Abstract
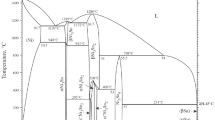
Ni/Ni-Sn/Ni sandwiched simulated package structures were successfully bonded under low temperature and low pressure by Ni-Sn transient liquid-phase sintering bonding. The results show that, after isothermally holding for 240 min at 300 °C and 180 min at 340 °C, Sn was completely transformed into Ni3Sn4 intermetallic compounds. When the Ni3Sn4 phases around Ni particles were pressed together, the porosity of the bonding layer increased, which obviously differed from the normal sintering densification process. With further analysis of this phenomenon, it was found that large volume shrinkage (14.94% at 340 °C) occurred when Ni reacted with Sn to form Ni3Sn4, which caused void formation. A mechanistic model of the microstructural evolution in the bonding layer was proposed. Meanwhile, the resistivity of the bonding layer was measured and analyzed by using the four-probe method; the microstructural evolution was well reflected by the resistivity of the bonding layer. The relationship between the resistivity and microstructure was also discussed in detail.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Iwasaki, Y. Hoshino, K. Tsuzuki, H. Kato, T. Makino, M. Ogura, D. Takeuchi, H. Okushi, S. Yamasaki, and M. Hatano, IEEE Electr. Dev. L. 34, 1175 (2013).
P. G. Neudeck, S. L. Garverick, D. J. Spry, L. Y. Chen, G. M. Beheim, M. J. Krasowski, and M. Mehregany, Phys. Status Solidi A. 206, 2329 (2009).
D. Maier, M. Alomari, N. Grandjean, J. Carlin, M. Diforte-Poisson, C. Dua, S. Delage, and E. Kohn, IEEE Electr. Dev. L. 33, 985 (2012).
N. S. Bosco and F. W. Zok, Acta Mater. 53, 2019 (2005).
T. Luu, A. Duan, K. E. Aasmundtvit, and N. Hoivik, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 3582 (2013).
T. A. Tollefsen, A. Larsson, M. M. V. Taklo, A. Neels, X. Maeder, K. Høydalsvik, D. W. Breiby, and K. Aasmundtveit, Metall. Mater. Trans B. 44B, 407 (2013).
Z. Pešina, V. Vykoukal, M. Palcut, and J. Sopoušek, Electron. Mater Lett. 10, 293 (2014).
J. Bultitude, J. McConnell, and C. Shearer, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 26, 9236 (2015).
P. O. Quintero and F. P. McCluskey, IMPAS J. Microelectron. Electron. Packag. 6, 66 (2009).
H. Greve, L. Y. Chen, I. Fox, and F. P. McCluskey, Proceedings of the 63rd Electronic Components & Technology Conference (ECTC), p. 435, IEEE, Las Vegas, USA (2013).
F. Q. Lang, H. Yamaguchi, H. Nakagawa, and H. Sato, J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, 315 (2013).
T. D’hondt and S. F. Corbin, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 37A, 217 (2006).
I. Ohnuma, R. Kainuma, and K. Ishida, J. Min. Metall. B. 48, 413 (2012).
H. Okamoto, J. Phase Equilib. Diff. 27, 535 (2006).
N. Saunders and A. Miodownik, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams. 11, 278 (1990).
I. Karakaya and W. Thompson, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams. 8, 340 (1987).
H. L. Feng, J. H. Huang, J. Zhang, and X. D. Zhai, Proceedings of the 17th Electronics Packaging and Technology Conference (EPTC). p. 1, IEEE, Singapore (2015).
H. Okamoto, J. Phase Equilib. Diff. 29, 297 (2008).
R. M. German, P. Suri, and S. J. Park, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1 (2009).
J. A. van Beek, S. A. Stolk, and F. J. J. van Loo, Z. Metallkde. 73, 441 (1982).
C. Ghosh, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 24, 2558 (2013).
C. E. Ho, S. C. Yang, and C. R. Kao, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 18, 155 (2007).
M. J. Assael, A. E. Kalyva, K. D. Antoniadis, R. Michael Banish, I. Egry, J. Wu, E. Kaschnitz, and W. A. Wakeham, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data. 39, 033105 (2010).
H. Preston-Thomas, Metrologia 27, 3 (1990).
H. P. R. Frederikse, R. J. Fields, and A. Felsman, J. Appl. Phys. 72, 2879 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, HL., Huang, JH., Yang, J. et al. Investigation of microstructural evolution and electrical properties for Ni-Sn transient liquid-phase sintering bonding. Electron. Mater. Lett. 13, 489–496 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-017-6317-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-017-6317-0