Abstract
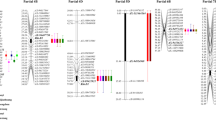
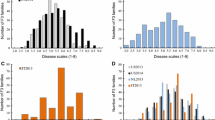
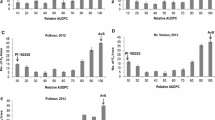
Agriculture will benefit from a rigorous characterization of genes for adult plant resistance (APR) since this gene class was recognized to provide more durable protection from plant diseases. The present study reports the identification of APR loci to powdery mildew in German winter wheat cultivars Cortez and Atlantis. Cortez was previously shown to carry all-stage resistance gene Pm3e. To avoid interference of Pm3e in APR studies, line 6037 that lacked Pm3e but showed field resistance from doubled-haploid (DH) population Atlantis/Cortez was used in two backcrosses to Atlantis for the establishment of DH population 6037/Atlantis//Atlantis. APR was assessed in the greenhouse 10, 15, and 20 days after inoculation (dai) from the 4-leaf stage onwards and combined with single-nucleotide polymorphism data in a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and a linkage map-based quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis. In GWAS, two QTL were detected: one on chromosome 1BL 10 dai, the other on chromosome 2BL 20 dai. In conventional QTL analysis, both QTL were detected with all three disease ratings: the QTL on chromosome 1BL explained a maximum of 35.2% of the phenotypic variation 10 dai, whereas the QTL on chromosome 2BL explained a maximum of 43.5% of the phenotypic variation 20 dai. Compared with GWAS, linkage map-based QTL analysis allowed following the dynamics of QTL action. The two large-effect QTL for APR to powdery mildew with dynamic gene action can be useful for the enhancement of wheat germplasm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo-Garcia J, Spencer D, Thieron H, Reinstadler A, Hammond-Kosack K, Phillips AL, Panstruga R (2017) mlo-based powdery mildew resistance in hexaploid bread wheat generated by a non-transgenic TILLING approach. Plant Biotechnol J 15:367–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12631
Anonymous (2004) Beschreibende Sortenliste. Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag GmbH, Hannover
Anonymous (2018) Judgment of the court of justice in case C-528/16. https://curia.europa.eu/jcms/upload/docs/application/pdf/2018-07/cp180111en.pdf. Accessed 11 Feb 2019
Asad MA, Bai B, Lan C, Yan J, Xia X, Zhang Y, He Z (2014) Identification of QTL for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat landrace Pingyuan 50. Crop J 2:308–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2014.04.009
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bender CM, Prins R, Pretorius ZA (2016) Development of a greenhouse screening method for adult plant response in wheat to stem rust. Plant Dis 100:1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-02-16-0163-RE
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 57:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Buerstmayr H, Mohler V, Kohli M (2017) Advances in control of wheat diseases: Fusarium head blight, wheat blast and powdery mildew. In: Langridge P (ed) Achieving sustainable cultivation of wheat, Breeding, quality traits, pests and diseases, vol 1. Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 345–370
Chen PD, Qi LL, Zhou B, Zhang SZ, Liu DJ (1995) Development and molecular cytogenetic analysis of wheat-Haynaldia villosa 6VS/6AL translocation lines specifying resistance to powdery mildew. Theor Appl Genet 91:1125–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224062
Chen J, Upadhyaya NM, Ortiz D, Sperschneider J, Li F, Bouton C, Breen S, Dong C, Xu B, Zhang X, Mago R, Newell K, Xia X, Bernoux M, Taylor JM, Steffenson B, Jin Y, Zhang P, Kanyuka K, Figueroa M, Ellis JG, Park RF, Dodds PN (2017) Loss of AvrSr50 by somatic exchange in stem rust leads to virulence for Sr50 resistance in wheat. Science 358:1607–1610. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao4810
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Dedryver F, Paillard S, Mallard S, Robert O, Trottet M, Nègre S, Verplancke G, Jahier J (2009) Characterization of genetic components involved in durable resistance to stripe rust in the bread wheat ‘Renan’. Phytopathology 99:968–973. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-99-8-0968
Denissen CJM (1993) Components of adult plant resistance to leaf rust in wheat. Euphytica 70:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029650
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142:285–294
Herrera-Foessel S, Singh R, Lillemo M, Huerta-Espino J, Bhavani S, Singh S, Lan C, Calvo-Salazar V, Lagudah E (2014) Lr67/Yr46 confers adult plant resistance to stem rust and powdery mildew in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 127:781.789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2256-9
Hickey LT, Lawson W, Platz GJ, Dieters M, Arief VN, German S, Franckowiak J (2011) Mapping Rph20: a gene conferring adult plant resistance to Puccinia hordei in barley. Theor Appl Genet 123:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1566-z
Hurni S, Brunner S, Stirnweis D, Herren G, Peditto D, McIntosh RA, Keller B (2014) The powdery mildew resistance gene Pm8 derived from rye is suppressed by its wheat ortholog Pm3. Plant J 79:904–913. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12593
Hwang JU, Song WY, Hong D, Ko D, Yamaoka Y, Jang S, Yim S, Lee E, Khare D, Kim K, Palmgren M, Yoon HS, Martinoia E, Lee Y (2016) Plant ABC transporters enable many unique aspects of a terrestrial plant’s lifestyle. Mol Plant 9:338–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-017-0632-6
International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 361: eaar7191. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar7191
Jia A, Ren Y, Gao F, Yin G, Liu J, Guo L, Zheng J, He Z, Xia X (2018) Mapping and validation of a new QTL for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese elite bread wheat line Zhou8425B. Theor Appl Genet 131:1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3058-x
Kao CH, Zeng ZB, Teasdale RD (1999) Multiple interval mapping for quantitative trait loci. Genetics 152:1203–1216
Klahr A, Zimmermann G, Wenzel G, Mohler V (2007) Effects of environment, disease progress, plant height and heading date on the detection of QTLs for resistance to Fusarium head blight in an European winter wheat cross. Euphytica 154:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9264-7
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, McFadden H, Bossolini E, Selter LL, Keller B (2009) A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 323:1360–1363. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1166453
Lan CX, Ni XW, Yan J, Zhang Y, Xia XC, Chen XM, He ZH (2010) Quantitative trait loci mapping of adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat cultivar Lumai 21. Mol Breed 25:615–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9358-8
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lapin D, Van den Ackerveken G (2013) Susceptibility to plant disease: more than a failure of host immunity. Trends Plant Sci 18:546–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.05.005
Lebreton CM, Visscher PM (1998) Empirical nonparametric bootstrap strategies in quantitative trait loci mapping: conditioning on the genetic model. Genetics 148:525–535
Li ZF, Lan CX, He ZH, Singh RP, Rosewarne GM, Chen XM, Xia XC (2014a) Overview and application of QTL for adult plant resistance to leaf rust and powdery mildew in wheat. Crop Sci 54:1907–1925. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2014.02.0162
Li N, Wen ZR, Wang J, Fu BS, Liu JJ, Xu HH, Kong ZX, Zhang LX, Jia HY, Ma ZQ (2014b) Transfer and mapping of a gene conferring later-growth-stage powdery mildew resistance in a tetraploid wheat accession. Mol Breed 33:669–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2568-z
Liang SS, Suenaga K, He ZH, Wang ZL, Liu HY, Wang DS, Singh RP, Sourdille P, Xia XC (2006) Quantitative trait loci mapping for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat. Phytopathology 96:784–789. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-96-0784
Lillemo M, Asalf B, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Chen XM, He ZH, Bjørnstad Å (2008) The adult plant rust resistance loci Lr34/Yr18 and Lr46/Yr29 are important determinants of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar. Theor Appl Genet 116:1155–1166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0743-1
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ, Gore MA, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28:2397–2399. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts444
Liu N, Bai G, Lin M, Xu X, Zheng W (2017) Genome-wide association analysis of powdery mildew resistance in U.S. winter wheat. Sci Rep 7:11743. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11230-z
Lu Q, Bjørnstad Å, Ren Y, Asad MA, Xia X, Chen X, Ji F, Shi J, Lillemo M (2012) Partial resistance to powdery mildew in German spring wheat ‘Naxos’ is based on multiple genes with stable effects in diverse environments. Theor Appl Genet 125:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1834-6
Luo PG, Luo HY, Chang ZJ, Zhang HY, Zhang M, Ren ZL (2009) Characterization and chromosomal location of Pm40 in common wheat: a new gene for resistance to powdery mildew derived from Elytrigia intermedium. Theor Appl Genet 118:1059–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0962-0
Marone D, Russo MA, Laidò G, De Vita P, Papa R, Blanco A, Mastrangelo AM (2013) Genetic basis of qualitative and quantitative resistance to powdery mildew in wheat: from consensus regions to candidate genes. BMC Genomics 14:562. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-562
McIntosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Dubcovsky J, Rogers J, Morris C, Appels R, Xia XC (2013) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. https://shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/download.jsp. Accessed 11 Feb 2019
Miller JC, Chezem WR, Clay NK (2016) Ternary WD40 repeat-containing protein complexes: evolution, composition and roles in plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 6:1108. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01108
Mohler V, Bauer A, Bauer C, Flath K, Schweizer G, Hartl L (2011) Genetic analysis of powdery mildew resistance in German winter wheat cultivar Cortez. Plant Breed 130:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2010.01824.x
Mohler V, Bauer C, Schweizer G, Kempf H, Hartl L (2013) Pm50: a new powdery mildew resistance gene in common wheat derived from cultivated emmer. J Appl Genet 54:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0158-9
Muranty H, Pavoine M-T, Jaudeau B, Radek W, Doussinault G, Barloy D (2009) Two stable QTL involved in adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in the winter wheat line RE714 are expressed at different times along the growing season. Mol Breed 23:445–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9248-5
Petre B, Morin E, Tisserant E, Hacquard S, Da Silva C, Poulain J, Delaruelle C, Martin F, Rouhier N, Kohler A (2012) RNA-Seq of early-infected poplar leaves by the rust pathogen Melampsora larici-populina uncovers PtSultr3;5, a fungal-induced host sulfate transporter. PLoS One 7:e44408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044408
Plaschke J, Ganal MW, Röder MS (1995) Detection of genetic diversity in closely related bread wheat using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 91:1001–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00223912
Poppe S, Dorsheimer L, Happel P, Stukenbrock EH (2015) Rapidly evolving genes are key players in host specialization and virulence of the fungal wheat pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici (Mycosphaerella graminicola). PLoS Pathog 11:e1005055. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005055
Pretorius ZA, Park RF, Wellings CR (2000) An accelerated method for evaluating adult-plant resistance to leaf and stripe rust in spring wheat. Acta Phytopathol Entomol Hung 35:359–364
Riaz A, Periyannan S, Aitken E, Hickey L (2016) A rapid phenotyping method for adult plant resistance to leaf rust in wheat. Plant Methods 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-016-0117-7
Rothwell CT, Singh D, van Ogtrop F, Sørensen C, Fowler R, Germán S, Park RF, Dracatos P (2019) Rapid phenotyping of adult plant resistance in barley (Hordeum vulgare) to leaf rust under controlled conditions. Plant Breed 138:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12660
Salcedo A, Rutter W, Wang S, Akhunova A, Bolus S, Chao S, Anderson N, De Soto MF, Rouse M, Szabo L, Bowden RL, Dubcovsky J, Akhunov E (2017) Variation in the AvrSr35 gene determines Sr35 resistance against wheat stem rust race Ug99. Science 358:1604–1606. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao7294
Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Bhavani S, Herrera-Foessel SA, Singh D, Singh PK, Velu G, Mason RE, Jin Y, Njau P, Crossa J (2011) Race non-specific resistance to rust diseases in CIMMYT wheats. Euphytica 179:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0322-9
Spielmeyer W, McIntosh RA, Kolmer J, Lagudah ES (2005) Powdery mildew resistance and Lr34/Yr18 genes for durable resistance to leaf and stripe rust cosegregate at a locus on the short arm of chromosome 7D of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 111:731–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-2058-9
Sunderwirth SD, Roelfs AP (1980) Greenhouse evaluation of the adult plant resistance of Sr2 to wheat stem rust. Phytopathology 70:634–637
Tang S, Hu Y, Zhong S, Luo P (2018) The potential role of powdery mildew-resistance gene Pm40 in Chinese wheat breeding programs in the post-Pm21 era. Engineering 4:500–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.06.004
Tucker DM, Griffey CA, Liu S, Saghai Maroof MA (2006) Potential for effective marker-assisted selection of three quantitative trait loci conferring adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in elite wheat breeding populations. Plant Breed 125:430–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2006.01233.x
Turner SD (2014) qqman: an R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and manhattan plots. biorRxiv 005165. https://doi.org/10.1101/005165
Vales MI, Schön CC, Capettini F, Chen XM, Corey AE, Mather DE, Mundt CC, Richardson KL, Sandoval-Islas JS, Utz HF, Hayes PM (2005) Effect of population size on the estimation of QTL: a test using resistance to barley stripe rust. Theor Appl Genet 111:1260–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0043-y
VanRaden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91:4414–4423. https://doi.org/10.3168/JDS.2007-0980
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wang Y, Cheng X, Shan Q, Zhang Y, Liu J, Gao C, Qiu JL (2014a) Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew. Nat Biotechnol 32:947–951. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2969
Wang S, Wong D, Forrest K, Allen A, Chao S, Huang BE, Maccaferri M, Salvi S, Milner SG, Cattivelli L, Mastrangelo AM, Whan A, Stephen S, Barker G, Wieseke R, Plieske J, International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium, Lillemo M, Mather D, Appels R, Dolferus R, Brown-Guedira G, Korol A, Akhunova AR, Feuillet C, Salse J, Morgante M, Pozniak C, Luo M-C, Dvorak J, Morell M, Dubcovsky J, Ganal M, Tuberosa R, Lawley C, Mikoulitch I, Cavanagh C, Edwards KJ, Hayden M, Akhunov E (2014b) Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90,000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol J 12:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12183
Welz HG, Schechert AW, Geiger HH (1999) Dynamic gene action at QTLs for resistance to Setosphaeria turcica in maize. Theor Appl Genet 98:1036–1045
Wimmer V, Albrecht T, Auinger HJ, Schön C-C (2012) Synbreed: a framework for the analysis of genomic prediction data using R. Bioinformatics 28:2086–2087. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts335
Winfield MO, Allen AM, Burridge AJ, Barker GLA, Benbow HR, Wilkinson PA, Coghill J, Waterfall C, Davassi A, Scopes G, Pirani A, Webster T, Brew F, Bloor C, King J, West C, Griffiths S, King I, Bentley AR, Edwards KJ (2016) High-density SNP genotyping array for hexaploid wheat and its secondary and tertiary gene pool. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1195–1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12485
Zhang Z, Ersoz E, Lai C-Q, Todhunter RJ, Tiwari HK, Gore MA, Bradbury PJ, Yu J, Arnett DK, Ordovas JM, Buckler ES (2010) Mixed linear model approach adapted for genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 42:355–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.546
Zhang R, Fan Y, Kong L, Wang Z, Wu J, Xing L, Cao A, Feng Y (2018) Pm62, an adult-plant powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed from Dasypyrum villosum chromosome arm 2VL into wheat. Theor Appl Genet 131:2613–2620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3176-5
Acknowledgments
We thank Lorenz Hartl for his continuous support of the study and Adalbert Bund for population development. Technical assistance provided by Sabine Schmidt (crossing work), Martin Müller and team (DH production), Petra Greim (DNA isolation), and the staff of working group Wheat and Oat Breeding Research (set-up and maintenance of field trial) of the Bavarian State Research Center for Agriculture is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VM conceived the research and performed QTL analysis. MS designed the GH experiment, scored disease response, analyzed the phenotypic and genotypic data, and performed GWAS. VM drafted the manuscript and MS commented on it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by: Barbara Naganowska
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohler, V., Stadlmeier, M. Dynamic QTL for adult plant resistance to powdery mildew in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Appl Genetics 60, 291–300 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-019-00518-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-019-00518-7