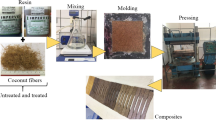
Abstract
High energy consumption in the building sector appeals for the implementation and the improvement of innovative approaches with low-environmental impact. The development of eco-friendly composites as insulating materials in buildings provides practical solutions for reducing energy consumption. Different mass proportions (2.5%, 10%, and 20%) of untreated and chemically treated palm fibers were mixed with (cement, water and sand) so as to prepare novel composites. Composites were characterized by measuring water absorption, thermal conductivity, compressive strength and acoustic transmission. The results reveal that the incorporation of untreated and chemically treated date palm fibers reduces novel composites’ thermal conductivity and the mechanical resistance. Thermal measurements have proved that the loading of fibers in composites decreases the thermal conductivity from 1.38 W m−1 K−1 for the reference material to 0.31 W m−1 K−1 for composites with 5% of treated and untreated fibers. The acoustical insulation capacity of untreated palm fiber-reinforced composites (DPF) was the highest at 20% fiber content, whereas treated palm fiber-reinforced composites (TPF) had the highest sound insulation coefficient for fiber content lower than 10%. Compressive strength, thermal conductivity and density correlation showed that only chemically treated fiber-reinforced composites (TPF) are good candidates for thermal and acoustic building insulations.
Graphic Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sripaiboonkij, P., Sripaiboonkij, N., Phanprasit, W., Jaakkola, M.S.: Respiratory and skin health among glass microfiber production workers: a cross-sectional study. Environ. Health 8, 1–10 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-8-36
Sellami, A., Merzoud, M., Amziane, S.: Improvement of mechanical properties of green concrete by treatment of the vegetals fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 47, 1117–1124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.05.073
Tonoli, G.H.D., Belgacem, M.N., Siqueira, G., Bras, J., Savastano, H., Rocco Lahr, F.A.: Processing and dimensional changes of cement based composites reinforced with surface-treated cellulose fibres. Cem. Concr. Compos. 37, 68–75 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.12.004
Pickering, K.L., Efendy, M.G.A., Le, T.M.: A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 83, 98–112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.038
Lahouioui, M., Fois, M., Ben Arfi, R., Ibos, L., Ghorbal, A.: Experimental investigation of palm fiber surface treatment effect on thermal, acoustical, and mechanical properties of a new bio-composite. In: Recent advances in environmental science from the Euro-Mediterranean and surrounding regions. pp. 1577–1579 (2018)
Sudin, R., Swamy, N.: Bamboo and wood fibre cement composites for sustainable infrastructure regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 6917–6924 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0224-3
Stefanidou, M., Anastasiou, E., Mantziou, O., Mpougla, E., Vasiliou, E., Konti, P.D., Antoniadis, K.: Incorporation of glass particles in high-performance mortars. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 7, 879–883 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9501-9
Wang, J., Hu, Y.: Novel particleboard composites made from coir fiber and waste banana stem fiber. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 7, 1447–1458 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9523-3
Ohenoja, K., Wigren, V., Österbacka, J., Illikainen, M.: Applicability of fly ash from fluidized bed combustion of peat, wood, or wastes to concrete. Waste Biomass Valoriz. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00615-y
Panyakaew, S., Fotios, S.: New thermal insulation boards made from coconut husk and bagasse. Energy Build. 43, 1732–1739 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2011.03.015
Essabir, H., Hilali, E., Elgharad, A., Minor, H.El, Imad, A., Elamraoui, A., Al Gaoudi, O.: Materials and design mechanical and thermal properties of bio-composites based on polypropylene reinforced with Nut-shells of Argan particles. Mater. Des. 49, 442–448 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.01.025
Morel, J.C., Mesbah, A., Oggero, M., Walker, P.: Building houses with local materials: means to drastically reduce the environmental impact of construction. Build. Environ. 36, 1119–1126 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1323(00)00054-8
Hamza, S., Saad, H., Charrier, B., Ayed, N., Bouhtoury, F.C.: Physico-chemical characterization of Tunisian plant fibers and its utilization as reinforcement for plaster based composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 49, 357–365 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.052
Ali, M.E., Alabdulkarem, A.: On thermal characteristics and microstructure of a new insulation material extracted from date palm trees surface fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 138, 276–284 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.012
Laborel, A., Camille, P., Jean, M., Aubert, E.: Characterization of barley straw, hemp shiv and corn cob as resources for bioaggregate based building materials. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 9, 1095–1112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9895-z
Chabriac, P.A., Gourdon, E., Gle, P., Fabbri, A., Lenormand, H.: Agricultural by-products for building insulation: acoustical characterization and modeling to predict micro-structural parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 112, 158–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.162
Bassyouni, M., Ul Hasan, S.W.: The use of rice straw and husk fibers as reinforcements in composites. (2015)
Berardi, U., Iannace, G.: Acoustic characterization of natural fibers for sound absorption. Build. Environ. 94, 840–852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.05.029
Alawar, A., Hamed, A.M., Al-Kaabi, K.: Characterization of treated date palm tree fiber as composite reinforcement. Compos. Part B Eng. 40, 601–606 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2009.04.018
Rashid, B., Leman, Z., Jawaid, M., Ghazali, M.J., Ishak, M.R.: Physicochemical and thermal properties of lignocellulosic fiber from sugar palm fibers: effect of treatment. Cellulose 23, 2905–2916 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1005-z
Arrakhiz, F.Z., Elachaby, M., Bouhfid, R., Vaudreuil, S., Essassi, M., Qaiss, A.: Mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene reinforced with Alfa fiber under different chemical treatment. Mater. Des. 35, 318–322 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.09.023
Ajouguim, S., Abdelouahdi, K., Waqif, M., Stefanidou, M., Saâdi, L.: Modifications of Alfa fibers by alkali and hydrothermal treatment. Cellulose (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2181-9
Panesar, D.K., Shindman, B.: The mechanical, transport and thermal properties of mortar and concrete containing waste cork. Cem. Concr. Compos. 34, 982–992 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.06.003
El-Abbassi, F.E., Assarar, M., Ayad, R., Lamdouar, N.: Effect of alkali treatment on Alfa fibre as reinforcement for polypropylene based eco-composites: mechanical behaviour and water ageing. Compos. Struct. 133, 451–457 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.07.112
Benmansour, N., Agoudjil, B., Gherabli, A., Kareche, A., Boudenne, A.: Thermal and mechanical performance of natural mortar reinforced with date palm fibers for use as insulating materials in building. Energy Build. 81, 98–104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.05.032
Chikhi, M., Agoudjil, B., Boudenne, A., Gherabli, A.: Experimental investigation of new biocomposite with low cost for thermal insulation. Energy Build. 66, 267–273 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2013.07.019
Haba, B., Agoudjil, B., Boudenne, A., Benzarti, K.: Hygric properties and thermal conductivity of a new insulation material for building based on date palm concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 154, 963–971 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.025
Belakroum, R., Gherfi, A., Bouchema, K., Gharbi, A., Kerboua, Y., Kadja, M., Maalouf, C., Mai, T.H., El Wakil, N., Lachi, M.: Hygric buffer and acoustic absorption of new building insulation materials based on date palm fibers. J. Build. Eng. 12, 132–139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2017.05.011
Boumhaout, M., Boukhattem, L., Hamdi, H., Benhamou, B., Ait Nouh, F.: Thermomechanical characterization of a bio-composite building material: mortar reinforced with date palm fibers mesh. Constr. Build. Mater. 135, 241–250 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.217
Oancea, I., Bujoreanu, C., Budescu, M., Benchea, M., Grădinaru, C.M.: Considerations on sound absorption coefficient of sustainable concrete with different waste replacements. J. Clean. Prod. 203, 301–312 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.273
Jayamani, E., Hamdan, S., Rahman, M.R., Bakri, M.K.B.: Investigation of fiber surface treatment on mechanical, acoustical and thermal properties of betelnut fiber polyester composites. Procedia Eng. 97, 545–554 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.282
Seddeq, H.S., Aly, N.M., Marwa, A., Elshakankery, M.H.: Investigation on sound absorption properties for recycled fibrous materials. J. Ind. Text. 43, 56–73 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083712446956
Mahzan, S., Ahmad Zaidi, A.M., Ghazali, M.I., Yahya, M.N., Ismail, M.: Investigation on sound absorption of rice-husk reinforced composite. In: Proceedings of MUCEET. pp. 19–22 (2009)
Kinnane, O., Reilly, A., Grimes, J., Pavia, S., Walker, R.: Acoustic absorption of hemp-lime construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 122, 674–682 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.106
Tang, X., Yan, X.: Acoustic energy absorption properties of fibrous materials: a review. Compos. Part A 101, 360–380 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.07.002
Levdik, I., Inshakov, M.D., Misyurova, E.P., Nikitin, V.N.: Study of pulp structure by infrared spectroscopy. Tr. Vses Nauch. Issled. Irst. Tsellyul Bum. Prom. 52, 109–111 (1967)
Ben Arfi, R., Karoui, S., Mougin, K., Ghorbal, A.: Adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution by utilizing almond shell as bioadsorbent. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2, 20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-017-0032-y
Ibos, L., Tlili, R., Boudenne, A., Fois, M., Dujardin, N., Candau, Y.: Thermophysical characterization of polymers according to the temperature using a periodic method. Polym. Test. 66, 235–243 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.01.023
Braiek, A., Karkri, M., Adili, A., Ibos, L., Nasrallah, S.B.: Estimation of the thermophysical properties of date palm fibers/gypsum composite for use as insulating materials in building. Energy Build. 140, 268–279 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.02.001
Neithalath, N., Weiss, J., Olek, J.: Acoustic performance and damping behavior of cellulose-cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 26, 359–370 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-9465(03)00020-9
Tonoli, G.H.D., Belgacem, M.N., Bras, J., Lahr, F.A.R.: Impact of bleaching pine fibre on the fibre/cement interface. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 4167–4177 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6271-z
Sreekumar, P.A., Thomas, S.P., marc Saiter, J., Joseph, K., Unnikrishnan, G., Thomas, S.: Effect of fiber surface modification on the mechanical and water absorption characteristics of sisal/polyester composites fabricated by resin transfer molding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 40, 1777–1784 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2009.08.013
Bederina, M., Marmoret, L., Mezreb, K., Khenfer, M.M., Bali, A., Quéneudec, M.: Effect of the addition of wood shavings on thermal conductivity of sand concretes: experimental study and modelling. Constr. Build. Mater. 21, 662–668 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.12.008
Taoukil, D., El bouardi, A., Ajzoul, T., Ezbakhe, H.: Effect of the incorporation of wood wool on thermo physical proprieties of sand mortars. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 16, 1003–1010 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-012-1470-3
Saygılı, A., Baykal, G.: A new method for improving the thermal insulation properties of fly ash. Energy Build. 43, 3236–3242 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2011.08.024
Balčiūnas, G., Žvironaitė, J., Vėjelis, S., Jagniatinskis, A., Gaidučis, S.: Ecological, thermal and acoustical insulating composite from hemp shives and sapropel binder. Ind. Crops Prod. 91, 286–294 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.06.034
Miraoui, I., Jaballi, S., Hassis, H.: Analysis of the mechanical properties of mortar reinforced with long unidirectional Alfa fibers in different curing conditions. Mech. Compos. Mater. 52, 545–554 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-016-9605-0
Oushabi, A., Sair, S., Abboud, Y., Tanane, O., Bouari, A.El: An experimental investigation on morphological, mechanical and thermal properties of date palm particles reinforced polyurethane composites as new ecological insulating materials in building. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 7, 128–137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2017.06.002
Samson, G., Lanos, C., Phelipot-mardelé, A.: A review of thermomechanical properties of lightweight concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 69, 201–216 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1680/jmacr.16.00324
Herrmann, N., McClements, D.J.: Influence of visco-inertial effects on the ultrasonic properties of monodisperse silica suspensions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106, 1178–1181 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1121/1.427127
Moretti, E., Belloni, E., Agosti, F.: Innovative mineral fiber insulation panels for buildings: thermal and acoustic characterization. Appl. Energy 169, 421–432 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.02.048
Haque, R., Saxena, M., Shit, S.C., Asokan, P.: Fibre-matrix adhesion and properties evaluation of sisal polymer composite. Fibers Polym. 16, 146–152 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-015-0146-2
Ilyas, R.A., Sapuan, S.M., Ishak, M.R.: Isolation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose from sugar palm fibres (Arenga Pinnata). Carbohydr. Polym. 181, 1038–1051 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.045
Kargarzadeh, H., Ahmad, I., Abdullah, I., Dufresne, A., Zainudin, S.Y., Sheltami, R.M.: Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 19, 855–866 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9684-6
Saha, P., Chowdhury, S., Roy, D., Adhikari, B., Kim, J.K., Thomas, S.: A brief review on the chemical modifications of lignocellulosic fibers for durable engineering composites. Polym. Bull. 73, 587–620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1489-y
Acknowledgements
The University of Gabes and the Tunisian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research are thanked for the financial support. Authors also thank Prof. Rim Najjar for help with English language corrections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahouioui, M., Ben Arfi, R., Fois, M. et al. Investigation of Fiber Surface Treatment Effect on Thermal, Mechanical and Acoustical Properties of Date Palm Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Composites. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 4441–4455 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00745-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00745-3