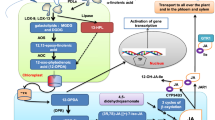
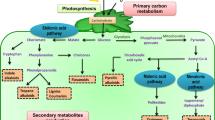
Abstract
Withania somnifera, also known as Indian ginseng is known to contain valuable bioactive compounds, called withanolides that structurally resemble ginsenosides of Panax ginseng. These compounds provide the basis of pharmacological relevance in traditional systems of medicine. In the present study, 150 hairy root lines of W. somnifera were induced of which nine fast growing lines were analysed for their growth and withanolide content. Hairy root line W9 was selected due to its high specific growth rate (0.196 ± 0.005 d−1) and high withanolide content. The response to different concentrations of elicitors (methyl jasmonate and P. indica cell homogenate) and various exposure durations was assessed in the W9 hairy root line. The withanolide content as well as the pattern of gene expression from MVA, MEP and sterol pathway, was evaluated using qPCR. Though gene expression and withanolide content were found to be elevated in almost all MeJ and CHP treatments, the exposure of hairy roots to 15 μM MeJ for 4 h gave the maximum withanolide yield. The results suggest that the elicitation potential of methyl jasmonate was higher than that of P. indica cell homogenate for increasing withanolide levels in hairy roots of W. somnifera.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- FW:
-
Fresh Weight
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- MVA:
-
Mevalonate pathway
- MEP:
-
Methyl erythreitol pathway
- MeJ:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- qPCR:
-
quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- CHP:
-
P. indica cell homogenate.
References
Ahlawat S, Saxena P, Alam P, et al. (2014) Modulation of artemisinin biosynthesis by elicitors, inhibitor, and precursor in hairy root cultures of Artemisia annua L. J Plant Interact 9:811–824. doi:10.1080/17429145.2014.949885
Akhtar N, Gupta P, Sangwan NS, et al. (2013) Cloning and functional characterization of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene from Withania somnifera: An important medicinal plant. Protoplasma 250:613–622. doi:10.1007/s00709-012-0450-2
Baldi A, Farkya S, Jain A, et al. (2010) Enhanced production of podophyllotoxins by co-culture of transformed Linum album cells with plant growth-promoting fungi. Pure Appl Chem 82:227–241. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-09-02-09
Banerjee S, Mandalt S, Ahuja PS (1994) Transformation of Withania somnifera ( L ) Dunal. Phytother Res 8:452–455
Bhat WW, Lattoo SK, Razdan S, et al. (2012) Molecular cloning, bacterial expression and promoter analysis of squalene synthase from Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. Gene 499:25–36. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2012.03.004
Chandra S, Chandra R (2011) Engineering secondary metabolite production in hairy roots. Phytochem Rev 10:371–395. doi:10.1007/s11101-011-9210-8
Chen L-X, He H, Qiu F (2011) Natural withanolides: an overview. Nat Prod Rep 28:705. doi:10.1039/c0np00045k
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2009) Nature: A vital source of leads for anticancer drug development. Phytochem Rev 8:313–331. doi:10.1007/s11101-009-9123-y
Dhar N, Rana S, Razdan S, et al. (2014) Cloning and Functional Characterization of Three Branch Point Oxidosqualene Cyclases from Withania somnifera ( L. ). J Biol Chem 289:17249–17267. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.571919
Gupta P, Akhtar N, Tewari SK, et al. (2011) Differential expression of farnesyl diphosphate synthase gene from Withania somnifera in different chemotypes and in response to elicitors. Plant Growth Regul 65:93–100. doi:10.1007/s10725-011-9578-x
Gupta N, Sharma P, Santosh Kumar RJ, et al. (2012) Functional characterization and differential expression studies of squalene synthase from Withania somnifera. Mol Biol Rep 39:8803–8812. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1743-4
Gupta P, Agarwal AV, Akhtar N, et al. (2013) Cloning and characterization of 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway genes for isoprenoid biosynthesis from Indian ginseng, Withania somnifera. Protoplasma 250:285–295. doi:10.1007/s00709-012-0410-x
Hill TW, Kafer E (2001) Improved protocols for Aspergillus minimal medium: trace element and minimal medium salt stock solutions. Fungal Genet Newsl 48:20–21
Jacobs S, Zechmann B, Molitor A, et al. (2011) Broad-spectrum suppression of innate immunity is required for colonization of Arabidopsis roots by the fungus Piriformospora indica. Plant Physiol 156:726–740. doi:10.1104/pp.111.176446
Kim OT, Bang KH, Kim YC, et al. (2009) Upregulation of ginsenoside and gene expression related to triterpene biosynthesis in ginseng hairy root cultures elicited by methyl jasmonate. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 98:25–33. doi:10.1007/s11240-009-9535-9
Krzyzanowska J, Czubacka A, Pecio L, et al. (2012) The effects of jasmonic acid and methyl jasmonate on rosmarinic acid production in Mentha × piperita cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 108:73–81. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-0014-8\r10.1007/s11240-011-9919-5
Kulkarni SK, Dhir A (2008) Withania somnifera: An Indian ginseng. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1093–1105. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.09.011
Kumar V, Rajauria G, Sahai V, Bisaria VS (2012) Culture filtrate of root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica promotes the growth and lignan production of Linum album hairy root cultures. Process Biochem 47:901–907
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mirjalili MH, Moyano E, Bonfill M, et al. (2009) Steroidal Lactones from Withania somnifera, an Ancient Plant for Novel Medicine. Molecules 14:2373–2393. doi:10.3390/molecules14072373
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1021/jf9040386
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2003) Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod 70:461–477. doi:10.1021/np068054v
Pal S, Singh S, Shukla AK, et al. (2011) Comparative withanolide profiles, gene isolation, and differential gene expression in the leaves and roots of Withania somnifera. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 86:391–397
Prasad R, Kamal S, Sharma PK, et al. (2013) Root endophyte Piriformospora indica DSM 11827 alters plant morphology, enhances biomass and antioxidant activity of medicinal plant Bacopa monniera. J Basic Microbiol 53:1016–1024. doi:10.1002/jobm.201200367
Rai M, Acharya D, Singh A, Varma A (2001) Positive growth responses of the medicinal plants Spilanthes calva and Withania somnifera to inoculation by Piriformospora indica in a field trial. Mycorrhiza 11:123–128. doi:10.1007/s005720100115
Rana S, Bhat WW, Dhar N, et al. (2014) Molecular characterization of two A-type P450s, WsCYP98A and WsCYP76A from Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal: expression analysis and withanolide accumulation in response to exogenous elicitations. BMC Biotechnol 14:89. doi:10.1186/s12896-014-0089-5
Razdan S, Bhat WW, Rana S, et al. (2013) Molecular characterization and promoter analysis of squalene epoxidase gene from Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. Mol Biol Rep 40:905–916. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2131-9
Sabir F, Mishra S, Sangwan RS, et al. (2013) Qualitative and quantitative variations in withanolides and expression of some pathway genes during different stages of morphogenesis in Withania somnifera Dunal. Protoplasma 250:539–549. doi:10.1007/s00709-012-0438-y
Satheesan J, Narayanan AK, Sakunthala M (2012) Induction of root colonization by Piriformospora indica leads to enhanced asiaticoside production in Centella asiatica. Mycorrhiza 22:195–202. doi:10.1007/s00572-011-0394-y
Schafer P, Pfiffi S, Voll LM, et al. (2009) Manipulation of plant innate immunity and gibberellin as factor of compatibility in the mutualistic association of barley roots with Piriformospora indica. Plant J 59:461–474. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03887.x
Senthil K, Jayakodi M, Thirugnanasambantham P, et al. (2015) Transcriptome analysis reveals in vitro cultured Withania somnifera leaf and root tissues as a promising source for targeted withanolide biosynthesis. BMC Genomics 16:1–16. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1214-0
Shilpha J, Satish L, Kavikkuil M, et al. (2015) Methyl jasmonate elicits the solasodine production and anti-oxidant activity in hairy root cultures of Solanum trilobatum L. Ind Crop Prod 71:54–64. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.083
Singh S, Pal S, Shanker K, et al. (2014) Sterol partitioning by HMGR and DXR for routing intermediates toward withanolide biosynthesis. Physiol Plant 152:617–633. doi:10.1111/ppl.12213
Singh V, Kaul SC, Wadhwa R, Pati PK (2015) Evaluation and Selection of Candidate Reference Genes for Normalization of Quantitative RT-PCR in Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. PLoS One 10:e0118860. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118860
Sivanandhan G, Arun M, Mayavan S, et al. (2012) Optimization of elicitation conditions with methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid to improve the productivity of withanolides in the adventitious root culture of Withania somnifera (L.) dunal. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168:681–696. doi:10.1007/s12010-012-9809-2
Sivanandhan G, Kapil Dev G, Jeyaraj M, et al. (2013a) A promising approach on biomass accumulation and withanolides production in cell suspension culture of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. Protoplasma 250:885–898. doi:10.1007/s00709-012-0471-x
Sivanandhan G, Kapil Dev G, Jeyaraj M, et al. (2013b) Increased production of withanolide A, withanone, and withaferin A in hairy root cultures of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal elicited with methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 114:121–129. doi:10.1007/s11240-013-0297-z
Sivanandhan G, Rajesh M, Arun M, et al. (2013c) Effect of culture conditions, cytokinins, methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid on the biomass accumulation and production of withanolides in multiple shoot culture of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal using liquid culture. Acta Physiol Plant 35:715–728. doi:10.1007/s11738-012-1112-x
Supe U, Dhote F, Roymon MG (2006) In vitro Plant Regeneration of Withania somnifera. Plant Tissue Cult & Biotech 16:111–115
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23:283–333. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.01.003
Zhou M, Zhu X, Shao J (2010) Transcriptional response of the catharanthine biosynthesis pathway to methyl jasmonate / nitric oxide elicitation in Catharanthus roseus hairy root culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:737–750. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2822-x
Acknowledgments
The research facilities developed from UGC-SAP (DRS-1) grant sanctioned to the Department of Biotechnology by University Grants Commission, Government of India and the senior research fellowship to PS under DRDO project DLS/81/48222/LSRB-207/SH&DD/2010, are gratefully acknowledged. SA is thankful to Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for providing WoS-A Fellowship. The authors thankfully acknowledge Dr. S. Banerjee, Chief Scientist, Plant Tissue Culture Division, Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, Lucknow, India for her valuable guidance in hairy root induction experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, P., Ahlawat, S., Ali, A. et al. Gene expression analysis of the withanolide biosynthetic pathway in hairy root cultures of Withania somnifera elicited with methyl jasmonate and the fungus Piriformospora indica . Symbiosis 71, 143–154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0416-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0416-9