Abstract
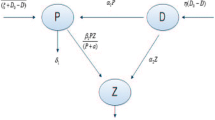
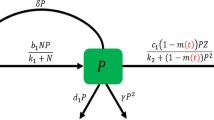
Sundarbans is the largest mangrove wetland ecosystem of the world with rich biodiversity suffering from deteriorated water quality due to excessive fertilization that leads to an uncontrolled increase in phytoplankton. Such eutrophication also changes the community structure and increases the harmful algal blooms (HABs). In this work, we propose an interacting population model for phytoplankton–zooplankton system in which the density of zooplankton is influenced by non-toxic phytoplankton (NTP) and toxin-producing phytoplankton (TPP) followed by Holling type II and Monod–Haldane (MH)-type functional response. The growth of zooplankton species is assumed to reduce due to toxic chemicals released by TPP population. The mathematical model of the proposed system includes the competition terms between TPP and NTP. System dynamics is studied in both cases, i.e., system with diffusion and without diffusion. For the non-diffusive system, we have investigated the condition for boundedness along with the existing criteria of all feasible equilibrium point. Stability analysis of the model system is carried out in detail for each equilibrium point. Forward and backward bifurcation diagrams are obtained for the temporal system in order to understand the behavior of different parameters that control the system dynamics. Theoretically, stability criteria and Turing instability of diffusive system are derived. In this study, we have taken a case of Sundarban mangrove wetland which is suffering from algal blooms due to the presence of toxic Dinoflagellates and Cyanophyceae. Our numerical investigation shows that the lower value of intraspecific interference of zooplankton promotes the complex spatiotemporal dynamics for the population of non-toxic, toxic phytoplankton and zooplankton. The higher value of inter-specific competition coefficient of NTP leads to reduction in zooplankton density that may cause bad health of the wetland system. This investigation renders the importance of diffusion in algal blooms by the occurrence of different Turing patterns and the role of time delay in destabilization of stationary points through the creation of limit cycles. We observed that the increasing value of diffusion coefficient of zooplankton and time allows the algal blooms to settle down from spot-strip mixture to spot patterns.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM (2009) Approaches to monitoring, control and management of harmful algal blooms (HABs). Ocean Coast Manag 52(7):342–347
Anderson DM, Garrison DJ (1997) The ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1009–1305
Andrews JF (1968) A mathematical model for the continuous culture of macroorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 10(6):707–723
Bairagi N, Pal S, Chatterjee S, Chattopadhyay J (2008) Nutrient, non-toxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton and zooplankton interaction in an open marine system. In: Hosking RJ, Venturino E (eds) Aspects of mathematical modelling. Mathematics and biosciences in interaction. Birkhäuser Verlag Basel, Switzerland, pp 41–63
Banerjee M, Venturino E (2011) A phytoplankton-toxic phytoplankton-zooplankton model. Ecol Complex 8(3):239–248
Barik J, Chowdhury S (2014) True mangrove species of Sundarbans delta, West Bengal, Eastern India. Check List 10(2):329–334
Blaxter JHS, Southward AJ (1997) Advances in marine biology. Academic Press, San Diego
Chakraborty K, Das K (2015) Modeling and analysis of a two-zooplankton one-phytoplankton system in the presence of toxicity. Appl Math Model 39(3–4):1241–1265
Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya S, Feudel U, Chattopadhyay J (2012) The role of avoidance by zooplankton for survival and dominance of toxic phytoplankton. Ecol Complex 11:144–153
Chakraborty S, Tiwari PK, Misra AK, Chattopadhyay J (2015) Spatial dynamics of a nutrient-phytoplankton system with toxic effect on phytoplankton. Math Biosci 264:94–100
Chatterjee A, Pal S (2016) Plankton nutrient interaction model with effect of toxin in presence of modified traditional Holling Type II functional response. Syst Sci Cont Eng 4(1):20–30
Chattopadhyay J, Sarkar RR, Mandal S (2000) Toxin producing plankton may act as a biological control for planktonic blooms-field study and mathematical modeling. J Theor Biol 215(3):333–344
Chattopadhyay J, Sarkar RR, Pal S (2004) Mathematical modelling of harmful algal blooms supported by experimental findings. Ecol Comp 1(3):225–235
Chaudhuri S, Chattopadhyay J, Venturino E (2012) Toxic phytoplankton-induced spatiotemporal patterns. J Biol Phys 38(2):331–348
Dahdouh-Guebas F, Jayatissa LP, Di Nitto D, Bosire JO, Lo Seen DL, Koedam N (2005) How effective were mangroves as a defence against the recent tsunami? Curr Biol 15(12):443–447
De Silva M, Jang SRJ (2017) Dynamical behavior of systems of two phytoplankton and one zooplankton populations with toxin producing phytoplankton. Math Methods Appl Sci 40(12):4295–4309
Dhar J, Baghel RS (2016) Role of dissolved oxygen on the plankton dynamics in spatio-temporal domain. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(1):6
Dubey B, Upadhyay RK (2004) Persistence and extinction of one-prey and two-predators system. Nonlinear Anal Model Contr 9(4):307–329
Elser JJ, Loladze I, Peace AL, Kuang Y (2012) Modeling trophic interactions under stoichiometric constraints. Ecol Model 245:3–11
Franks PJS (1997) Models of harmful algal blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 42(5part2):1273–1282
Garvie MR (2007) Finite-difference schemes for reaction-diffusion equations modeling predator-prey interactions in MATLAB. Bull Math Biol 69(3):931–956
Ghosh A, Schmidt S, Fickert T, Nüsser M (2015) The Indian Sundarban mangrove forests: history, utilization, conservation strategies and local perception. Diversity 7(2):149–169
Gopal B, Chauhan M (2006) Biodiversity and its conservation in the Sundarban mangrove ecosystem. Aquat Sci 68(3):338–354
Hale JK, Waltman P (1989) Persistence in infinite-dimensional systems. SIAM J Math Anal 20(2):388–395
Hallegraeff GM (1993) A review of harmful algae blooms and the apparent global increase. Phycologia 32(2):79–99
Han R, Dai B (2019) Spatiotemporal pattern formation and selection induced by nonlinear cross-diffusion in a toxic-phytoplankton zooplankton model with Allee effect. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 45:822–853
Kretzschmar M, Nisbet RM, McCauley E (1993) A predator-prey model for zooplankton grazing on competing algal populations. Theor Popul Biol 44(1):32–66
Kumar V, Dhar J, Bhatti HS (2018) Stability and Hopf bifurcation dynamics of a food chain system: plant-pest-natural enemy with dual gestation delay as a biological control strategy. Model Earth Syst Environ 4(2):881–889
Malchow H, Petrovskii SV, Medvinsky AB (2002) Numerical study of plankton-fish dynamics in a spatially structured and noisy environment. Ecol Model 149(3):247–255
Manna S, Chaudhuri K, Bhattacharyya S, Bhattacharyya M (2010) Dynamics of Sundarban estuarine ecosystem: eutrophication induced threat to mangroves. Saline Syst 6(1):1–16
Misra OP, Raveendra Babu A (2016) Modelling effect of toxicant in a three-species food-chain system incorporating delay in toxicant uptake process by prey. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(2):77
Mondal A, Pal AK, Samanta GP (2020) Rich dynamics of non-toxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton and zooplankton system with multiple gestation delays. Int J Dyn Contr 8(1):112–131
Nagelkerken I, Blaber SJM, Bouillon S, Green P, Haywood M, Kirton LG, Meynecke JO, Pawlik J, Penrose HM, Sasekumar A, Somerfield PJ (2008) The habitat function of mangroves for terrestrial and marine fauna: A review. Aquat Bot 89(2):155–185
Ojha A, Thakur NK (2020) Exploring the complexity and chaotic behavior in plankton-fish system with mutual interference and time delay. BioSystems 198:104283
Pal R, Basu D, Banerjee M (2009a) Modelling of phytoplankton allelopathy with Monod-Haldane-type functional response-a mathematical study. Biosystems 95(3):243–253
Pal S, Chatterjee S, Das KP, Chattopadhyay J (2009b) Role of competition in phytoplankton population for the occurrence and control of plankton bloom in the presence of environmental fluctuations. Ecol Model 220(2):96–110
Pal J, Bhattacharya S, Chattopadhyay J (2010) Does predator go for size selection or preferential toxic-nontoxic species under limited resource? Online J Biol Sci 10:11–16
Pascual M (1993) Diffusion-induced chaos in a spatial predator-prey system. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 251(1330):1–7
Petrovskii SV, Malchow H (1999) A minimal model of pattern formation in a prey-predator system. Math Comput Model 29(8):49–63
Petrovskii SV, Malchow H (2001) Wave of chaos: new mechanism of pattern formation in spatio-temporal population dynamics. Theor Popul Biol 59(2):157–174
Rahman MM, Jiang Y, Irvine K (2018) Assessing wetland services for improved development decision-making: a case study of mangroves in coastal Bangladesh. Wetl Ecol Manag 26(4):563–580
Rao F (2013) Spatiotemporal dynamics in a reaction-diffusion toxic-phytoplankton-zooplankton model. J Stat Mech Theory Exp 8:P08014
Roy S (2008) Spatial interaction among non-toxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton, and zooplankton: emergence in space and time. J Biol Phys 34(5):459–474
Roy S, Alam S, Chattopadhyay J (2006) Competing effects of toxin-producing phytoplankton on the overall plankton populations in the Bay of Bengal. Bull Math Biol 68(08):2303–2320
Roy S, Bhattacharya S, Das P, Chattopadhyay J (2007) Interaction among non-toxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton and zooplankton: inferences from field observations. J Biol Phys 33(1):1–17
Roy S, Majee NC, Ray S (2016) Temperature dependent growth rate of phytoplankton and salinity induced grazing rate of zooplankton as determinants of realistic multi-delayed food chain model. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(3):161
Schultz M, Kiørboe T (2009) Active prey selection in two pelagic copepods feeding on potentially toxic and non-toxic dinoflagellates. J Plankton Res 31(5):553–561
Scotti T, Mimura M, Wakano JY (2015) Avoiding toxic prey may promote harmful algal blooms. Ecol Complex 21:157–165
Sharma A, Sharma AK, Agnihotri K (2016) Complex dynamic of plankton-fish interaction with quadratic harvesting and time delay. Model Earth Syst Environ 2(4):1–17
Sokol W, Howell JA (1981) Kinetics of phenol oxidation by washed cell. Biotechnol Bioeng 3(9):2039–2049
Spalding M, Kainuma M, Collins L (2010) World atlas of Mangroves. Earthscan, London, p 319
Thakur NK, Ojha A (2020a) Complex plankton dynamics induced by adaptation and defense. Model Earth Sys Environ 6(2):907–916
Thakur NK, Ojha A (2020b) Complex dynamics of delay-induced plankton-fish interaction exhibiting defense. SN Appl Sci 2(6):1–25
Thakur NK, Tiwari SK, Upadhyay RK (2016) Harmful algal blooms in fresh and marine water systems: the role of toxin producing phytoplankton. Int J Biomath 9(3):1650043
Thakur NK, Tiwari SK, Dubey B, Upadhyay RK (2017) Diffusive three species plankton model in the presence of toxic prey: application to Sundarban mangrove wetland. J Biol Syst 25(2):185–206
Thakur NK, Ojha A, Jana D, Upadhyay RK (2020) Modeling the plankton-fish dynamics with top predator interference and multiple gestation delays. Nonlinear Dny 100:4003–4029
Truscott J, Brindley J (1994) Ocean plankton populations as excitable media. Bull Math Biol 56(5):981–998
Upadhyay RK, Thakur NK, Dubey B (2010) Nonlinear non-equilibrium pattern formation in a spatial aquatic system: effect of fish predation. J Biol Syst 18(1):129–159
Wang P, Zhao M, Yu H, Dai C, Wang N, Wang B (2016) Nonlinear dynamics of a toxin-phytoplankton-zooplankton system with self-and cross-diffusion. Dis Dyn Nat Soc 2016. Article ID: 4893451
Wyatt T (1988) Harmful algae, marine blooms, and simple population models. Nat Resour 34:40–51
Yang F, Fu S (2008) Global solutions for a tritrophic food chain model with diffusion. Rocky Mt J Math 38:1–28
Zhao J, Wei J (2015) Dynamics in a diffusive plankton system with delay and toxic substances effect. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 22:66–83
Zingone A, Enevoldsen HO (2000) The diversity of harmful algal blooms: a challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast Manag 43(8–9):725–748
Acknowledgements
This research work is supported by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Govt. of India under Grant no. EMR/2017/000607 to the first author (Nilesh Kumar Thakur).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, N.K., Singh, R. & Ojha, A. Dynamical study of harmful algal bloom in Sundarban mangrove wetland with spatial interaction and competing effects. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 8, 555–577 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01088-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01088-6