Abstract
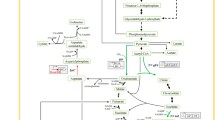
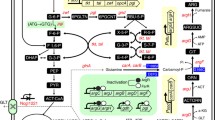
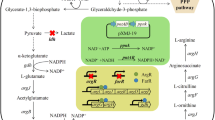
Genome-scale metabolic network model (GSMM) is an important in silico tool that can efficiently predict the target genes to be modulated. A Corynebacterium crenatum argB-M4 Cc_iKK446_arginine model was constructed on the basis of the GSMM of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 Cg_iKK446. Sixty-four gene deletion sites, twenty-four gene enhancement sites, and seven gene attenuation sites were determined for the improvement of l-arginine production in engineered C. crenatum. Among these sites, the effects of disrupting putP, cgl2310, pta, and Ncgl1221 and overexpressing lysE on l-arginine production were investigated. Moreover, the strain CCM007 with deleted putP, cgl2310, pta, and Ncgl1221 and overexpressed lysE produced 24.85 g/L l-arginine. This finding indicated a 106.8% improvement in l-arginine production compared with that in CCM01. GSMM is an excellent tool for identifying target genes to promote l-arginine accumulation in engineered C. crenatum.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba-Roth J, Müller OA, Schopoh J, Werder KV (1988) Arginine stimulates growth hormone secretion by suppressing endogenous somatostatin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 67:1186–1189
Alzoubi D, Desouki AA, Lercher MJ (2018) Alleles of a gene differ in pleiotropy, often mediated through currency metabolite production, in E. coli and yeast metabolic simulations. Sci Rep 8:17252–17261
Ankri S, Serebrijski I, Reyes O, Leblon G (1996) Mutations in the Corynebacterium glutamicum proline biosynthetic pathway: a natural bypass of th proA step. J Bacteriol 178:4412–4419
Becker J, Wittmann C (2012) Bio-based production of chemicals, materials and fuels Corynebacterium glutamicum as versatile cell factory. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:631–640
Bronte V, Zanovello P (2005) Regulation of immune responses by l-arginine metabolism. Nat Rev Immunol 5:641–654
Dobson PD, Smallbone K, Jameson D, Simeonidis E, Lanthaler K, Pir P, Lu C, Swainston N, Dunn WB, Fisher P, Hull D, Brown M, Oshota O, Stanford NJ, Kell DB, King RD, Oliver SG, Stevens RD, Mendes P (2010) Further developments towards a genome-scale metabolic model of yeast. BMC Syst Biol 4:145–152
Dou W, Xu M, Cai D, Zhang X, Rao Z, Xu Z (2011) Improvement of l-arginine production by overexpression of a bifunctional ornithine acetyltransferase in Corynebacterium crenatum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165:845–855
Duarte NC, Becker SA, Jamshidi N, Thiele I, Mo ML, Vo TD, Srivas R, Palsson BØ (2007) Global reconstruction of the human metabolic network based on genomic and bibliomic data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:1777–1782
Hashimoto K, Murata J, Konishi T, Yabe I, Nakamatsu T, Kawasaki H (2012) Glutamate is excreted across the cytoplasmic membrane through the NCgl1221 channel of Corynebacterium glutamicum by passive diffusion. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:1422–1424
Henry CS, Zinner JF, Cohoon MP, Stevens RL (2009) iBsu1103: a new genome-scale metabolic model of Bacillus subtilis based on SEED annotations. Genome Biol 10:R69
Henry CS, DeJongh M, Best AA, Frybarger PM, Linsay B, Stevens RL (2010) High-throughput generation, optimization and analysis of genome-scale metabolic models. Nat Biotechnol 28:977–982
Jensen JVK, Wendisch VF (2009) Ornithine cyclodeaminase-based proline production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Cell Fact 2:63–73
Kieldsen KR, Nielse J (2009) In silico genome-scale reconstruction and validation of the Corynebacterium glutamicum metabolic network. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:583–597
Kim K, Hurr C, Patik JC, Matthew BR (2018a) Attenuated cutaneous microvascular function in healthy young African Americans: role of intradermal l-arginine supplementation. Microvasc Res 118:1–6
Kim OD, Rocha M, Maia P (2018b) A review of dynamic modeling approaches and their application in computational strain optimization for metabolic engineering. Front Microbiol 9:1690–1712
Koduru L, Lakshmanan M, Lee DY (2009) In silico model-guided identification of transcriptional regulator targets for efficient strain design. Microb Cell Fact 17:167–179
Lee SY, Cho JY, Lee HJ, Kim YH, Min J (2010) Enhancement of ornithine production in proline-supplemented Corynebacterium glutamicum by ornithine cyclodeaminase. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:127–131
Lieven C, Petersen LAH, Jørgensen SB (2018) A genome-scale metabolic model for Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath) suggests reduced efficiency electron transfer to the particulate methane monooxygenase. Front Microbiol 9:2947–2962
Lubitz D, Jorge JM, Pérez-García F, Taniguchi H, Wendisch VF (2016) Roles of export genes cgmA and lysE for the production of l-arginine and l-citrulline by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:8465–8474
Man Z, Xu M, Rao Z, Guo J, Yang T, Zhang X, Xu Z (2016) Systems pathway engineering of Corynebacterium crenatum for improved l-arginine production. Sci Rep 6:28629
Mei J, Xu N, Ye C, Liu L, Wu J (2016) Reconstruction and analysis of a genome-scale metabolic network of Corynebacterium glutamicum S9114. Gene 575:615–622
Meng H, Wang Y, Hua Q, Zhang S, Wang X (2011) In silico analysis and experimental improvement of taxadiene heterologous biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioproc Eur 16:205–215
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Nakai N, Kawano F, Murakami T, Nakata K, Higashida K (2018) Leucine supplementation after mechanical stimulation activates protein synthesis via L-type aminoacid transporter 1 in vitro. J Cell Biochem 19:2094–2101
Orth JD, Conrad TM, Na J, Lerman JA, Nam H, Feist AMA, Feist AM, Palsson BØ (2011) Comprehensive genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli metabolism. Mol Syst Biol 7:535–544
Quay SC, Dick TE, Oxender DL (1977) Role of transport systems in amino acid metabolism: leucine toxicity and the branched chain amino acid transport systems. J Bacteriol 129:1257–1265
Shin JH, Lee SY (2014) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for the production of l-arginine and its derivatives. Microb Cell Fact 13:66–72
Shlomi T, Berkman O, Ruppin E (2005) Regulatory on/off minimization of metabolic flux changes after genetic perturbations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:7695–7700
Thams P, Capito K (1999) l-Arginine stimulation of glucose-induced insulin secretion through membrane depolarization and independent of nitric oxide. Eur J Endocrinol 140:87–93
Veit A, Rittmann D, Georgi T, Youn JW, Eikmanns BJ, Wendisch VF (2009) Pathway identification combining metabolic flux and functional genomics analyses: acetate and propionate activation by Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 140:75–83
Xu M, Rao Z, Yang J, Xia H, Dou W, Jin J, Xu Z (2012) Heterologous and homologous expression of the arginine biosynthetic argC~H cluster from Corynebacterium crenatum for improvement of l-arginine production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:495–502
Xu M, Rao Z, Yang J, Dou W, Xu Z (2013) The effect of a LYSE exporter overexpression on l-arginine production in Corynebacterium crenatum. Curr Microbiol 67:271–278
Xu J, Xia X, Zhang J, Guo Y, Qian H, Zhang W (2014) A method for gene amplifcation and simultaneous deletion in Corynebacterium glutamicum genome without any genetic markers. Plasmid 72:9–17
Yamashita C, Hashimoto K, Kumagai K, Nakata K, Higashida K (2013) l-Glutamate secretion by the N-terminal domain of the Corynebacterium glutamicum NCgl1221 mechanosensitive channel. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:1008–1013
Zhan M, Kan B, Dong J, Xu G, Ni Y (2019) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for improved l-arginine synthesis by enhancing NADPH supply. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46:45–54
Zhang B, Wan F, Qiu YL, Chen XL, Tang L, Chen JC, Xiong YH (2015) Increased l-arginine production by site-directed mutagenesis of N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase and proB gene deletion in Corynebacterium crenatum. Biomed Environ Sci 28:864–874
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31660019), “5511” Superior Technology Innovation Team Project of Jiangxi (No. 20165BCB19004) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi (No. 2016BAB204173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Zhao, Y., Li, R. et al. Improvement of l-arginine production by in silico genome-scale metabolic network model guided genetic engineering. 3 Biotech 10, 126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2114-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2114-9