Abstract
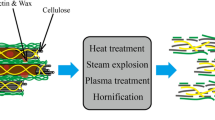
This paper deals with the enhancement of thermal insulation of building construction materials by the incorporation of treated natural fibers (posidonia oceanica and esparto grass). The surface treatment of the natural fibers aimed at the improvement of the adhesion between fibers and construction material matrices. Untreated and treated posidonia oceanica and esparto grass fibers have been characterized through Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy. The obtained results indicated a clear change in the surface morphology, enhancement in the crystallinity, and modification in the chemical structure of the treated posidonia oceanica and esparto grass fibers in comparison with untreated fibers. Experimental investigations have been carried out to examine the effect of the incorporation of treated posidonia oceanica and esparto grass fibers on the interfacial adhesion with matrices, the compressive strength of cement and gypsum composite samples compared to those with untreated fibers and their thermal properties. Results indicated, on the one hand, an improvement of the interfacial adhesion and compressive strength of matrices filled with treated fibers compared to those filled with untreated fibers. On the other hand, results have shown a clear reduction in thermal diffusivity, thermal conductivity, and bulk density of composites with the addition of treated fibers compared to those of composites without fibers. Finally, the treated posidonia oceanica and esparto grass utilized can replace conventional synthetic fibers and will be an interesting alternative that would solve simultaneously environmental and energy concerns.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinyemi BA, Dai C (2020) Development of banana fibers and wood bottom ash modified cement mortars. Constr Build Mater 241:118041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118041
Asadi I, Shafigh P, Hashemi M et al (2021) Thermophysical properties of sustainable cement mortar containing oil palm boiler clinker (OPBC) as a fine aggregate. Constr Build Mater 268:121091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121091
Statistical Review BP (2021) Statistical Review of World Energy globally consistent data on world energy markets and authoritative publications in the field of energy. BP Energy Outlook 70:8–20
Bamaga SO (2022) Physical and mechanical properties of mortars containing date palm fibers. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac48b7
Bayraktar OY, Citoglu GS, Belgin CM et al (2019a) Investigation of effect of brick dust and silica fume on the properties of portland cement mortar. Fresenius Environ Bull 28:7823–7832
Bayraktar OY, Citoglu GS, Belgin CM, Cetin M (2019b) Investigation of the mechanical properties of marble dust and silica fume substituted portland cement samples under high temperature effect. Fresenius Environ Bull 28:3865–3875
Benmansour N, Agoudjil B, Gherabli A et al (2014) Thermal and mechanical performance of natural mortar reinforced with date palm fibers for use as insulating materials in building. Energy Build 81:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.05.032
Boumhaout M, Boukhattem L, Hamdi H et al (2017) Thermomechanical characterization of a bio-composite building material: Mortar reinforced with date palm fibers mesh. Constr Build Mater 135:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.217
Braiek A, Karkri M, Adili A et al (2017) Estimation of the thermophysical properties of date palm fibers/gypsum composite for use as insulating materials in building. Energy Build 140:268–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.02.001
Chaiwong W, Samoh N, Eksomtramage T, Kaewtatip K (2019) Surface-treated oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber improved tensile strength and water resistance of wheat gluten-based bioplastic. Compos Part B Eng 176:107331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107331
Charai M, Sghiouri H, Mezrhab A, Karkri M (2021) Thermal insulation potential of non-industrial hemp (Moroccan cannabis sativa L.) fibers for green plaster-based building materials. J Clean Prod 292:126064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126064
Colinart T, Pajeot M, Vinceslas T et al (2021) Thermal conductivity of biobased insulation building materials measured by hot disk: possibilities and recommendation. J Build Eng 43:102858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102858
El Wardi FZ, Cherki AB, Mounir S et al (2019) Thermal characterization of a new multilayer building material based on clay, cork and cement mortar. Energy Procedia 157:480–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.212
Fiore V, Di Bella G, Valenza A (2020) Effect of sheep wool fibers on thermal insulation and mechanical properties of cement-based composites. J Nat Fibers 17:1532–1543. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2019.1584075
Holechek JL, Geli HME, Sawalhah MN, Valdez R (2022) A global assessment: can renewable energy replace fossil fuels by 2050? Sustain 14:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14084792
Horma O, Charai M, El Hassani S et al (2022) Thermo-physical and mechanical characterization of cement-based mortar incorporating spent tea. J Build Eng 52:104392. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOBE.2022.104392
Hung Anh LD, Pásztory Z (2021) An overview of factors influencing thermal conductivity of building insulation materials. J Build Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102604
Karimah A, Ridho MR, Munawar SS et al (2021) A review on natural fibers for development of eco-friendly bio-composite: characteristics, and utilizations. J Mater Res Technol 13:2442–2458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.014
Koohestani B, Darban AK, Mokhtari P et al (2019) Comparison of different natural fiber treatments: a literature review. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:629–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1890-9
Koru M (2016) Determination of thermal conductivity of closed-cell insulation materials that depend on temperature and density. Arab J Sci Eng 41:4337–4346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2122-6
Kumar S, Vedrtnam A, Pawar SJ (2019) Effect of wood dust type on mechanical properties, wear behavior, biodegradability, and resistance to natural weathering of wood-plastic composites. Front Struct Civ Eng 13:1446–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-019-0568-9
Lertwattanaruk P, Suntijitto A (2015) Properties of natural fiber cement materials containing coconut coir and oil palm fibers for residential building applications. Constr Build Mater 94:664–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.07.154
Momoh EO, Osofero AI (2020) Recent developments in the application of oil palm fibers in cement composites. Front Struct Civ Eng 14:94–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-019-0576-9
Nam S, French AD, Condon BD, Concha M (2016) Segal crystallinity index revisited by the simulation of X-ray diffraction patterns of cotton cellulose Iβ and cellulose II. Carbohydr Polym 135:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.08.035
Neto JSS, Lima RAA, Cavalcanti DKK et al (2019) Effect of chemical treatment on the thermal properties of hybrid natural fiber-reinforced composites. J Appl Polym Sci 136:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47154
Oushabi A (2019) The pull-out behavior of chemically treated lignocellulosic fibers/polymeric matrix interface (LF/PM): a review. Compos Part B Eng 174:107059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107059
Reddy KO, Ashok B, Reddy KRN et al (2014) Extraction and characterization of novel lignocellulosic fibers from Thespesia lampas plant. Int J Polym Anal Charact 19:48–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/1023666X.2014.854520
Ren D, Yu Z, Li W et al (2014) The effect of ages on the tensile mechanical properties of elementary fibers extracted from two sympodial bamboo species. Ind Crops Prod 62:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.08.014
Rokbi M, Baali B, Rahmouni ZEA, Latelli H (2019) Mechanical properties of polymer concrete made with jute fabric and waste marble powder at various woven orientations. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:5087–5094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02367-7
Santoni A, Bonfiglio P, Fausti P et al (2019) Improving the sound absorption performance of sustainable thermal insulation materials: natural hemp fibres. Appl Acoust 150:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.02.022
Sena Neto AR, Araujo MAM, Barboza RMP et al (2015) Comparative study of 12 pineapple leaf fiber varieties for use as mechanical reinforcement in polymer composites. Ind Crops Prod 64:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.10.042
Taban E, Khavanin A, Faridan M et al (2020) Comparison of acoustic absorption characteristics of coir and date palm fibers: experimental and analytical study of green composites. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02304-8
Taoukil D, El-bouardi A, Ezbakhe H, Ajzoul T (2011) Thermal proprieties of concrete lightened by wood aggregates. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 3:113–116
Uma Maheswari C, Obi Reddy K, Muzenda E et al (2012) Extraction and characterization of cellulose microfibrils from agricultural residue—Cocos nucifera L. Biomass Bioenerg 46:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.06.039
Vitiello D, Nait-Ali B, Tessier-Doyen N et al (2021) Thermal conductivity of insulating refractory materials: comparison of steady-state and transient measurement methods. Open Ceram 6:100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceram.2021.100118
Zhou Y, Fan M, Chen L (2016) Interface and bonding mechanisms of plant fibre composites: an overview. Compos Part B Eng 101:31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPOSITESB.2016.06.055
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Research and Technology Centre of Energy for providing the necessary instruments to realize this research work.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: S. R. Sabbagh-Yazdi.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guesmi, H., Adili, A. & Dehmani, L. Effect of fibers surface treatments on the mechanical and thermal properties of composites reinforced by eco-friendly fibers. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 9505–9520 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04611-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04611-z