Abstract
Polymeric composites reinforced with plant fibers have numerous advantages, such as low cost, high raw material availability and good physical, mechanical and thermal properties. Thus, in recent years, they have been studied as thermal insulation substitutes for synthetic polymers in buildings. The aim of this study was to evaluate the technological properties of castor oil–based polyurethane composites reinforced with coconut fibers treated with hot water, alkaline solutions of NaOH and Ca(OH)2 and corona discharge and without surface treatment as materials for the thermal insulation of buildings. The composites were produced by the hand lay–up method followed by compression; 10% by weight coconut fibers were used to replace the synthetic polymer. Specimens were produced, and physical, mechanical, thermal and microstructural tests were performed. The results showed that the polymer had a thermal conductivity of 0.016 W/(mK), while the composites produced with fibers treated with NaOH had a thermal conductivity of 0.028 W/(mK); therefore, these polymers are considered insulating materials (k = 0.01 to 1.0 W/(mK)). Thus, the composites produced with coconut fibers can be considered as lighter, less expensive and environmentally friendly alternatives to synthetic polymers.

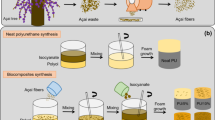
Adapted from Faria et al. (2020b)










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions are included in the manuscript. Furthermore, the datasets analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Abidin NIZ, Sabri MFM, Kalantari K, Afifi AM, Ahmad R (2019) Corrosion detection for natural/synthetic/textiles fiber polymer composites. In: Jawaid M, Thariq M, Saba N (eds) Structural health monitoring of biocomposites, fibre-reinforced composites andhybrid composites, 1st edn. Woodhead Publishing. Cambridge, pp 93–112
ABNT NBR 13999 (2017) Paper, board, pulps, and wood-determination of residue (ash) on ignition at 525 °C. https://www.abntcatalogo.com.br/norma.aspx?ID=369837. Accessed 12 Jan 2023
ABNT NBR 14853 (2010) Wood-determination of soluble matter in ethanol-toluene and in dichloromethane and in acetone. https://www.abntcatalogo.com.br/norma.aspx?ID=57842. Accessed 12 Jan 2023
ABNT NBR 7989 (2010) Pulp and wood-determination of acid-insoluble lignin. https://www.abntcatalogo.com.br/norma.aspx?ID=57843. Accessed 10 Jan 2023
Adeniyi AG, Onifade DV, Ighalo JO, Adeoye AS (2019) A review of coir fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos B Eng 176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107305
Anuchi SO, Campbell KLS, Hallett J (2022) Effective pretreatment of lignin-rich coconut wastes using a low-cost ionic liquid. Sci Rep 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09629-4
Arsyad M (2017) Effect of alkali treatment on the coconut fiber surface. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci 12:1870–1875
Arsyad M, Kondo Y, Arman, Anzarih AM, Wahyuni N (2019) Effect of sodium hydroxide concentration on the tensile strength of coconut fiber. J Phys Conf Ser 1341. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1341/5/052001
ASTM D2734–16 (2016) Standard test methods for void content of reinforced plastics. https://www.astm.org/d2734-16.html. Accessed 08 Jan 2023
ASTM D-3379–75 (1989) Standard test method for tensile strength and Young’s modulus for high modulus single filament materials. https://www.astm.org/standards/d3379. Accessed 13 Jan 2023
ASTM D-570–98 (2018) Standard test method for water absorption of plastics. https://www.astm.org/d0570-98r10e01.html. Accessed 15 Jan 2023
ASTM D-638–14 (2014) Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics. https://www.astm.org/d0638-14.html. Accessed 12 Jan 2023
Bergman TL, Lavine AS, Incropera FP, Dewitt DP (2018) Fundamentals of heat and mass transfer, eight. John Wiley and Sons, Nova Jersey
Browning BL (1963) The chemistry of wood. John Wiley, New York
Bui H, Sebaibi N, Boutouil M, Levacher D (2020) Determination and review of physical and mechanical properties of raw and treated coconut fibers for their recycling in construction materials. Fibers 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8060037
Cabral MMS, Abud AKS, Silva CEF, Almeida RMRG (2016) Bioethanol production from coconut husk fiber. Ciência Rural 46:1872–1877. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20151331
Callister WD Jr, Rethwisch DG (2019) Ciência e engenharia de materiais: uma introdução, 5th edn. LTC, Rio de Janeiro
Cangemi JM, Claro Neto S, Chierice GO (2006) Study of the biodegradation of a polymer derived from castor oil by scanning electron microscopy, thermogravimetry and infrared spectroscopy. Polímeros 16:129–135
Capela C, Oliveira SE, Pestana J, Ferreira JAM (2017) Effect of fiber length on the mechanical properties of high dosage carbon reinforced. Procedia Struct Integr 5:539–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostr.2017.07.159
Cardoso GT, Vecchia F, Claro Neto S (2011) Espuma rígida de poliuretano (PU) derivada de óleo vegetal (Ricinus communis) para isolamento térmico em sistemas de cobertura, in: 4° Seminário Mato-grossense de Habitação de Interesse Social. http://pt.scribd.com/doc/86797225/Espuma-rigida-poliuretano-derivada-oleo-vegetal-para-isolamento-termico-em-sistemas-cobertura-versao-final. Accessed 10 Jan 2023
Carriço CS, Fraga T, Carvalho VE, Pasa VMD (2017) Polyurethane foams for thermal insulation uses produced from castor oil and crude glycerol biopolyols. Mol. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071091
Carvalho JE, Chierice GO, Claro Neto S (2014) Caracterização térmica do poliuretano derivado de óleo vegetal utilizado para a confecção de dispositivo de assistência ventricular. Braz J Therm Anal 3:16–19
Carvalho JPRG, Simonassi NT, Lopes FPD, Monteiro SN, Vieira CMF (2022) Novel sustainable castor oil-based polyurethane biocomposites reinforced with piassava fiber powder waste for high-performance coating floor. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095082
Chua PS, Dai SR, Piggott MR (1992) Mechanical properties of the glass fibre polyester interphase. J Mater Sci 27:913–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197642
Claro Neto S (1997) Caracterização físico-química de um poliuretano derivado de óleo de mamona utilizado para implantes ósseos. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo
Danso H, Martinson DB, Ali M, Williams J (2015) Effect of fibre aspect ratio on mechanical properties of soil building blocks. Constr Build Mater 83:314–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.03.039
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.epa.gov/formaldehyde, 2016 (accessed 16 October 2022)
Faria DL, Mesquita Júnior L, Mesquita RGA, Guimarães Júnior M, Pires NJ, Mendes LM, Guimarães Junior JB (2020b) Production of castor oil-based polyurethane resin composites reinforced with coconut husk fibres. J Polym Res 27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02238-7
Faria DL, Mesquita Júnior L, Resende AA, Lopes DE, Mendes LM, Martins MA, Marconcini JM, Guimarães Junior JB (2020a) Physical and mechanical properties of polyurethane thermoset matrices reinforced with green coconut fibres. J Compos Mater 1–12.https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998320940023
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations-FAO. Forestry production and trade. https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FO/visualize, 2022 (accessed 16 October 2022)
Gaspar F, Bakatovish A, Davydenko N, Joshi A (2020) Building insulation materials based on agricultural wastes. In: Pacheco-Torgal F, Ivanov V, Tsang DCW (eds) Bio-based materials and biotechnologies for eco-efficient construction, 1st edn. Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering. Cambridge, pp 149–170
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 3. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782
Hasan KMF, Horváth PG, Kóczán Z, Alpár T (2021) Thermo-mechanical properties of pretreated coir fiber and fibrous chips reinforced multilayered composites. Sci Rep 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83140-0
Hassani FO, Merbahi N, Oushabi A, Elfadili MH, Kammouni A, Oueldna N (2019) Effects of corona discharge treatment on surface and mechanical properties of Aloe Vera fibers. Mater Today Proc 24:46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.527
Irawan D, Muslimah N, Arifin Z (2018) Lignin isolation from coconut coir with variation of time and concentration of NaOH in the process of alkaline delignification. Rasāyan J Chem 11:1458–1460. https://doi.org/10.31788/RJC.2018.1144039
Kabir MM, Wang H, Lau KT, Cardona F (2012) Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: an overview. Compos B Eng 43:2883–2892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.04.053
Kaikade DS, Sabnis AS (2022) Polyurethane foams from vegetable oil-based polyols: a review. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04155-9
Karthikeyan A, Balamurugan K, Kalpana A (2014) The effect of sodium hydroxide treatment and fiber length on the tensile property of coir fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. Sci Eng Compos Mater 21:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1515/secm-2013-0130
Khlif M, Chaari R, Bradai C (2022) Physico-mechanical characterization of poly (butylene succinate) and date palm fiber-based biodegradable composites. Polym Polym Compos 30. https://doi.org/10.1177/09673911221080157
Klock U, Andrade AS (2013) Química da madeira, 4th edn. UFPR, Curitiba
Ku H, Wang H, Pattarachaiyakoop N, Trada M (2011) A review on the tensile properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos B Eng 42:856–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.01.010
Kumar RN, Pizzi A (2019) Wood surface inactivation due to extractives. In: Kumar RN, Pizzi A (eds) Adhesives for wood and lignocellulosic materials. Wiley Online Library. New York, pp 211–222
Laskowska A, Kozakiewicz P (2017) Surface wettability of wood species from tropical and temperate zones by polar and dispersive liquids. Drv Ind 68:299–306. https://doi.org/10.5552/drind.2017.1704
Leão RM, Luz SM, Araujo JA, Novack K (2015) Surface treatment of coconut fiber and its application in composite materials for reinforcement of polypropylene. J Nat Fibers 12:574–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2014.984048
Levy Neto F, Pardini LC (2016) Compósitos Estruturais – Ciência e Tecnologia, 2nd edn. Blucher, São Paulo
Liu Y, Lv X, Bao J, Xie J, Tang X, Che J, Ma Y, Tong J (2019) Characterization of silane treated and untreated natural cellulosic fibre from corn stalk waste as potential reinforcement in polymer composites. Carbohydr Polym 218:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.088
Malchiodi B, Barbieri L, Lancellotti I, Pozzi P (2022) Char valorization into sustainable and performant polyurethane insulating panels. Macromol Symp 404. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.202100333
Merlini C, Soldi V, Barra G (2011) Influence of fiber surface treatment and length on physico-chemical properties of short random banana fiber-reinforced castor oil polyurethane composites. Polym Test 30:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2011.08.008
Mohammed L, Ansari MNM, Pua G, Jawaid M, Islam MS (2015) A review on natural fiber reinforced polymer composite and its applications. Int J Polym Sci 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/243947
Morandim-Giannetti AA, Agnelli JAM, Lanças BZ, Magnabosco R, Casarin SA, Bettini SHP (2012) Lignin as additive in polypropylene/coir composites: thermal, mechanical and morphological properties. Carbohydr Polym 87:2563–2568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.11.041
Moura AS, Demori R, Leão RM, Frankenberg CLC, Santana RMC (2019) The influence of the coconut fiber treated as reinforcement in PHB (polyhydroxybutyrate) composites. Mater Today Commun 18:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2018.12.006
Patel JP, Parsania PH (2018) Characterization, testing, and reinforcing materials of biodegradable composites. In: Shimpi NG (ed) Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polymer Composites – Processing, Properties and Applications. Woodhead Publishing. Cambridge, pp 55–79
Pereira PHL (2010) Estudo das propriedades físico-químicas da poliuretana derivada do óleo de mamona com potencial aplicação na área médica. Dissertation. Universidade de São Paulo
Pérez-Fonseca AA, Arellano M, Rodrigue D, Gonzalez-Núñez R, Robledo-Ortíz JR (2015) Effect of coupling agent content and water absorption on the mechanical properties of coir-agave fibers reinforced polyethylene hybrid composites. Polym Compos 37:3015–3024. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23498
Pizzi A (1994) Advanced wood adhesives technology. Wiley, New York
Protásio TP, Costa JS, Scatolino MV, Lima MDR, Assis MR, Silva MG, Bufalino L, Dias Junior AF, Trugilho PF (2021) Revealing the influence of chemical compounds on the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic wastes from the Amazonian production chains. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03416-w
Ramlee NA, Jawaid M, Yamani SAK, Zainudin ES, Alamery S (2021) Effect of surface treatment on mechanical, physical and morphological properties of oil palm/bagasse fiber reinforced phenolic hybrid composites for wall thermal insulation application. Constr Build Mater 276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.122239
Renreng I, Soenoko R, Pratikto IYS (2017) Effect of turmeric (Curcumae longae) treatment on morphology and chemical properties of Akaa (Corypha) single fiber. J Eng Sci Technol 12:2229–2237
Rojas-Valencia MN, Galeana-Olvera E, Fernández-Rojas DY, Mendoza-Buenrostro C, Nájera-Aguilar HA, Vaca-Mier M (2018) Isolation of cellulose nanofibrils from coconut waste for the production of sewing thread. Adv Mater Sci 3:1–3. https://doi.org/10.15761/AMS.1000135
Sair S, Oushabi A, Kammouni A, Tanane O, Abboud Y, El Bouari A (2018) Mechanical and thermal conductivity properties of hemp fiber reinforced polyurethane composites. Case Stud Constr Mater 8:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2018.02.001
Salazar VLP, Leão AL, Rosa DS, Gomez JGC, Alli RCP (2011) Biodegradation of coir and sisal applied in the automotive industry. J Polym Environ 19:677–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-011-0315-3
Sanal I, Verma D (2019) Construction materials reinforced with natural products. In: Martínez LMT et al (eds) Handbook of Ecomaterials. Springer Nature. Switzerland, pp 1–24
Selvi ST, Sunitha R, Ammayappan L, Prakash C (2022) Impact of chemical treatment on surface modification of Agave Americana fibres for composite application – a futuristic approach. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2022.2142726
Suardana NPG, Piao Y, Lim JK (2011) Mechanical properties of hemp fibers and hemp/PP composites: effects of chemical surface treatment. Mater Phys Mech 11:1–8
Sudhakara P, Jagadeesh D, Wang Y, Prasad CV, Devi AK, Balakrishnan G, Kim B, Song J (2013) Fabrication of Borassus fruit lignocellulose fiber/PP composites and comparison with jute, sisal and coir fibers. Carbohydr Polym 98:1002–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.06.080
Tahir MH, Zhao Z, Ren J, Rasool T, Naqvi SR (2019) Thermo-kinetics and gaseous product analysis of banana peel pyrolysis for its bioenergy potential. Biomass Bioenergy 122:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.01.009
Tan S, Abraham T, Ference D, Macosko CW (2011) Rigid polyurethane foams from a soybean oil-based polyol. Polym 52:2840–2846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2011.04.040
Tran LQN, Fuentes C, Dupont-Gillain C, Van Vuure A, Verpoest I (2013) Understanding the interfacial compatibility and adhesion of natural coir fibre thermoplastic composites. Compos Sci Technol 80:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.03.004
United Nations Environment Programme (2022) Global status report for buildings and construction: towards a zero-emission, efficient and resilient buildings and construction sector. https://wedocs.unep.org/handle/20.500.11822/41133, 2022 (accessed 18 November 2022)
Verma D, Gope P, Shandilya A, Gupta A, Maheshwari M (2013) Coir fibre reinforcement and application in polymer composites: a review. J Mater Environ Sci 4:263–276
Vilar WD (1993) Química e tecnologia dos poliuretanos. Grupo Pronor, São Paulo
Wang B, Yan L, Kasal B (2022) A review of coir fibre and coir fibre reinforced cement-based composite materials (2000–2021). J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130676
Widnyana A, Rian IG, Surata IW, Nindhia TGT (2020) Tensile properties of coconut coir single fiber with alkali treatment and reinforcement effect on unsaturated polyester polymer. Mater Today Proc 22:300–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.08.155
Yan L, Chouw N, Huang L, Kasal B (2016) Effect of alkali treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of coir fibres, coir fibre reinforced-polymer composites and reinforced-cementitious composites. Constr Build Mater 112:168–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.182
Yussof RB, Takagi H, Nakagaito AN (2016) Tensile and flexural properties of polylactic acid-based hybrid green composites reinforced by kenaf, bamboo and coir fibers. Ind Crops Prod 94:562–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.017
Zanini NC, Souza AG, Barbosa RFS, Rosa DS, Mulinari DR (2021) Eco-friendly composites of polyurethane and sheath palm residues. J Cell Plast. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021955X20987150
Zhang L, Hu Y (2014) Novel lignocellulosic hybrid particleboard composites made from rice straws and coir fibers. Mater Des 55:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.066
Zhou Y, Zhang L, Zhang M, Lihong H (2013) The study of mechanical behavior and fame retardancy of castor oil phosphate-based rigid polyurethane foam composites containing expanded graphite and triethyl phosphate. Polym Degrad Stab 98:2784–2794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.10.015
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Postgraduate Program in Biomaterials Engineering (PPGBIOMAT) of the Federal University of Lavras (UFLA) for providing material and infrastructure. The authors are also grateful to the National Council for Scientifc and Technological Development (CNPq) and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES). We also thank the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) for the postdoctoral scholarships (Process APQ-04368-22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Douglas Lamounier Faria: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing the original draft; Lourival Marin Mendes and José Benedito Guimarães Junior: supervision, funding acquisition, and project administration. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable. This manuscript does not involve researching humans or animals.
Consent to participate
All of the authors consented to participate in the drafting of this manuscript.
Consent for publication
All of the authors consented to publish this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Faria, D.L., Mendes, L.M. & Junior, J.B.G. Effect of surface treatment on the technological properties of coconut fiber–reinforced plant polyurethane composites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 52124–52140 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25946-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25946-1