Abstracts
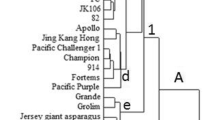
Table top banana (AAA) and cooking type plantines (BBB/ABB) are cultivated commercially for high yield and lucrative market value. Morphological similarities among the banana clones make identification difficult under field conditions. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and inter-retrotransposon amplified polymorphism (IRAP), were used to characterize genetic variations among 21 banana germplasm. IRAP primers were designed to determine ‘AA’ and ‘BB’ specific markers on the basis of repetitive and genome-wide dispersed long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons. RAPD markers successfully detected genetic variation between genotypes. IRAP markers amplified either by a single primer or a combination of primers, based on LTR orientation, successfully amplified different retrotransposons dispersed in the Musa genome. The average level of polymorphism exhibited by RAPD and IRAP markers were 71.47 % and 81.3 % respectively that suggests substantial genetic variations among the tested varieties. All the 12 table-top varieties were clustered together while four cooking varieties i.e. Bantala-I, Bantala-II, Dakhkhnisagar and Athiakol with ‘BB’ formed a distinct group. These results suggested that IRAP markers were found more robust than RAPD markers to study the intra-group genetic diversity between table top and cooking banana.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nair AS, Teo CH, Schwarzacher T, Pat Heslop Harrison JS (2005) Genome classification of banana cultivars from South India using IRAP markers. Euphytica 144:285–290
FAO (2014) Banana market review and banana statistics 2012–2013., Rome, pp.1–33
Saraswathi MS, Uma S, Selvam KP, Ramaraj S, Durai P, Mustaffa MM (2011) Assessing the robustness of IRAP and RAPD marker systems to study intra-group diversity among Cavendish (AAA) clones of banana. J Hortic Sci Biotech 86:7–12
D’Hont A, Denoeud F, Aury J-M, Baurens F-C, Carreel F, Garsmeur O, Noel B, Bocs S, Droc G, Rouard M et al (2012) The banana (Musa acuminata) genome and the evolution of monocotyledonous plants. Nature 488:213–217
Finnegan DJ (1992) Transposable elements. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2:861–867
Vicient CM, Kalendar R, Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Schulman AH (1999) Structure, functionality, and evolution of the BARE-1 retrotransposon of barley. Genetica 107:53–63
Meyers BC, Tingey SV, Morgante M (2001) Abundance, distribution, and transcriptional activity of repetitive elements in the maize genome. Genome Res 11:1660–1676
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Annu Rev Genet 33:479–532
Kalendar R, Tanskanen J, Immonen S, Nevo E, Schulman AH (2000) Genome evolution of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) by BARE-1 retrotransposon dynamics in response to sharp microclimatic divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6603–6607
Pearce SR, Pich U, Harrison G, Flavell AJ, Heslop-Harrison JS, Schubert I, Kumar A (1996) The Ty1-copia group retrotransposons of Allium cepa are distributed throughout the chromosomes but are enriched in the terminal heterochromatin. Chromosome Res 4:357–364
Todorovska E (2007) Retrotransposons and their role in plant—genome evolution. Biotechnol Biotechnol Eq 21(3):294–305
Flavell AJ, Dunbar E, Anderson R, Pearce SR, Hartley R, Kumar A (1992) Tyl-copia group retrotransposons are ubiquitous and heterogeneous in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res 20(14):3639–3644
Bhat KV, Jarret RL (1995) Random amplified polymorphic DNA and genetic diversity in Indian Musa germplasm. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42:107–118
Chen HB, Wang QJ, Qin YH, Zhang GA, Hu GB (2011) Study on the genetic relationship of 35 cavendish Banana (Musa AAA) varieties by RAPD molecular marker. Acta Hort (ISHS) 894:97–104
Mukunthakumar S, Padmesh P, Vineesh PS, Skaria R, Kumar KH, Krishnan PN (2013) Genetic diversity and differentiation analysis among wild antecedents of Banana (Musa acuminata Colla) using RAPD markers. IJBT 12(4):493–498
Lassois L, Frettinger P, de Ballaire LL, Lepoivre P, Jijakli H (2011) Identification of genes involved in the response of banana to crown root disease. MBMI 24(1):143–153
Gawel NJ, Jarret RL, Whittemore AP (1992) Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-based phylogenetic analysis of Musa. Theor Appl Genet 84(3–4):286–290
Jarret RL, Gawel N, Whittemore A, Sharrock S (1992) RFLP-based phylogeny of Musa species in Papua New Guinea. Theor Appl Genet 84(5–6):579–584
Nwakanma DC, Pillay M, Okoli BE, Tenkouano A (2003) PCR-RFLP of the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers (ITS) provides markers for the A and B genomes in Musa L. Theor Appl Genet 108(1):154–159
Raboin LM, Carreel F, Noyer JL, Baurens FC, Horry JP, Bakry F, Du Montcel HT, Ganry J, Lanaud C, Lagoda PJL (2005) Diploid ancestors of triploid export Banana cultivars: molecular identification of 2n restitution gamete donors and n gamete donors. Mol Breed 16(4):333–341
Ning SP, Xu LB, Lu Y, Huang BZ, Ge XJ (2007) Genome composition and genetic diversity of Musa germplasm from China revealed by PCR-RFLP and SSR Markers. Sci Hortic 114(4):281–288
Kalendar R, Grob T, Regina M, Suoniemi A, Schulman I (1999) IRAP and REMAP: two new retrotransposon-based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theor Appl Genet 98:704–711
Branco CJS, Vieira EA, Malone G, Kopp MM, Malone E, Bernardes A, Mistura CC, Carvalho FIF, Oliveira CA (2007) IRAP and REMAP assessments of genetic similarity in rice. J Appl Genet 48:107–113
Smykal P (2006) Development of an efficient retrotransposon-based fingerprinting method for rapid pea variety identification. J Appl Genet 47:221–230
Guo D, Zhang H, Luo Z (2006) Genetic relationships of Diospyros kaki Thunb. and related species revealed by IRAP and REMAP analysis. Plant Sci 170:528–533
Teo CH, Tan SH, Othman YR, Schwarzacher T (2002) The cloning of Ty1-copia-like retrotransposons from 10 varieties of banana (Musa sp.). J Biochem Mol Biol Biophys 6:193–201
Alavi-Kia SS, Mohammadi SA, Aharizad S, Moghaddam M (2008) Analysis of genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships in Crocus genus of Iran using inter-retrotransposon amplified polymorphism. Biotechnol Biotechnol Eq 22:795–800
Achrem M, Rogalska SM, Kalinka A (2010) Possible ancient origin of heterochromatic JNK sequences in chromosome 2R of Secale vavilovii Grossh. J Appl Genet 51:1–8
Schmidt T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1996) The physical and genomic organization of microsatellites in sugar beet. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8761–8765
Cuadrado A, Schwarzacher T, Jouve N (2000) Identification of different chromatin classes in wheat using in situ hybridization with simple sequence repeat oligonucleotides. Theor Appl Genet 101:711–717
Camacho MV, Matos M, Gonzales C, Perez-Flores V, Pernauta B, Pinto-Carnida O, Benito C (2005) Secale cereale intermicrosatellites (SCIMs): chromosomal location and genetic inheritance. Genetica 123:303–311
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Teo CH, Tan SH, Ho CH, Faridah QZ, Othman YR, Heslop-Harrison JS, Kalendar R, Schulman AH (2005) Genome constitution and classification using retrotransposon-based markers in the orphan crop banana. J Plant Biol 48(1):96–105
Williams JGK, Kuhelik AR, Liuak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful a genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Rohlf FJ (1993) NTSYS-pc. Numerical and reproductive adaptations of Australian mangroves. In: Chapman VJ (ed) Ecosystems of the world. Vol. 1: Wet Coastal Ecosystems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 232–238
Sneath PHA, Sokal R (1973) Numerical taxonomy. Freeman, San Francisco
Kalendar R, Vicient CM, Peleg O, Anamthawat-Jonsson K, Bolshoy A, Schulman AH (2004) Large retrotransposon derivatives: abundant, conserved but nonautonomous retroelements of barley and related genomes. Genetics 166:1437–1450
Bernet GP, Asins MJ (2004) Identification and genomic distribution of gypsy like retrotransposons in Citrus and Poncirus. Theor Appl Genet 108:121–130
Boronnikova SV, Kalendar RN (2010) Using IRAP markers for analysis of genetic variability in populations of resource and rare species of plants. Russ J Genet 46(1):36–42
Cuadrado A, Jouve N (2002) Evolutionary trends of different repetitive DNA sequences during speciation in the genus Secale. J Hered 93:339–345
Achrem M, Rogalska SM (2006) Localization specific nucleotide sequences of DNA on rye chromosomes by FISH. Agricultura 247:7–14
Shang HY, Wei YM, Wang XR, Zheng YL (2006) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships in the rye genus Secale L. (rye) based on Secale cereale microsatellite markers. Genet Mol Biol 29:685–691
Ren TH, Chen F, Zou YT, Jia YH, Zhang HQ, Yan BJ, Ren ZL (2011) Evolutionary trends of microsatellites during the speciation process and phylogenetic relationships within the genus Secale. Genome 54:316–326
De Bustos A, Jouve N (2002) Phylogenetic relationships of the genus Secale based on the characterization of rDNA ITS sequences. Plant Syst Evol 235:147–154
Acknowledgments
Financial support to Rahul Gunvantrao Shelke by Post Graduate HRD programme, Department of Biotechnology, Government of India is highly acknowledged. The authors are grateful to Professor J. S. (Pat) Heslop-Harrison, Department of Biology, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 7RH UK for his valuable advice time to time for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shelke, R.G., Das, A.B. Analysis of Genetic Diversity in 21 Genotypes of Indian Banana Using RAPDs and IRAPs Markers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 85, 1027–1038 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0505-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-015-0505-1