad1 in both mitogenomes. In this region, a conserved motif ATACTAA is present in all previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes [25–27], while the corresponding sequence is ATACTAT in T. renzhiensis and ATACTAC in T. yunnanensis.
Like other insect mitogenomes, the two newly sequenced mitogenomes contain overlapping genes. A total of 16-bp overlapping sequences occupy the same three locations in each of the two mitogenomes. One 8-bp overlap is located between trnW and trnC oriented on opposite strands; the other two locations are between atp8 and atp6 (7 bp) and between trnK and trnD (1 bp) on the majority strand (Table.1).
The nucleotide compositions of the two Thitarodes mitogenomes are significantly biased toward A and T. The A + T content of the majority strand in T. yunnanensis is 82.34 %, higher than that of T. renzhiensis (81.28 %; see Table 2). These values fall within the range of the A + T content for other Lepidoptera species; from 77.84 % in Ochrogaster lunifer to 82.66 % in Coreana raphaelis[26, 28, 29]. The nucleotide skew statistics for the entire majority strand of T. renzhiensis (AT-skew = 0.011, GC-skew = −0.194) and T. yunnanensis (AT-skew = −0.006, GC-skew = −0.173) indicate slight A or T skews and a moderate C skew. A similar trend has been observed in other Lepidoptera mitogenomes (Figure 2); the AT-skew ranges from −0.04742 (C. raphaelis) to 0.05878 (Bombyx mori) and the GC-skew is always negative varying from −0.31769 (O. lunifer) to −0.15802 (C. raphaelis).
Scatter plot of AT- and GC-skews in the lepidopteran superfamilies. Values were calculated for the majority strand of the full-length mitogenome sequences. All the species that are represented are listed in Table 3. AT-skew = (A-T)/(A + T); GC-skew = (G-C)/(G + C).
Transfer and ribosomal RNA genes
The two mitogenomes have the complete set of 22 tRNA genes (Table 1) that are present in most metazoan mitogenomes. The predicted cloverleaf structures for the tRNA genes are presented in Figures 3 and 4. All tRNA genes were determined by tRNAscan-SE 1.21 [30] and the program ARWEN [31] except for trnS(AGN) in T. yunnanensis. The trnS(AGN) could not form the typical cloverleaf structure, because the dihydrouridine (DHU) arm is replaced by an unpaired stretch of 5 and 6 nucleotides in T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis, respectively. This feature is common to many arthropod mitogenomes [12, 32]. The trnS(AGN) in T. yunnanensis, therefore, was determined by comparison with that of T. renzhiensis and previously determined Lepidoptera mitogenomes. The trnQ trnK, and trnN genes each have an identical sequence between T. yunnanensis and T. renzhiensis. A total of 39 mismatched base pairs and G-U wobble pairs are located in the acceptor (10), DHU (12), TψC (7), and anticodon (10) stems of the tRNA secondary structures in the two mitogenomes. In T. renzhiensis, 11 mismatched base pairs (2 A-A, 3 A-C, 1 C-U, and 5 U-U) and 10 G-U wobble pairs have been identified in 16 tRNA genes; in T. yunnanensis, 1 A-C, 1 C-U, and 5 U-U mismatched pairs as well as 11 G-U wobble pairs occur in 15 tRNA genes. As in the Korean hairstreak C. raphaelis[28], the anticodon of trnS(AGN) in T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis is UCU instead of GCU that is present in other sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes. The anticodons of the remaining tRNAs are each identical to those of all other available Lepidoptera mitogenomes.
Various gene orders have been found in holometabolous insect mitogenomes, and tRNA genes have frequently been involved in mitogenome rearrangements [6, 25, 33–36]. In the ancestral type, the tRNA gene order between the A + T-rich region and nad2 is trnI trnQ trnM[1, 3, 6]. In all previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes, the order is trnM trnI trnQ, implying that translocation of trnM has taken place [11, 25, 26]. By contrast, the present study revealed the ancestral gene arrangement in T. renzhiensis T. yunnanensis, and Thitarodes sp.. Therefore, the translocation of trnM is not a mitochondrial signature for the whole Lepidoptera order. Rather, the translocation event(s) likely occurred after Hepialoidea diverged from other lepidopteran lineages.
The tRNA rearrangements are generally considered to be a consequence of tandem duplication of part of mitogenome, followed by random and/or nonrandom loss of duplicated copies [37–39]. Similar non-coding sequences, ranging from 40 bp in Parnassius bremeri[40] to 87 bp in Sasakia charonda (GenBank: NC014223), are present at the position originally occupied by the transposed trnM in all previously sequenced Lepidoptera species but not in the three currently reported Thitarodes species. Because these intergenic sequences have similar lengths to those of typical tRNA genes, they were presumed to be remnants of the trnM gene and its boundary sequences [41]. If this is the case, the tandem duplication of mtDNA sequences including trnM followed by loss could be responsible for the tRNA rearrangement patterns in previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes. However, the intergenic sequences have also been considered to be products of a partial duplication of the neighboring nad2 because of the high levels of sequence identities (up to 74 % in Eumenis autonoe) between these intergenic sequences and nad2[40, 42]. If so, the duplication of partial nad2 should be a relatively recent event considering the high sequence identities. However, low identities (<40 %) between the intergenic sequences and nad2 were also detected in other sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes [40]. We should note that the short length (40–87 bp) and high A + T content (76.60–98.18 %) of the intergenic sequences make it difficult to determine the origin of the intergenic sequences based solely on sequence identities. Therefore, cautions should be taken before definite conclusions regarding the source of the intergenic sequences are drawn. Regardless of the origin of the intergenic sequences, the most likely mechanism for the tRNA rearrangement in the previously sequenced Lepidoptera species is through a tandem duplication of the region that includes trnI trnQ, and trnM, followed by losses of the supernumerary genes. Clearly, more work is required in future studies to test this assumption.
The ribosomal RNA genes (rrnL and rrnS) are located between trnL(CUN) and trnV, and between trnV and the A + T-rich region, respectively. The rrnL gene is 1,335 bp long in T. renzhiensis and 1,329 bp in T. yunnanensis; their A + T content is 85.39 % and 86.00 %, respectively (Table 2). In T. renzhiensis, rrnS is 779 bp long and the A + T content is 85.37 %; in T. yunnanensis, it is 777 bp long with an A + T content of 86.10 % (Table 2).
Protein-coding genes
The mitogenomes of T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis contain the 13 PCGs that are usually present in animal mitogenomes and they are arranged along the mitogenome in congruence with the standard order in insects [1]. In T. renzhiensis, the start codons for cox1 and nad1 are CGA and TTG, respectively; the other PCGs start with the typical ATN codons, three (nad2 nad3, and nad5) with ATT, two (atp8 and nad6) with ATA, and the remainder with ATG (Table 1). Compared with T. renzhiensis T. yunnanensis has a different initiation codon ATA in nad3. Ambiguities always arise when attempting to annotate the initiation codon for cox1 in a wide variety of species including Lepidoptera and many irregular initiation codons, including ATTACG [43], TTAG [28, 44–47] and CGA [25, 26, 29, 40, 42, 48–50], have been postulated for cox1 in the sequenced Lepidoptera species. A study based on the transcript information of Anopheles funestus revealed that the translation initiation codon for the cox1 gene is TCG, rather than the atypical, longer codons that had been proposed earlier [3]. Recently, expressed sequence tag data from the legume pod borer Maruca vitrata have shown that cox1 may start with the CGA codon for arginine [51]. Here, we tentatively designate CGA as the cox1 start codon, partly because this start codon has been found previously to be well conserved in 39 Lepidoptera species [40]. Further investigations are required to clarify the mechanism of cox1 initiation in Lepidoptera. In both T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis, the annotated start codon of nad1 is TTG, consistent with those in A. funestus[3] and M. vitrata[51], which were annotated based on transcript information.
The atp8 cob cox3 nad1, and nad4 genes in T. renzhiensis have the conventional stop codon TAA; the remaining 8 have incomplete stop codons T or TA, 6 that are located in the genes that have tRNA genes at their 3' end, and 2 belonging to atp6 and nad6 upstream of cox3 and cob, respectively (Table 1). The only difference between the stop codons in the two mitogenomes is for nad2 which uses the complete stop codon TAA in T. yunnanensis and the incomplete stop codon T in T. renzhiensis. Partial stop codons are common in the mitogenomes of most insects including all sequenced Lepidoptera species [1, 25, 41]. The polycistronic transcript molecule is processed into mature RNA by precise endonucleolytic cleavages using the recognition signals of tRNA secondary structures; the truncated stop codons are presumed to be completed via post-transcriptional polyadenylation [52, 53]. The atp8 and atp6 genes in the two mitogenomes have a 7-bp overlap, a common feature of Lepidoptera and many other arthropod mitogenomes [25, 54].
The A + T content of the PCGs, excluding stop codons, is 78.99 % and 80.58 % in T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis, respectively, which is lower than the A + T content of the mitogenomes as a whole (Table 2). In T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis, the third codon positions have a considerably higher A + T content (91.24 % and 95.22 %, respectively) than the first and second codon positions; the strongest bias toward T is in the second codon positions (48.82 % and 49.90 %, respectively), and the lowest content of G is in the third codon positions (3.87 % and 1.88 %, respectively; Table 2).
The codon usage bias has been detected in the currently sequenced Thitarodes mitogenomes. There are a total of 3720 codons, excluding stop codons, in each of the two Thitarodes mitogenomes. Among them, the three most abundant codons in both mitogenomes are UUA [Leu (UUR)], AUU (Ile), and UUU (Phe). As a consequence, Leu (UUR), Ile, and Phe are the three most frequently used codon families (Figure 5). The rarest used codon family is Cys. When PCGs on the majority and minority strands are considered separately, the three most abundant codon families are also Leu (UUR), Ile, and Phe (Figure 5). The usage of both four- and two-fold degenerate codons exhibits a strong A + T-bias in the third codon positions. G + C-rich codons are less preferred, with UGC absent in T. renzhiensis, and CUG, CCG, and ACC lost in T. yunnanensis (Figure 5). A similar codon usage pattern and A + T-bias in the third codon positions are present in previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes, which were analyzed and averaged for each superfamily (Additional file 1: Figure S1, Additional file 2: Figure S2).
The A + T-rich region
The length and A + T content of the A + T-rich regions are 1,367 bp and 90.56 % in T. renzhiensis, 978 bp and 89.37 % in T. yunnanensis, and 559 bp and 92.84 % in Thitarodes sp.. The A + T-rich region of T. renzhiensis is the longest of all the sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes; the shortest is 319 bp in O. lunifer[26].
The A + T-rich region of T. renzhiensis includes a tandem repeat region consisting of eight 113-bp copies and one partial copy of a 57-bp sequence (Figure 1). In T. yunnanensis, the A + T-rich region includes four complete repeat units (107 bp) and one truncated repeat unit (101 bp). However, the A + T-rich region of Thitarodes sp. consists entirely of non-repetitive sequences (Figure 1). The conspicuous macrorepeat units (>50 bp long) commonly found in other insects are also present in previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes, for example, Bombyx mandarina (126 bp) [55], Papilio maraho (252 bp) [56], and Spilonota lechriaspis (124 bp) [57]. An explanation for the origin of these repeat sequences is slipped-strand mispairing during mtDNA replication [58, 59]. These repeat sequences mainly account for length variations in Lepidoptera mitogenomes.
Downstream of the rrnS gene in the previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes, there is a widely conserved structure that includes the motif ‘ATAGA’ and a 16–22 bp poly-T stretch. It has been suggested that this structure might function as a signal for mtDNA replication initiation [42, 60, 61]. However, these conserved elements are not found in the mitogenomes of T. yunnanensis T. renzhiensis, and Thitarodes sp., indicating that these structural motifs are not conserved in the non-ditrysian Lepidoptera species. The Thitarodes mitogenomes may adopt a different strategy for replication initiation. The absence of the conserved elements in the A + T-rich region, together with above mentioned structures, such as the presence of the ancestral gene arrangement, and the absence of the intergenic spacer upstream of nad2, demonstrates that the Thitarodes mitogenomes have unusual features compared with the previously determined Lepidoptera mitogenomes. Therefore, in future studies, more attention should be paid to non-ditrysian lineages when comparing Lepidoptera mitogenomes.
Conclusions
Thitarodes renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis mitogenomes are the first representatives of non-ditrysian lineages of Lepidoptera. The arrangement of the tRNA genes between the A + T-region and nad2 is trnI-trnQ-trnM, different from those of previously sequenced Lepidoptera mitogenomes but identical to the ancestral gene order. Therefore, the previously identified tRNA rearrangement is not a synapomorphy for Lepidoptera mitogenomes. This result indicates that the tRNA rearrangement event(s) likely occurred after Hepialoidea diverged from other lepidopteran lineages. In addition, compared with other Lepidoptera mitogenomes, T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis mitogenomes have other unique structural characters such as the lack of the intergenic spacer upstream of nad2. Therefore, non-ditrysian lineages should be taken into consideration in future comparative mitogenomic studies of Lepidoptera. Characterization of the two mitogenomes has contributed to our understanding of Lepidoptera mitogenomes and provided insights into mitogenome evolution, especially gene rearrangements.
Methods
Specimen collection and DNA extraction
Samples of T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis were obtained from cultures in Diqing, Yunnan Province, China. Specimens of Thitarodes sp., whose complete binomial name has not been specified, were collected in the Qilian Mountain, Qinghai Province, China. All the specimens were preserved in anhydrous ethanol and stored at −20 °C until used for DNA extraction. Whole genomic DNA was extracted from an ethanol-preserved larva with the DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, California, USA). DNA quality was assessed by electrophoresis in a 1 % agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide.
PCR amplification and sequencing
The entire mitogenomes of both T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis were amplified in 10 overlapping fragments (F1 to F10) using long PCR. All primers were designed based on the conserved nucleotide sequences of the known Lepidoptera mitogenome sequences (Table 3). Primer sequences and locations for each long PCR are listed in Additional file 3: Table S1. The fragments were amplified using LA Taq (TaKaRa Co., Dalian, China) with an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 30 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 48–60 °C for 45 s, and extension at 68 °C for 3–5 min, with a final elongation at 70 °C for 7–10 min after the last cycle. All the amplified products were sequenced directly except for the F10 which was sequenced after being cloned into pGEM-T Easy Vector (TianGen Biotech Co., Beijing, China). For each PCR product, the full double-stranded sequence was determined by primer walking.
Sequence assembly and annotation
Raw sequence files were proof read and assembled into contigs using ContigExpress included in the Vector NTI (9.1) package.
PCGs were determined and translated into putative proteins using the ORF finder in the DNAStar package (DNAStar Inc., Madison, WI, USA). The identity of these polypeptides was established using the BLAST program available on the NCBI web site. To determine the gene boundaries, the 5' ends of PCGs were assumed to be at the first legitimate in-frame start codon (ATN, GTG, TTG, GTT) in an open reading frame (ORF) that was not located within an upstream gene encoded on the same strand; the 3' ends were inferred to be at the first in-frame stop codon encountered downstream of the start codon. When the stop codon was located within the sequence of a downstream gene encoded on the same strand, a truncated stop codon (T or TA) adjacent to the beginning of the downstream gene was designated as the termination codon [2, 11]. This codon was assumed to be completed by polyadenylation after transcript processing [26].
Identification of tRNA genes was performed using the tRNAscan-SE Search Server [30] with invertebrate mitochondrial codon predictors and the program ARWEN [31]. The predicted tRNA secondary structures were compared and manually adjusted. The rrnL was annotated to extend to boundaries of the flanking trnL(CUN) and trnV. The 3' end of rrnS was annotated to be adjacent to the start of trnV, while the 5' end was determined via comparison with orthologous sequences of other Lepidoptera mitogenomes using MEGA ver4.0 [74].
Genomic analysis
Nucleotide sequences of the 13 mitochondrial PCGs of the previously determined 37 Lepidoptera species (Table 3) were downloaded from the METAMiGA database (http://amiga.cbmeg.unicamp.br/) [75]. Nucleotide compositions and codon usage (excluding stop codons) in T. renzhiensis and T. yunnanensis mitogenomes were calculated with MEGA. To measure synonymous codon usage bias, RSCU values were also computed. Average codon usage and RSCU values were further analyzed for each superfamily used in this study. GC-skew = (G-C)/(G + C) and AT-skew = (A-T)/(A + T) were used to measure base compositional differences [76]. The tandem repeats in the A + T-rich region were predicted using the Tandem Repeats Finder [77].
Abbreviations
- atp6 and atp8:
-
ATP synthase subunits 6 and 8
- cob:
-
cytochrome b
- cox1–3:
-
cytochrome c oxidase subunits 1–3
- nad1–6 and nad4L:
-
NADH dehydrogenase subunits 1–6 and 4 L
- rrnS and rrnL:
-
small and large ribosomal RNA (rRNA) subunits
- trnX:
-
transfer RNA (tRNA) genes with X representing the one-letter abbreviation of the corresponding amino acid.
References
Boore JL: Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27: 1767-1780. 10.1093/nar/27.8.1767.
Wolstenholme DR: Animal mitochondrial DNA: structure and evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1992, 141: 173-216.
Krzywinski J, Grushko OG, Besansky NJ: Analysis of the complete mitochondrial DNA from Anopheles funestus: an improved dipteran mitochondrial genome annotation and a temporal dimension of mosquito evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2006, 39: 417-423. 10.1016/j.ympev.2006.01.006.
Clary DO, Wolstenholme DR: The mitochondrial DNA molecule of Drosophila yakuba: Nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J Mol Evol. 1985, 22: 252-271. 10.1007/BF02099755.
Boore JL, Lavrov DV, Brown WM: Gene translocation links insects and crustaceans. Nature. 1998, 392: 667-668. 10.1038/33577.
Cha SY, Yoon HJ, Lee EM, Yoon MH, Hwang JS, Jin BR, Han YS, Kim I: The complete nucleotide sequence and gene organization of the mitochondrial genome of the bumblebee, Bombus ignitus (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Gene. 2007, 392: 206-220. 10.1016/j.gene.2006.12.031.
Beckenbach AT: Mitochondrial genome sequences of representatives of three families of scorpionflies (Order Mecoptera) and evolution in a major duplication of coding sequence. Genome. 2011, 54: 368-376. 10.1139/g11-006.
Wei SJ, Shi M, Sharkey MJ, Achterberg C, Chen XX: Comparative mitogenomics of Braconidae (Insecta: Hymenoptera) and the phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial genomes with special reference to Holometabolous insects. BMC Genomics. 2010, 11: 371-10.1186/1471-2164-11-371.
Tan HW, Liu GH, Dong X, Lin RQ, Song HQ, Huang SY, Yuan ZG, Zhao GH, Zhu XQ: The complete mitochondrial genome of the Asiatic cavity-nesting honeybee Apis cerana (Hymenoptera: Apidae). PLoS ONE. 2011, 6: e23008-10.1371/journal.pone.0023008.
Cameron SL, Beckenbach AT, Dowton M, Whiting M: Evidence from mitochondrial genomics on interordinal relationships in insects. Arthropod Syst Phyl. 2006, 64: 27-34.
Negrisolo E, Babbucci M, Patarnello T: The mitochondrial genome of the ascalaphid owlfly Libelloides macaronius and comparative evolutionary mitochondriomics of neuropterid insects. BMC Genomics. 2011, 12: 221-10.1186/1471-2164-12-221.
Sheffield NC, Song H, Cameron SL, Whiting MF: A comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in Coleoptera (Arthropoda: Insecta) and genome descriptions of six new beetles. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25: 2499-2509. 10.1093/molbev/msn198.
Dowton M, Cameron SL, Dowavic JI, Austin AD, Whiting MF: Characterization of 67 mitochondrial tRNA gene rearrangements in the Hymenoptera suggests that mitochondrial tRNA gene position is selectively neutral. Mol Biol Evol. 2009, 26: 1607-1617. 10.1093/molbev/msp072.
Kristensen NP, Scoble MJ, Karsholt O: Lepidoptera phylogeny and systematics: the state of inventorying moth and butterfly diversity. Zootaxa. 2007, 1668: 699-747.
Powell JA: Lepidoptera (Moths, Butterflies). In Encyclopedia of Insects. 2nd edition. Edited by Resh VH, CArdé RG. Burlington: Academic Press. , 587: 559-587.
Nielsen ES, Robinson GS, Wagner DL: Ghost-moths of the world: a global inventory and bibliography of the Exoporia (Mnesarchaeoidea and Hepialoidea) (Lepidoptera). J Nat Hist. 2000, 34: 823-878. 10.1080/002229300299282.
Maczey N, Dhendup K, Cannon P, Hywel-Jones N, Rai TB: Thitarodes namnai sp nov and T. caligophilus sp nov (Lepidoptera: Hepialidae), hosts of the economically important entomopathogenic fungus Ophiocordyceps sinensis in Bhutan. Zootaxa. 2010, : 42-52.
Wang XL, Yao YJ: Host insect species of Ophiocordyceps sinensis: a review. Zookeys. 2011, : 43-59.
Zou ZW, Liu X, Zhang GR: Two new species of Thitarodes (Lepidoptera: Hepialidae) from Tibet in China. Pan-Pac Entomol. 2011, 87: 106-113. 10.3956/2010-24.1.
Zhang Y, Xu L, Zhang S, Liu X, An Z, Wang M, Guo Y: Genetic diversity of Ophiocordyceps sinensis, a medicinal fungus endemic to the Tibetan Plateau: implications for its evolution and conservation. BMC Evol Biol. 2009, 9: 290-10.1186/1471-2148-9-290.
Yang DR, Li CD, Shu C, Yang YX: Studies on Chinese species of the genus Hepialus and their geographical distribution. Acta Entomol Sin. 1996, 39: 413-422.
Yang DR, Peng YQ, Chen JY, Cao YQ, Yang P: Advances in genus Hepialus moth of Cordyceps sinensis host. Zool Res. 2009, 30 (Suppl): 285-229.
Yang DR, Shen FR, Yang YX, Lang XC, Dong DZ, Chen S, Lu Z: Sinaduji: Biological studies and notes on a new species of the genus Hepialus from Yunnan. Acta Entomol Sin. 1991, 34: 218-224.
Yang DR, Li CD, Shen FR: Three new species of the genus Hepialus from Yunnan and Xizang. Zool Res. 1992, 13: 245-250.
Cameron SL, Whiting MF: The complete mitochondrial genome of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta, (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Sphingidae), and an examination of mitochondrial gene variability within butterflies and moths. Gene. 2008, 408: 112-123. 10.1016/j.gene.2007.10.023.
Salvato P, Simonato M, Battisti A, Negrisolo E: The complete mitochondrial genome of the bag-shelter moth Ochrogaster lunifer (Lepidoptera, Notodontidae). BMC Genomics. 2008, 9: 331-10.1186/1471-2164-9-331.
Kim MJ, Jeong HC, Kim SR, Kim I: Complete mitochondrial genome of the nerippe fritillary butterfly, Argynnis nerippe (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Mitochondr DNA. 2011, 22: 86-88. 10.3109/19401736.2011.624604.
Kim I, Lee EM, Seol KY, Yun EY, Lee YB, Hwang JS, Jin BR: The mitochondrial genome of the Korean hairstreak, Coreana raphaelis (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Insect Mol Biol. 2006, 15: 217-225. 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00630.x.
Jiang ST, Hong GY, Yu M, Li N, Yang Y, Liu YQ, Wei ZJ: Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of the giant silkworm moth, Eriogyna pyretorum (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Int J Biol Sci. 2009, 5: 351-365.
Lowe TM, Eddy SR: tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25: 955-964.
Laslett D, Canbäck B: ARWEN: a program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. 2008, 24: 172-175. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm573.
Lin CP, Chen MY, Huang JP: The complete mitochondrial genome and phylogenomics of a damselfly, Euphaea formosa support a basal Odonata within the Pterygota. Gene. 2010, 468: 20-29. 10.1016/j.gene.2010.08.001.
Silvestre D, Dowton M, Arias MC: The mitochondrial genome of the stingless bee Melipona bicolor (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini): Sequence, gene organization and a unique tRNA translocation event conserved across the tribe Meliponini. Genet Mol Biol. 2008, 31: 451-460. 10.1590/S1415-47572008000300010.
Gotzek D, Clarke J, Shoemaker D: Mitochondrial genome evolution in fire ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). BMC Evol Biol. 2010, 10: 300-10.1186/1471-2148-10-300.
Song H, Sheffield NC, Cameron SL, Miller KB, Whiting MF: When phylogenetic assumptions are violated: base compositional heterogeneity and among-site rate variation in beetle mitochondrial phylogenomics. Syst Entomol. 2010, 35: 429-448. 10.1111/j.1365-3113.2009.00517.x.
Wei SJ, Tang P, Zheng LH, Shi M, Chen XX: The complete mitochondrial genome of Evania appendigaster (Hymenoptera: Evaniidae) has low A + T content and a long intergenic spacer between atp8 and atp6. Mol Biol Rep. 2010, 37: 1931-1942. 10.1007/s11033-009-9640-1.
Lavrov DV, Boore JL, Brown WM: Complete mtDNA sequences of two millipedes suggest a new model for mitochondrial gene rearrangements: duplication and nonrandom loss. Mol Biol Evol. 2002, 19: 163-169. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004068.
Carapelli A, Vannini L, Nardi F, Boore JL, Beani L, Dallai R, Frati F: The mitochondrial genome of the entomophagous endoparasite Xenos vesparum (Insecta: Strepsiptera). Gene. 2006, 376: 248-259. 10.1016/j.gene.2006.04.005.
Juhling F, Putz J, Bernt M, Donath A, Middendorf M, Florentz C, Stadler PF: Improved systematic tRNA gene annotation allows new insights into the evolution of mitochondrial tRNA structures and into the mechanisms of mitochondrial genome rearrangements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40: 2833-2845. 10.1093/nar/gkr1131.
Kim MI, Baek JY, Kim MJ, Jeong HC, Kim KG, Bae CH, Han YS, Jin BR, Kim I: Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of the red-spotted apollo butterfly, Parnassius bremeri (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) and comparison with other lepidopteran insects. Mol Cells. 2009, 28: 347-363. 10.1007/s10059-009-0129-5.
Gong YJ, Shi BC, Kang ZJ, Zhang F, Wei SJ: The complete mitochondrial genome of the oriental fruit moth Grapholita molesta (Busck) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Mol Biol Rep. 2012, 39: 2893-2900. 10.1007/s11033-011-1049-y.
Kim MJ, Wan X, Kim KG, Hwang JS, Kim I: Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of endangered Eumenis autonoe (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Afr J Biotechnol. 2010, 9: 735-754.
Feng X, Liu DF, Wang NX, Zhu CD, Jiang GF: The mitochondrial genome of the butterfly Papilio xuthus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) and related phylogenetic analyses. Mol Biol Rep. 2010, 37: 3877-3888. 10.1007/s11033-010-0044-z.
Pan MH, Yu QY, Xia YL, Dai FY, Liu YQ, Lu C, Zhang Z, Xiang ZH: Characterization of mitochondrial genome of Chinese wild mulberry silkworm, Bomyx mandarina (Lepidoptera: Bombycidae). Sci China Ser C. 2008, 51: 693-701. 10.1007/s11427-008-0097-6.
Liu Y, Li Y, Pan M, Dai F, Zhu X, Lu C, Xiang Z: The complete mitochondrial genome of the Chinese oak silkmoth, Antheraea pernyi (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2008, 40: 693-703.
Kim SR, Kim MI, Hong MY, Kim KY, Kang PD, Hwang JS, Han YS, Jin BR, Kim I: The complete mitogenome sequence of the Japanese oak silkmoth, Antheraea yamamai (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Mol Biol Rep. 2009, 36: 1871-1880. 10.1007/s11033-008-9393-2.
Hu XL, Cao GL, Xue RY, Zheng XJ, Zhang X, Duan HR, Gong CL: The complete mitogenome and phylogenetic analysis of Bombyx mandarina strain Qingzhou. Mol Biol Rep. 2010, 37: 2599-2608. 10.1007/s11033-009-9781-2.
Liao F, Wang L, Wu S, Li YP, Zhao L, Huang GM, Niu CJ, Liu YQ, Li MG: The complete mitochondrial genome of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Int J Biol Sci. 2010, 6: 172-186.
Yang L, Wei ZJ, Hong GY, Jiang ST, Wen LP: The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Phthonandria atrilineata (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Mol Biol Rep. 2009, 36: 1441-1449. 10.1007/s11033-008-9334-0.
Hong GY, Jiang ST, Yu M, Yang Y, Li F, Xue FS, Wei ZJ: The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the cabbage butterfly, Artogeia melete (Lepidoptera: Pieridae). Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2009, 41: 446-455. 10.1093/abbs/gmp030.
Margam VM, Coates BS, Hellmich RL, Agunbiade T, Seufferheld MJ, Sun W, Ba MN, Sanon A, Binso-Dabire CL, Baoua I, Ishiyaku MF, Covas FG, Srinivasan R, Armstrong J, Murdock LL, Pittendrigh BR: Mitochondrial Genome Sequence and Expression Profiling for the Legume Pod Borer Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). PLoS ONE. 2011, 6: e16444-10.1371/journal.pone.0016444.
Ojala D, Montoya J, Attardi G: tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature. 1981, 290: 470-474. 10.1038/290470a0.
Ojala D, Merkel C, Gelfand R, Attardi G: The tRNA genes punctuate the reading of genetic information in human mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1980, 22: 393-403. 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90350-5.
Ma C, Liu CX, Yang PC, Kang L: The complete mitochondrial genomes of two band-winged grasshoppers. Gastrimargus marmoratus and Oedaleus asiaticus. BMC Genomics. 2009, 10: 12-
Yukuhiro K, Sezutsu H, Itoh M, Shimizu K, Banno Y: Significant levels of sequence divergence and gene rearrangements have occurred between the mitochondrial genomes of the wild mulberry silkmoth, Bombyx mandarina, and its close relative, the domesticated silkmoth, Bombyx mori. Mol Biol Evol. 2002, 19: 1385-1389. 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004200.
Wu LW, Lees DC, Yen SH, Liu CC, Hsu YF: The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Near-Threatened Swallowtail, Agehana maraho (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae): Evaluating Sequence Variability and Suitable Markers for Conservation Genetic Studies. Entomol News. 2010, 121: 267-280. 10.3157/021.121.0308.
Zhao JL, Zhang YY, Luo AR, Jiang GF, Cameron SL, Zhu CD: The complete mitochondrial genome of Spilonota lechriaspis Meyrick (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Mol Biol Rep. 2011, 38: 3757-3764. 10.1007/s11033-010-0491-6.
Levinson G, Gutman GA: Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1987, 4: 203-221.
Moritz C, Brown WM: Tandem duplications in animal mitochondrial DNAs: variation in incidence and gene content among lizards. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987, 84: 7183-10.1073/pnas.84.20.7183.
Hu J, Zhang DX, Hao JS, Huang DY, Cameron S, Zhu CD: The complete mitochondrial genome of the yellow coaster, Acraea issoria (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae: Heliconiinae: Acraeini): sequence, gene organization and a unique tRNA translocation event. Mol Biol Rep. 2010, 37: 3431-3438. 10.1007/s11033-009-9934-3.
Yin JA, Hong GY, Wang AM, Cao YZ, Wei ZJ: Mitochondrial genome of the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and comparison with other Lepidopterans. Mitochondr DNA. 2010, 21: 160-169. 10.3109/19401736.2010.503242.
Lu C, Liu YQ, Liao SY, Li B, Xiang ZH, Han H, Wang XG: Complete Sequence Determination and Analysis of Bombyx mori Mitochondrial Genome. J Agri Biotechnol. 2002, 10: 163-170.
Hong MY, Lee EM, Jo YH, Park HC, Kim SR, Hwang JS, Jin BR, Kang PD, Kim KG, Han YS: Complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the mitogenome of the silk moth Caligula boisduvalii (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae) and comparison with other lepidopteran insects. Gene. 2008, 413: 49-57. 10.1016/j.gene.2008.01.019.
Zhu YJ, Fang R, Ye J, Yi JP: The complete sequence determination and analysis of Lymantria dispar (Lepidoptera:Lymantriidae) mitochondrial genome. Plant Quarantine. 2010, 24: 6-11.
Kim MJ, Kang AR, Jeong HC, Kim KG, Kim I: Reconstructing intraordinal relationships in Lepidoptera using mitochondrial genome data with the description of two newly sequenced lycaenids, Spindasis takanonis and Protantigius superans (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2011, 61: 436-445. 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.07.013.
Wang XC, Sun XY, Sun QQ, Zhang DX, Hu J, Yan Q, Hao JS: Complete mitochondrial genome of the laced fritillary Argyreus hyperbius (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Zool Res. 2011, 32: 465-475.
Xia J, Hu J: zhu GP, zhu CD, Hao JS: Sequencing and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of Calinaga davidis Oberthür (Lepidoptera:Nymphalidae). Zool Res. 2011, 54: 555-565.
Mao ZH, Hao JS, Zhu GP, Hu J, Si MM, Zhu CD: Sequencing and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of Pieris rapae Linnaeus (Lepidoptera:Pieridae). Acta Entomol Sin. 2010, 53: 1295-1304.
Chai HN, Du YZ, Zhai BP: Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genomes of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Int J Biol Sci. 2012, 8: 561-579.
Li WW, Zhang XY, Fan ZX, Yue BS, Huang FN, King E, Ran JH: Structural characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genome of the sugarcane borer, Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). DNA Cell Biol. 2011, 30: 3-8. 10.1089/dna.2010.1058.
Coates BS, Sumerford DV, Hellmich RL, Lewis LC: Partial mitochondrial genome sequences of Ostrinia nubilalis and Ostrinia furnicalis. Int J Biol Sci. 2005, 1: 13-18.
Lee ES, Shin KS, Kim MS, Park H, Cho S, Kim CB: The mitochondrial genome of the smaller tea tortrix Adoxophyes honmai (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Gene. 2006, 373: 52-57.
Son Y, Kim Y: The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am. 2011, 104: 788-799. 10.1603/AN10167.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M: Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007, 24: 1596-1599.
Feijao PC, Neiva LS, de Azeredo-Espin AM, Lessinger AC: AMiGA: the arthropodan mitochondrial genomes accessible database. Bioinformatics. 2006, 22: 902-903. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl021.
Perna N, Kocher T: Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J Mol Evol. 1995, 41: 353-358. 10.1007/BF01215182.
Benson G: Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27: 573-580. 10.1093/nar/27.2.573.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Key Innovative Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China (Grant Nos. KSCX2-YW-G-024 and KSCX2-YW-G-076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
DRY conceived and designed this study. JYC collected specimens and extracted DNA. YQC carried out molecular experiments. YQC and CM analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. DRY thoroughly revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the final version.
Yong-Qiang Cao, Chuan Ma contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
12864_2012_4215_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Additional file 1 :Figure S1. Codon distribution in mitogenomes of currently used lepidopteran superfamilies. CDspT, codons per thousand codons. (PDF 343 KB)
12864_2012_4215_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Additional file 2 :Figure S2. The relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) in mitogenomes of currently used lepidopteran superfamilies. (PDF 404 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, YQ., Ma, C., Chen, JY. et al. The complete mitochondrial genomes of two ghost moths, Thitarodes renzhiensis and Thitarodes yunnanensis: the ancestral gene arrangement in Lepidoptera. BMC Genomics 13, 276 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-276
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-276