Abstract
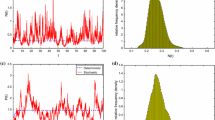
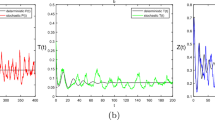
Here we consider a reaction diffusion system of three plankton populations, a zooplankton feeding on two phytoplankton populations, in two different settings. Firstly, the two phytoplanktons are both non-toxic and both enhance the growth of the grazing zooplankton. Secondly, we assume that one of the phytoplankton releases toxin and thereby inhibits the growth of the zooplankton. Our analytic and numerical study shows that the spatiotemporal distribution of the plankton species is uniform when both phytoplankton populations are non-toxic. However, in the presence of toxin-producing phytoplankton, the biomass distribution of all the plankton populations becomes inhomogeneous.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malchow, H., Petrovskii, S., Venturino, E.: Spatiotemporal patterns in Ecology and Epidemiology, CRC (2008)
Anderson, D.M.: Toxic algae blooms and red tides: a global perspective. In: Okaichi, T., Anderson, D.M., Nemoto, T. (eds.) Red Tides: Biology, Environmental Science and Toxicology, pp. 11–21. Elsevier, New York, USA (1989)
Hallegraeff, G.M.: A review of harmful algae blooms and the apparent global increase. Phycologia 32, 79–99 (1993)
Smayda T.: Novel and nuisance phytoplankton blooms in the sea: evidence for a global epidemic. In: Graneli, E., Sundstrom, B., Edler, L., Anderson, D.M. (eds.) Toxic Marine Phytoplankton, pp. 29–40. Elsevier, New York, USA (1990)
Chattopadhyay, J., Sarkar, R.R., Mandal, S.: Toxin-producing plankton may act as a biological control for planktonic blooms-field study and mathematical modelling. J. Theor. Biol 215, 333–344 (2002)
Chattopadhyay, J., Sarkar, R.R., El Abdllaoui, A.: A delay differential equation model on harmful algal blooms in the presence of toxic substances. IMA J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 19, 137–161 (2002)
Roy, S., Alam, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Competitive effects of toxin-producing phytoplankton on overall plankton populations in the Bay of Bengal. Bull. Math. Biol. 68(8), 2303–2320 (2006)
Roy, S., Bhattacharya, S., Das, P., Chattopadhyay, J.: Interaction among non-toxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton and zooplankton: inferences from field observations. J. Biol. Phys. 33(1), 1–17 (2007)
Hutchinson, G.E.: The paradox of the plankton. Am. Nat. 95, 137–145 (1961)
Huisman, J., Pham Thi, N.N., Karl, D.M., Sommeijer, B.: Reduced mixing generates oscillations and chaos in the oceanic deep chlorophyll maximum. Nature 439, 322–325 (2006)
Huisman, J., Weissing, F.J.: Biodiversity of plankton by species oscillation and chaos. Nature 402, 407–410 (1999)
Richerson, P.J., Armstrong, R., Goldman, C.R.: Contemporaneous disequilibrium: a new hypothesis to explain the paradox of plankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 67, 1710–1714 (1970)
Roy, S.: Spatial interaction among nontoxic phytoplankton, toxic phytoplankton, and zooplankton: emergence in space and time. J. Biol. Phys. 34, 459–474 (2008)
Chaudhuri, S., Roy, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Comparison of plankton dynamics in the ‘presence’ or ‘absence’ of toxic phytoplankton. Appl. Math. Comput. (submitted for publication)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sanjay Chaudhuri has been supported by “MIUR Bando per borse a favore di giovani ricercatori indiani” during his visit at the University of Torino.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhuri, S., Chattopadhyay, J. & Venturino, E. Toxic phytoplankton-induced spatiotemporal patterns. J Biol Phys 38, 331–348 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-011-9251-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-011-9251-7