Abstract
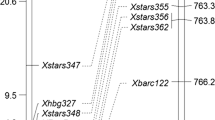
Fungal diseases of wheat, including powdery mildew, cause significant crop, yield and quality losses throughout the world. Knowledge of the genetic basis of powdery mildew resistance will greatly support future efforts to develop and cultivate resistant cultivars. Studies were conducted on cultivated emmer-derived wheat line K2 to identify genes involved in powdery mildew resistance at the seedling and adult plant growth stages using a BC1 doubled haploid population derived from a cross between K2 and susceptible cultivar Audace. A single gene was located distal to microsatellite marker Xgwm294 on the long arm of chromosome 2A. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis indicated that the gene was also effective at the adult plant stage, explaining up to 79.0 % of the variation in the progeny. Comparison of genetic maps indicated that the resistance gene in K2 was different from Pm4, the only other formally named resistance gene located on chromosome 2AL, and PmHNK54, a gene derived from Chinese germplasm. The new gene was designated Pm50.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari M, Wenzl P, Caig V, Carling J, Xia L, Yang S, Uszynski G, Mohler V, Lehmensiek A, Kuchel H, Hayden MJ, Howes N, Sharp P, Vaughan P, Rathmell B, Huttner E, Kilian A (2006) Diversity arrays technology (DArT) for high-throughput profiling of the hexaploid wheat genome. Theor Appl Genet 113:1409–1420
Anonymous (2011) Beschreibende Sortenliste. Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag GmbH, Hannover
Briggle LW (1966) Transfer of resistance to Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici from Khapli emmer and Yuma durum to hexaploid wheat. Crop Sci 6:459–461
Cowger C, Miranda L, Griffey C, Hall M, Murphy JP, Maxwell J (2012) Wheat powdery mildew. In: Sharma I (ed) Disease resistance in wheat. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 84–119
Hao Y, Liu A, Wang Y, Feng D, Gao J, Li X, Liu S, Wang H (2008) Pm23: a new allele of Pm4 located on chromosome 2AL in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 117:1205–1212
Huang XQ, Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK, Wenzel G, Mohler V (2000) Chromosomal location of AFLP markers in common wheat utilizing nulli-tetrasomic stocks. Genome 43:298–305
Huang BE, George AW, Forrest KL, Kilian A, Hayden MJ, Morell MK, Cavanagh CR (2012) A multiparent advanced generation inter-cross population for genetic analysis in wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 10:826–839
Korol A, Ronin Y, Minkov D, Britvin E, Mester D, Korostishevsky M, Malkin I, Frenkel Z, Orion O, Brailovsky A (2005) MultiQTL version 2.5. Institute of Evolution, Haifa University, Haifa, Israel
Laurie DA, Bennett MD (1986) Wheat × maize hybridization. Can J Genet Cytol 28:313–316
McFadden ES (1930) A successful transfer of emmer characters to vulgare wheat. J Am Soc Agron 22:1020–1034
McIntosh RA, Luig NH, Baker EP (1967) Genetic and cytogenetic studies of stem rust, leaf rust, and powdery mildew resistances in Hope and related wheat cultivars. Aust J Biol Sci 20:1181–1192
McIntosh RA, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ, Morris C, Appels R, Xia XC (2011) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2011 supplement. Available online at: http://www.shigen.nig.ac.jp/wheat/komugi/genes/macgene/supplement2011.pdf
Niu JS, Wang BQ, Wang YH, Cao AZ, Qi ZJ, Shen TM (2008) Chromosome location and microsatellite markers linked to a powdery mildew resistance gene in wheat line ‘Lankao 90(6)’. Plant Breed 127:346–349
R Development Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Home page at: http://www.R-project.org. Current at 2 April 2013
Schmolke M, Mohler V, Hartl L, Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK (2012) A new powdery mildew resistance allele at the Pm4 wheat locus transferred from einkorn (Triticum monococcum). Mol Breeding 29:449–456
Schubert V, Blüthner W-D, Junghanns W, Oertel C, Schuster M (1994) Agronomische leistung hohenthurmer weizenlinien mit resistenz gegenüber echtem mehltau. Vortr Pflanzenzüchtung 28:162–164
Schuster M, Blüthner WD (1992) Übertragung der Resistenz gegenüber Weizenmehltau, Erysiphe graminis DC F. sp. tritici March., aus tetraploiden Weizenarten in den Saatweizen. Kühn-Arch 86:51–58
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
The TT, McIntosh RA, Bennett FGA (1979) Cytogenetical studies in wheat. IX. Monosomic analyses, telocentric mapping and linkage relationships of genes Sr21, Pm4 and Mle. Aust J Biol Sci 32:115–125
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® version 3.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Xu W, Li C, Hu L, Wang H, Dong H, Zhang J, Zan X (2011) Identification and molecular mapping of PmHNK54: a novel powdery mildew resistance gene in common wheat. Plant Breed 130:603–607
Zaharieva M, Ayana NG, Al Hakimi A, Misra SC, Monneveux P (2010) Cultivated emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccon Schrank), an old crop with promising future: a review. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57:937–962
Zhu ZD, Zhou RH, Kong XY, Dong YC, Jia JZ (2005) Microsatellite markers linked to 2 powdery mildew resistance genes introgressed from Triticum carthlicum accession PS5 into common wheat. Genome 48:585–590
Acknowledgements
The technical assistance provided by Petra Greim and Sabine Schmidt is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would like to thank Prof. Bob McIntosh, The University of Sydney, Plant Breeding Institute Cobbitty, NSW, Australia, for the valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohler, V., Bauer, C., Schweizer, G. et al. Pm50: a new powdery mildew resistance gene in common wheat derived from cultivated emmer. J Appl Genetics 54, 259–263 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0158-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0158-9