Abstract
Survivin is a 16.5 kDa protein that functions to inhibit apoptosis, promote proliferation, and enhance invasion. Absent in most adult tissues, survivin is selectively upregulated in many human tumors, where its overexpression correlates with poor outcome and treatment resistance. Consequently, survivin is a promising target for cancer therapy. Preclinical data demonstrate that survivin inhibition reduces cell proliferation, increases apoptosis, and sensitises cells to cytotoxic agents and radiotherapy. The pharmacological survivin inhibitors LY2181308 and YM155 have demonstrated acceptable toxicity and evidence of therapeutic efficacy as single agents in early-phase clinical trials. Current efforts seek to define the optimum use of survivin inhibitors in combination with cytotoxic therapies, where it is hoped that preclinical evidence of treatment synergy will translate into improved therapeutic efficacy. Results from these ongoing studies are keenly awaited.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: •Of importance ••Of major importance
Altieri DC. New wirings in the survivin networks. Oncogene. 2008;27:6276–84.
• Altieri DC. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:61-70. Excellent review which presents an elegant summary of current knowledge of survivin biology.
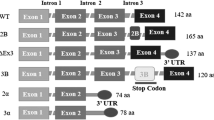
Caldas H, Honsey LE, Altura RA. Survivin 2alpha: a novel Survivin splice variant expressed in human malignancies. Mol Cancer. 2005;4:11.
Badran A, Yoshida A, Ishikawa K, et al. Identification of a novel splice variant of the human anti-apoptopsis gene survivin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;314:902–7.
Mahotka C, Wenzel M, Springer E, Gabbert HE, Gerharz CD. Survivin-deltaEx3 and survivin-2B: two novel splice variants of the apoptosis inhibitor survivin with different antiapoptotic properties. Cancer Res. 1999;59:6097–102.
Adida C, Crotty PL, McGrath J, Berrebi D, Diebold J, Altieri DCC. Developmentally regulated expression of the novel cancer anti-apoptosis gene survivin in human and mouse differentiation. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:43–9.
Uren AG, Wong L, Pakusch M, et al. Survivin and the inner centromere protein INCENP show similar cell-cycle localization and gene knockout phenotype. Curr Biol. 2000;10:1319–28.
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3:917–21.
Zhang T, Otevrel T, Gao Z, Ehrlich SM, Fields JZ, Boman BM. Evidence that APC regulates survivin expression: a possible mechanism contributing to the stem cell origin of colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:8664–7.
Fukuda S, Pelus LM. Regulation of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis family member survivin in normal cord blood and bone marrow CD34(+) cells by hematopoietic growth factors: implication of survivin expression in normal hematopoiesis. Blood. 2001;98:2091–100.
Gianani R, Jarboe E, Orlicky D, et al. Expression of survivin in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic colonic mucosa. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:119–25.
Fukuda S, Pelus LM. Survivin, a cancer target with an emerging role in normal adult tissues. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:1087–98.
Altieri DC. The case for survivin as a regulator of microtubule dynamics and cell-death decisions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:609–15.
Lens SM, Vader G, Medema RH. The case for Survivin as mitotic regulator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:616–22.
Aoki Y, Feldman GM, Tosato G. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood. 2003;101:1535–42.
Vaira V, Lee CW, Goel HL, Bosari S, Languino LR, Altieri DC. Regulation of survivin expression by IGF-1/mTOR signaling. Oncogene. 2007;26:2678–84.
Oh SH, Jin Q, Kim ES, Khuri FR, Lee HY. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway induces resistance to the apoptotic activities of SCH66336 (lonafarnib) through Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated increases in survivin expression. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1581–9.
Zhao J, Tenev T, Martins LM, Downward J, Lemoine NR. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway regulates survivin degradation in a cell cycle-dependent manner. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 23):4363–71.
Vong QP, Cao K, Li HY, Iglesias PA, Zheng Y. Chromosome alignment and segregation regulated by ubiquitination of survivin. Science. 2005;310:1499–504.
O’Connor DS, Wall NR, Porter AC, Altieri DC. A p34(cdc2) survival checkpoint in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:43–54.
Wheatley SP, Barrett RM, Andrews PD, et al. Phosphorylation by aurora-B negatively regulates survivin function during mitosis. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:1220–30.
Dohi T, Xia F, Altieri DC. Compartmentalized phosphorylation of IAP by protein kinase A regulates cytoprotection. Mol Cell. 2007;27:17–28.
Verdecia MA, Huang H, Dutil E, Kaiser DA, Hunter T, Noel JP. Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:602–8.
Chantalat L, Skoufias DA, Kleman JP, Jung B, Dideberg O, Margolis RL. Crystal structure of human survivin reveals a bow tie-shaped dimer with two unusual alpha-helical extensions. Mol Cell. 2000;6:183–9.
Jeyaprakash AA, Klein UR, Lindner D, Ebert J, Nigg EA, Conti E. Structure of a Survivin-Borealin-INCENP core complex reveals how chromosomal passengers travel together. Cell. 2007;131:271–85.
Kang BH, Altieri DC. Regulation of survivin stability by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-interacting protein. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24721–7.
Fortugno P, Beltrami E, Plescia J, et al. Regulation of survivin function by Hsp90. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:13791–6.
Altieri DC. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:46–54.
Riedl SJ, Shi Y. Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:897–907.
Altieri DC. Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22:8581–9.
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, et al. IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5315–20.
Banks DP, Plescia J, Altieri DC, et al. Survivin does not inhibit caspase-3 activity. Blood. 2000;96:4002–3.
Li C, Wu Z, Liu M, Pazgier M, Lu W. Chemically synthesized human survivin does not inhibit caspase-3. Protein Sci. 2008;17:1624–9.
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS, Scott FL. Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep. 2006;7:988–94.
Marusawa H, Matsuzawa S, Welsh K, et al. HBXIP functions as a cofactor of survivin in apoptosis suppression. EMBO J. 2003;22:2729–40.
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, et al. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 1998;396:580–4.
Yang D, Welm A, Bishop JM. Cell division and cell survival in the absence of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:15100–5.
Bolton MA, Lan W, Powers SE, McCleland ML, Kuang J, Stukenberg PTC. Aurora B kinase exists in a complex with survivin and INCENP and its kinase activity is stimulated by survivin binding and phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13:3064–77.
Wheatley SP, Carvalho A, Vagnarelli P, Earnshaw WC. INCENP is required for proper targeting of Survivin to the centromeres and the anaphase spindle during mitosis. Curr Biol. 2001;11:886–90.
Sampath SC, Ohi R, Leismann O, Salic A, Pozniakovski A, Funabiki H. The chromosomal passenger complex is required for chromatin-induced microtubule stabilization and spindle assembly. Cell. 2004;118:187–202.
Sandall S, Severin F, McLeod IX, et al. A Bir1-Sli15 complex connects centromeres to microtubules and is required to sense kinetochore tension. Cell. 2006;127:1179–91.
Rosa J, Canovas P, Islam A, Altieri DC, Doxsey SJ. Survivin modulates microtubule dynamics and nucleation throughout the cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:1483–93.
Ghosh JC, Dohi T, Raskett CM, Kowalik TF, Altieri DC. Activated checkpoint kinase 2 provides a survival signal for tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11576–9.
O’Connor DS, Schechner JS, Adida C, et al. Control of apoptosis during angiogenesis by survivin expression in endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:393–8.
Tran J, Master Z, Yu JL, Rak J, Dumont DJ, Kerbel RS. A role for survivin in chemoresistance of endothelial cells mediated by VEGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:4349–54.
Zwerts F, Lupu F, De Vriese A, et al. Lack of endothelial cell survivin causes embryonic defects in angiogenesis, cardiogenesis, and neural tube closure. Blood. 2007;109:4742–52.
• Mehrotra S, Languino LR, Raskett CM, Mercurio AM, Dohi T, Altieri DC. IAP regulation of metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:53-64. Exciting paper demonstrating new role for survivin in promotion of tumor invasion and metastasis.
Velculescu VE, Madden SL, Zhang L, et al. Analysis of human transcriptomes. Nat Genet. 1999;23:387–8.
Adida C, Berrebi D, Peuchmaur M, Reyes-Mugica M, Altieri DC. Anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, and prognosis of neuroblastoma. Lancet. 1998;351:882–3.
Chakravarti A, Noll E, Black PM, et al. Quantitatively determined survivin expression levels are of prognostic value in human gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1063–8.
Lu CD, Altieri DC, Tanigawa N. Expression of a novel antiapoptosis gene, survivin, correlated with tumor cell apoptosis and p53 accumulation in gastric carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1808–12.
Monzo M, Rosell R, Felip E, et al. A novel anti-apoptosis gene: Re-expression of survivin messenger RNA as a prognosis marker in non-small-cell lung cancers. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2100–4.
Tanaka K, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Nohara T, Iwamoto M, Tanigawa N. Expression of survivin and its relationship to loss of apoptosis in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:127–34.
Kawasaki H, Altieri DC, Lu CD, Toyoda M, Tenjo T, Tanigawa N. Inhibition of apoptosis by survivin predicts shorter survival rates in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5071–4.
Cohen C, Lohmann CM, Cotsonis G, Lawson D, Santoianni R. Survivin expression in ovarian carcinoma: correlation with apoptotic markers and prognosis. Mod Pathol. 2003;16:574–83.
Sarela AI, Verbeke CS, Ramsdale J, Davies CL, Markham AF, Guillou PJC. Expression of survivin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis and cell cycle regulatory protein, in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;86:886–92.
Grabowski P, Kuhnel T, Muhr-Wilkenshoff F, et al. Prognostic value of nuclear survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:115–9.
Nasr MR, El-Zammar O. Comparison of pHH3, Ki-67, and survivin immunoreactivity in benign and malignant melanocytic lesions. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:117–22.
Hoffman WH, Biade S, Zilfou JT, Chen J, Murphy M. Transcriptional repression of the anti-apoptotic survivin gene by wild type p53. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:3247–57.
Guha M, Plescia J, Leav I, Li J, Languino LR, Altieri DC. Endogenous tumor suppression mediated by PTEN involves survivin gene silencing. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4954–8.
Jiang Y, Saavedra HI, Holloway MP, Leone G, Altura RA. Aberrant regulation of survivin by the RB/E2F family of proteins. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:40511–20.
Wang RH, Zheng Y, Kim HS, et al. Interplay among BRCA1, SIRT1, and Survivin during BRCA1-associated tumorigenesis. Mol Cell. 2008;32:11–20.
Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich M, Dohoney K, et al. Gene expression profiling of ATL patients: compilation of disease-related genes and evidence for TCF4 involvement in BIRC5 gene expression and cell viability. Blood. 2009;113:4016–26.
Nguyen HG, Ravid K. Tetraploidy/aneuploidy and stem cells in cancer promotion: The role of chromosome passenger proteins. J Cell Physiol. 2006;208:12–22.
Vogel C, Hager C, Bastians H. Mechanisms of mitotic cell death induced by chemotherapy-mediated G2 checkpoint abrogation. Cancer Res. 2007;67:339–45.
Goga A, Yang D, Tward AD, Morgan DO, Bishop JM. Inhibition of CDK1 as a potential therapy for tumors over-expressing MYC. Nat Med. 2007;13:820–7.
You L, He B, Xu Z, et al. Inhibition of Wnt-2-mediated signaling induces programmed cell death in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:6170–4.
Sommer KW, Schamberger CJ, Schmidt GE, Sasgary S, Cerni C. Inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) survivin is upregulated by oncogenic c-H-Ras. Oncogene. 2003;22:4266–80.
Guha M, Xia F, Raskett CM, Altieri DC. Caspase 2-mediated tumor suppression involves survivin gene silencing. Oncogene. 2010;29:1280–92.
Shinohara ET, Gonzalez A, Massion PP, et al. Nuclear survivin predicts recurrence and poor survival in patients with resected nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103:1685–92.
Islam A, Kageyama H, Takada N, et al. High expression of Survivin, mapped to 17q25, is significantly associated with poor prognostic factors and promotes cell survival in human neuroblastoma. Oncogene. 2000;19:617–23.
Kato J, Kuwabara Y, Mitani M, et al. Expression of survivin in esophageal cancer: correlation with the prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2001;95:92–5.
Zhang M, Latham DE, Delaney MA, Chakravarti A. Survivin mediates resistance to antiandrogen therapy in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:2474–82.
Lu J, Tan M, Huang WC, et al. Mitotic deregulation by survivin in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells contributes to Taxol resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:1326–34.
Wall NR, O’Connor DS, Plescia J, Pommier Y, Altieri DC. Suppression of survivin phosphorylation on Thr34 by flavopiridol enhances tumor cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:230–5.
Kappler M, Bache M, Bartel F, et al. Knockdown of survivin expression by small interfering RNA reduces the clonogenic survival of human sarcoma cell lines independently of p53. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;11:186–93.
Grossman D, McNiff JM, Li F, Altieri DC. Expression and targeting of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 1999;113:1076–81.
Yamanaka K, Nakata M, Kaneko N, et al. YM155, a selective survivin suppressant, inhibits tumor spread and prolongs survival in a spontaneous metastatic model of human triple negative breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2011;39:569–75.
Blanc-Brude OP, Mesri M, Wall NR, Plescia J, Dohi T, Altieri DC. Therapeutic targeting of the survivin pathway in cancer: initiation of mitochondrial apoptosis and suppression of tumor-associated angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:2683–92.
Hayashi N, Asano K, Suzuki H, et al. Adenoviral infection of survivin antisense sensitizes prostate cancer cells to etoposide in vivo. Prostate. 2005;65:10–9.
Vivas-Mejia PE, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Han HD, et al. Silencing survivin splice variant 2B leads to antitumor activity in taxane-resistant ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:3716–26.
Iwasa T, Okamoto I, Takezawa K, et al. Marked anti-tumour activity of the combination of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, and platinum-based drugs. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:36–42.
Nakahara T, Yamanaka K, Hatakeyama S, et al. YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, enhances taxane-induced apoptosis and tumor regression in a human Calu 6 lung cancer xenograft model. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22:454–62.
Yamanaka K, Nakahara T, Yamauchi T, et al. Antitumor Activity of YM155, a Selective Small-Molecule Survivin Suppressant, Alone and in Combination with Docetaxel in Human Malignant Melanoma Models. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5423–31.
Carrasco RA, Stamm NB, Marcusson E, Sandusky G, Iversen P, Patel BK. Antisense inhibition of survivin expression as a cancer therapeutic. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:221–32.
•• Talbot DC, Ranson M, Davies J, et al. Tumor survivin is downregulated by the antisense oligonucleotide LY2181308: a proof-of-concept, first-in-human dose study. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:6150-6158. Phase I, proof-of-principle study of survivin inhibition with LY2181308, showing acceptable toxicity and confirming target inhibtion.
Tanioka M, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, et al. Phase I study of LY2181308, an antisense oligonucleotide against survivin, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;68:505–11.
Hansen JB, Fisker N, Westergaard M, et al. SPC3042: a proapoptotic survivin inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:2736–45.
Nakahara T, Takeuchi M, Kinoyama I, et al. YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, induces regression of established human hormone-refractory prostate tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8014–21.
•• Tolcher AW, Mita A, Lewis LD, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of YM155, a small-molecule inhibitor of survivin. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5198-5203. Phase I study of YM155 in humans showing acceptable toxicity and therapeutic efficacy in heavily pretreated patients.
Satoh T, Okamoto I, Miyazaki M, et al. Phase I study of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:3872–80.
Giaccone G, Zatloukal P, Roubec J, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of YM155, a small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in patients with advanced, refractory, non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4481–6.
Chang CC, Heller JD, Kuo J, Huang RC. Tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid induces growth arrest and cellular apoptosis by inhibiting Cdc2 and survivin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:13239–44.
Khanna N, Dalby R, Tan M, Arnold S, Stern J, Frazer N. Phase I/II clinical safety studies of terameprocol vaginal ointment. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;107:554–62.
Andersen MH, Pedersen LO, Becker JC, Straten PT. Identification of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to the apoptosis inhibitor protein survivin in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001;61:869–72.
Andersen MH, Pedersen LO, Capeller B, Brocker EB, Becker JC, thor Straten P. Spontaneous cytotoxic T-cell responses against survivin-derived MHC class I-restricted T-cell epitopes in situ as well as ex vivo in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5964–8.
Andersen MH, Soerensen RB, Becker JC. thor Straten P. HLA-A24 and survivin: possibilities in therapeutic vaccination against cancer. J Transl Med. 2006;4:38.
Plescia J, Salz W, Xia F, et al. Rational design of shepherdin, a novel anticancer agent. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:457–68.
Siegelin MD, Plescia J, Raskett CM, Gilbert CA, Ross AH, Altieri DC. Global targeting of subcellular heat shock protein-90 networks for therapy of glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9:1638–46.
Herrington WG, Talbot DC, Lahn MM, et al. Association of long-term administration of the survivin mRNA-targeted antisense oligonucleotide LY2181308 with reversible kidney injury in a patient with metastatic melanoma. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57:300–3.
Acknowledgment
Dr. Church and Dr. Talbot acknowledge financial support from Cancer Research UK.
Disclosure
D. N. Church: none; D. C. Talbot: advisory board member for Lilly UK, and honoraria and an unrestricted research grant from Lilly UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Church, D.N., Talbot, D.C. Survivin in Solid Tumors: Rationale for Development of Inhibitors. Curr Oncol Rep 14, 120–128 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-012-0215-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-012-0215-2