Abstract
Survivin, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family, is one of the most cancer-specific proteins identified to date. Survivin expression is low or undetectable in most adult tissues, but, alternatively, is overexpressed in a large number of tumors. This multifunctional protein is recognized as a key regulator in apoptosis, proliferation and angiogenesis in the tumor environment. Several studies have shown a correlation between survivin upregulation and poor cancer prognosis, and, as expected, its downregulation or inactivation leads to inhibition of tumor growth. Therefore, survivin has attracted increasing attention both as a potential cancer biomarker and as a new target for anticancer therapies. This review summarizes and discusses survivin expression and its potential as a prognostic and diagnostic biomarker in different types of tumors, as well as provides an overview of the current therapeutic challenges of targeting survivin as a treatment strategy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3(8):917–21.
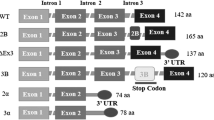
Mahotka C, Wenzel M, Springer E, Gabbert HE, Gerharz CD. Survivin-deltaEx3 and survivin-2B: two novel splice variants of the apoptosis inhibitor survivin with different antiapoptotic properties. Cancer Res. 1999;59(24):6097–102.
Ouhtit A, Matrougui K, Bengrine A, Koochekpour S, Zerfaoui M, Yousief Z. Survivin is not only a death encounter but also a survival protein for invading tumor cells. Front Biosci. 2007;12:1260–70.
Caldas H, Jiang Y, Holloway MP, Fangusaro J, Mahotka C, Conway EM, et al. Survivin splice variants regulate the balance between proliferation and cell death. Oncogene. 2005;24(12):1994–2007.
Moniri Javadhesari S, Gharechahi J, Hosseinpour Feizi MA, Montazeri V, Halimi M. Transcriptional expression analysis of survivin splice variants reveals differential expression of survivin-3α in breast cancer. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2013;17(4):314–20.
Mola G, Vela E, Fernández-Figueras MT, Isamat M, Muñoz-Mármol AM. Exonization of Alu-generated splice variants in the survivin gene of human and non-human primates. J Mol Biol. 2007;366(4):1055–63.
Noton EA, Colnaghi R, Tate S, Starck C, Carvalho A, Ko Ferrigno P, et al. Molecular analysis of survivin isoforms: evidence that alternatively spliced variants do not play a role in mitosis. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(2):1286–95.
Miura K, Fujibuchi W, Unno M. Splice isoforms as therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33(12):2311–9.
Troeger A, Siepermann M, Escherich G, Meisel R, Willers R, Gudowius S, et al. Survivin and its prognostic significance in pediatric acute B-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2007;92(8):1043–50.
Kanwar JR, Kamalapuram SK, Kanwar RK. Survivin signaling in clinical oncology: a multifaceted dragon. Med Res Rev. 2013;33(4):765–89.
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA, Vigna N, Oltersdorf T, et al. IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1998;58(23):5315–20.
Riedl SJ, Shi Y. Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5(11):897–907.
Ryan BM, O’Donovan N, Duffy MJ. Survivin: a new target for anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009;35(7):553–62.
Coumar MS, Tsai F-Y, Kanwar JR, Sarvagalla S, Cheung CHA. Treat cancers by targeting survivin: just a dream or future reality? Cancer Treat Rev. 2013.
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, et al. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 1998;396(6711):580–4.
Blanc-Brude OP, Mesri M, Wall NR, Plescia J, Dohi T, Altieri DC. Therapeutic targeting of the survivin pathway in cancer: initiation of mitochondrial apoptosis and suppression of tumor-associated angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(7):2683–92.
Kawasaki H, Toyoda M, Shinohara H, Okuda J, Watanabe I, Yamamoto T, et al. Expression of survivin correlates with apoptosis, proliferation, and angiogenesis during human colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer. 2001;91(11):2026–32.
Tu SP, Jiang XH, Lin MCM, Cui JT, Yang Y, Lum CT, et al. Suppression of survivin expression inhibits in vivo tumorigenicity and angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63(22):7724–32.
Dean EJ, Ranson M, Blackhall F, Holt SV, Dive C. Novel therapeutic targets in lung cancer: inhibitor of apoptosis proteins from laboratory to clinic. Cancer Treat Rev. 2007;33(2):203–12.
Kawasaki H, Altieri DC, Lu CD, Toyoda M, Tenjo T, Tanigawa N. Inhibition of apoptosis by survivin predicts shorter survival rates in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58(22):5071–4.
Jiang G, Ren B, Xu L, Song S, Zhu C, Ye F. Survivin may enhance DNA double-strand break repair capability by up-regulating Ku70 in human KB cells. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(1):223–8.
Lu CD, Altieri DC, Tanigawa N. Expression of a novel antiapoptosis gene, survivin, correlated with tumor cell apoptosis and p53 accumulation in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998;58(9):1808–12.
Monzó M, Rosell R, Felip E, Astudillo J, Sánchez JJ, Maestre J, et al. A novel anti-apoptosis gene: re-expression of survivin messenger RNA as a prognosis marker in non-small-cell lung cancers. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(7):2100–4.
Sarela AI, Verbeke CS, Ramsdale J, Davies CL, Markham AF, Guillou PJ. Expression of survivin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis and cell cycle regulatory protein, in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;86(6):886–92.
Tanaka K, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Nohara T, Iwamoto M, Tanigawa N. Expression of survivin and its relationship to loss of apoptosis in breast carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000;6(1):127–34.
Chakravarti A, Noll E, Black PM, Finkelstein DF, Finkelstein DM, Dyson NJ, et al. Quantitatively determined survivin expression levels are of prognostic value in human gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(4):1063–8.
Vogel C, Hager C, Bastians H. Mechanisms of mitotic cell death induced by chemotherapy-mediated G2 checkpoint abrogation. Cancer Res. 2007;67(1):339–45.
Altieri DC. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(1):46–54.
Kelly RJ, Lopez-Chavez A, Citrin D, Janik JE, Morris JC. Impacting tumor cell-fate by targeting the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:35.
Hernandez JM, Farma JM, Coppola D, Hakam A, Fulp WJ, Chen D-T, et al. Expression of the antiapoptotic protein survivin in colon cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011;10(3):188–93.
Swana HS, Grossman D, Anthony JN, Weiss RM, Altieri DC. Tumor content of the antiapoptosis molecule survivin and recurrence of bladder cancer. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(6):452–3.
Als AB, Dyrskjøt L, von der Maase H, Koed K, Mansilla F, Toldbod HE, et al. Emmprin and survivin predict response and survival following cisplatin-containing chemotherapy in patients with advanced bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(15 Pt 1):4407–14.
Atlasi Y, Mowla SJ, Ziaee SA-M. Differential expression of survivin and its splice variants, survivin-DeltaEx3 and survivin-2B, in bladder cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 2009;32(4):308–13.
Gonzalez S, Aubert S, Kerdraon O, Haddad O, Fantoni J-C, Biserte J, et al. Prognostic value of combined p53 and survivin in pT1G3 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129(2):232–7.
Kogiku M, Ohsawa I, Matsumoto K, Sugisaki Y, Takahashi H, Teramoto A, et al. Prognosis of glioma patients by combined immunostaining for survivin, Ki-67 and epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15(11):1198–203.
Shirai K, Suzuki Y, Oka K, Noda S, Katoh H, Suzuki Y, et al. Nuclear survivin expression predicts poorer prognosis in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2009;91(3):353–8.
Xu C, Yamamoto-Ibusuki M, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto S, Fujiwara S, Murakami K, et al. High survivin mRNA expression is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer: a comparative study at the mRNA and protein level. Breast Cancer. 2012 [Epub ahead of print].
Petrarca CR, Brunetto AT, Duval V, Brondani A, Carvalho GP, Garicochea B. Survivin as a predictive biomarker of complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage II and stage III breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2011;11(2):129–34.
Yamashita S-I, Masuda Y, Kurizaki T, Haga Y, Murayama T, Ikei S, et al. Survivin expression predicts early recurrence in early-stage breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(4C):2803–8.
Brennan DJ, Rexhepaj E, O’Brien SL, McSherry E, O’Connor DP, Fagan A, et al. Altered cytoplasmic-to-nuclear ratio of survivin is a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008;14(9):2681–9.
Fang YJ, Lu ZH, Wang GQ, Pan ZZ, Zhou ZW, Yun JP, et al. Elevated expressions of MMP7, TROP2, and survivin are associated with survival, disease recurrence, and liver metastasis of colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24(8):875–84.
Kim K, Chie EK, Wu H-G, Kim SG, Lee S-H, Kang GH, et al. High survivin expression as a predictor of poor response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26(8):1019–23.
Takasu C, Shimada M, Kurita N, Iwata T, Sato H, Nishioka M, et al. Survivin expression can predict the effect of chemoradiotherapy for advanced lower rectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2012 [Epub ahead of print].
Brunner A, Riss P, Heinze G, Brustmann H. pHH3 and survivin are co-expressed in high-risk endometrial cancer and are prognostic relevant. Br J Cancer. 2012;107(1):84–90.
Zhu H, Wang Q, Hu C, Zhang W, Quan L, Liu M, et al. High expression of survivin predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma following radiotherapy. Tumour Biol. 2011;32(6):1147–53.
Meng J-R, Tang H-Z, Zhou K-Z, Shen W-H, Guo H-Y. TFF3 and survivin expressions associate with a lower survival rate in gastric cancer. Clin Exp Med. 2012 [Epub ahead of print].
Deng J-Y, Sun D, Liu X-Y, Pan Y, Liang H. STAT-3 correlates with lymph node metastasis and cell survival in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(42):5380–7.
Preuss SF, Weinell A, Molitor M, Stenner M, Semrau R, Drebber U, et al. Nuclear survivin expression is associated with HPV-independent carcinogenesis and is an indicator of poor prognosis in oropharyngeal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(3):627–32.
Semrau R, Duerbaum H, Temming S, Huebbers C, Stenner M, Drebber U, et al. Prognostic impact of human papillomavirus status, survivin, and epidermal growth-factor receptor expression on survival in patients treated with radiochemotherapy for very advanced nonresectable oropharyngeal cancer. Head Neck. 2012 [Epub ahead of print].
Carter BZ, Qiu Y, Huang X, Diao L, Zhang N, Coombes KR, et al. Survivin is highly expressed in CD34(+)38(−) leukemic stem/progenitor cells and predicts poor clinical outcomes in AML. Blood. 2012;120(1):173–80.
Schlette EJ, Medeiros LJ, Goy A, Lai R, Rassidakis GZ. Survivin expression predicts poorer prognosis in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(9):1682–8.
Wang M, Liu B-G, Yang Z-Y, Hong X, Chen G-Y. Significance of survivin expression: prognostic value and survival in stage III non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3(6):983–8.
Nakano J, Huang C, Liu D, Masuya D, Yokomise H, Ueno M, et al. The clinical significance of splice variants and subcellular localisation of survivin in non-small cell lung cancers. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(6):1109–17.
Kren L, Brazdil J, Hermanova M, Goncharuk VN, Kallakury BVS, Kaur P, et al. Prognostic significance of anti-apoptosis proteins survivin and bcl-2 in non-small cell lung carcinomas: a clinicopathologic study of 102 cases. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2004;12(1):44–9.
Dai C-H, Li J, Shi S-B, Yu L-C, Ge L-P, Chen P. Survivin and Smac gene expressions but not livin are predictors of prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010;40(4):327–35.
Shariat SF, Lotan Y, Saboorian H, Khoddami SM, Roehrborn CG, Slawin KM, et al. Survivin expression is associated with features of biologically aggressive prostate carcinoma. Cancer. 2004;100(4):751–7.
Akhtar M, Gallagher L, Rohan S. Survivin: role in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of bladder cancer. Adv Anat Pathol. 2006;13(3):122–6.
Song J, Su H, Zhou Y-Y, Guo L-L. Prognostic value of survivin expression in breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(4):2053–62.
Krieg A, Werner TA, Verde PE, Stoecklein NH, Knoefel WT. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of survivin in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(6):e65338.
Da C-L, Xin Y, Zhao J, Luo X-D. Significance and relationship between Yes-associated protein and survivin expression in gastric carcinoma and precancerous lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(32):4055–61.
Fukuda S, Pelus LM. Survivin, a cancer target with an emerging role in normal adult tissues. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(5):1087–98.
Fulda S. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in hematological malignancies. Leukemia. 2009;23(3):467–76.
Tamm I, Richter S, Oltersdorf D, Creutzig U, Harbott J, Scholz F, et al. High expression levels of x-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and survivin correlate with poor overall survival in childhood de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(11):3737–44.
Adida C, Haioun C, Gaulard P, Lepage E, Morel P, Briere J, et al. Prognostic significance of survivin expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2000;96(5):1921–5.
Adida C, Recher C, Raffoux E, Daniel MT, Taksin AL, Rousselot P, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000;111(1):196–203.
Sugahara K, Uemura A, Harasawa H, Nagai H, Hirakata Y, Tomonaga M, et al. Clinical relevance of survivin as a biomarker in neoplasms, especially in adult T-cell leukemias and acute leukemias. Int J Hematol. 2004;80(1):52–8.
Tröger A, Siepermann M, Mahotka C, Wethkamp N, Bülle H, Laws H-J, et al. Role of survivin splice variants in pediatric acute precursor B lymphoblastic leukemia. Klin Padiatr. 2007;219(3):127–33.
Huang L-N, Wang D-S, Chen Y-Q, Zhao C-L, Gong B-L, Jiang A-B, et al. Expression of survivin and patients survival in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of the published studies. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(2):917–24.
Ku JH, Godoy G, Amiel GE, Lerner SP. Urine survivin as a diagnostic biomarker for bladder cancer: a systematic review. BJU Int. 2012;110(5):630–6.
Wu Y-K, Chen K-T, Kuo Y-B, Huang Y-S, Chan E-C. Quantitative detection of survivin in malignant pleural effusion for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009;273(2):331–5.
Li J, Chen P, Li X-Q, Bao Q-L, Dai C-H, Ge L-P. Elevated levels of survivin and livin mRNA in bronchial aspirates as markers to support the diagnosis of lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(5):1098–104.
Van der Pol E, Böing AN, Harrison P, Sturk A, Nieuwland R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64(3):676–705.
Khan S, Jutzy JMS, Valenzuela MMA, Turay D, Aspe JR, Ashok A, et al. Plasma-derived exosomal survivin, a plausible biomarker for early detection of prostate cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(10):e46737.
Yie S-M, Luo B, Ye N-Y, Xie K, Ye S-R. Detection of Survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in the peripheral blood of breast cancer patients by a RT-PCR ELISA. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2006;23(5–6):279–89.
Yie S, Lou B, Ye S, Cao M, He X, Li P, et al. Detection of survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells (CCCs) in peripheral blood of patients with gastric and colorectal cancer reveals high risks of relapse. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(11):3073–82.
Cao M, Yie S-M, Wu S-M, Chen S, Lou B, He X, et al. Detection of survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in the peripheral blood of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(7):751–8.
Yie S, Lou B, Ye S, He X, Cao M, Xie K, et al. Clinical significance of detecting survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2009;63(2):284–90.
Church DN, Talbot DC. Survivin in solid tumors: rationale for development of inhibitors. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012;14(2):120–8.
Lu J, Tan M, Huang W-C, Li P, Guo H, Tseng L-M, et al. Mitotic deregulation by survivin in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells contributes to Taxol resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(4):1326–34.
Zhang M, Latham DE, Delaney MA, Chakravarti A. Survivin mediates resistance to antiandrogen therapy in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(15):2474–82.
Belyanskaya LL, Hopkins-Donaldson S, Kurtz S, Simões-Wüst AP, Yousefi S, Simon H-U, et al. Cisplatin activates Akt in small cell lung cancer cells and attenuates apoptosis by survivin upregulation. Int J Cancer. 2005;117(5):755–63.
Wall NR, O’Connor DS, Plescia J, Pommier Y, Altieri DC. Suppression of survivin phosphorylation on Thr34 by flavopiridol enhances tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2003;63(1):230–5.
Asanuma K, Moriai R, Yajima T, Yagihashi A, Yamada M, Kobayashi D, et al. Survivin as a radioresistance factor in pancreatic cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2000;91(11):1204–9.
Kappler M, Kotzsch M, Bartel F, Füssel S, Lautenschläger C, Schmidt U, et al. Elevated expression level of survivin protein in soft-tissue sarcomas is a strong independent predictor of survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(3):1098–104.
Hayashi N, Asano K, Suzuki H, Yamamoto T, Tanigawa N, Egawa S, et al. Adenoviral infection of survivin antisense sensitizes prostate cancer cells to etoposide in vivo. Prostate. 2005;65(1):10–9.
Vivas-Mejia PE, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Han H-D, Shahzad MMK, Valiyeva F, Shibayama M, et al. Silencing survivin splice variant 2B leads to antitumor activity in taxane-resistant ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(11):3716–26.
Nakahara T, Yamanaka K, Hatakeyama S, Kita A, Takeuchi M, Kinoyama I, et al. YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, enhances taxane-induced apoptosis and tumor regression in a human Calu 6 lung cancer xenograft model. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22(5):454–62.
Yamanaka K, Nakahara T, Yamauchi T, Kita A, Takeuchi M, Kiyonaga F, et al. Antitumor activity of YM155, a selective small-molecule survivin suppressant, alone and in combination with docetaxel in human malignant melanoma models. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(16):5423–31.
Carrasco RA, Stamm NB, Marcusson E, Sandusky G, Iversen P, Patel BKR. Antisense inhibition of survivin expression as a cancer therapeutic. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(2):221–32.
Zaffaroni N, Daidone MG. Survivin expression and resistance to anticancer treatments: perspectives for new therapeutic interventions. Drug Resist Updat. 2002;5(2):65–72.
Dash P, Lotan I, Knapp M, Kandel ER, Goelet P. Selective elimination of mRNAs in vivo: complementary oligodeoxynucleotides promote RNA degradation by an RNase H-like activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84(22):7896–900.
Talbot DC, Ranson M, Davies J, Lahn M, Callies S, André V, et al. Tumor survivin is downregulated by the antisense oligonucleotide LY2181308: a proof-of-concept, first-in-human dose study. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(24):6150–8.
Tanioka M, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Goto Y, et al. Phase I study of LY2181308, an antisense oligonucleotide against survivin, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;68(2):505–11.
Erba HP, Sayar H, Juckett M, Lahn M, Andre V, Callies S, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of the antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) LY2181308 as a single-agent or in combination with idarubicin and cytarabine in patients with refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Invest New Drugs. 2013;31(4):1023–34.
Nakahara T, Kita A, Yamanaka K, Mori M, Amino N, Takeuchi M, et al. Broad spectrum and potent antitumor activities of YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, in a wide variety of human cancer cell lines and xenograft models. Cancer Sci. 2011;102(3):614–21.
Iwasa T, Okamoto I, Takezawa K, Yamanaka K, Nakahara T, Kita A, et al. Marked anti-tumour activity of the combination of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, and platinum-based drugs. Br J Cancer. 2010;103(1):36–42.
Nakahara T, Kita A, Yamanaka K, Mori M, Amino N, Takeuchi M, et al. YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, induces regression of established human hormone-refractory prostate tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2007;67(17):8014–21.
Tolcher AW, Mita A, Lewis LD, Garrett CR, Till E, Daud AI, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of YM155, a small-molecule inhibitor of survivin. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(32):5198–203.
Satoh T, Okamoto I, Miyazaki M, Morinaga R, Tsuya A, Hasegawa Y, et al. Phase I study of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(11):3872–80.
Cheson BD, Bartlett NL, Vose JM, Lopez-Hernandez A, Seiz AL, Keating AT, et al. A phase II study of the survivin suppressant YM155 in patients with refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 2012;118(12):3128–34.
Giaccone G, Zatloukal P, Roubec J, Floor K, Musil J, Kuta M, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of YM155, a small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in patients with advanced, refractory, non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(27):4481–6.
Lewis KD, Samlowski W, Ward J, Catlett J, Cranmer L, Kirkwood J, et al. A multi-center phase II evaluation of the small molecule survivin suppressor YM155 in patients with unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29(1):161–6.
Holmes D. Cancer drug’s survivin suppression called into question. Nat Med. 2012;18(6):842–3.
Arora R, Shuda M, Guastafierro A, Feng H, Toptan T, Tolstov Y, et al. Survivin is a therapeutic target in Merkel cell carcinoma. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(133):133ra56.
Acknowledgments
No sources of funding were used to prepare this manuscript.
Disclosures
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guindalini, R.S.C., Mathias Machado, M.C. & Garicochea, B. Monitoring Survivin Expression in Cancer: Implications for Prognosis and Therapy. Mol Diagn Ther 17, 331–342 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-013-0048-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-013-0048-1