Abstract
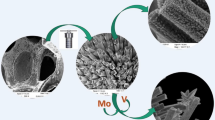
The development of efficient, low-cost, stable, non-noble-metal electrocatalysts for water splitting, particularly those that can catalyze both the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) at the cathode and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) at the anode, is a challenge. We have developed a facile method for synthesizing CoSe2 nanoparticles uniformly anchored on carbon fiber paper (CoSe2/CF) via pyrolysis and selenization of in situ grown zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67). CoSe2/CF shows high and stable catalytic activity in both the HER and OER in alkaline solution. At a low cell potential, i.e., 1.63 V, a water electrolyzer equipped with two CoSe2/CF electrodes gave a water-splitting current of 10 mA·cm−2. At a current of 20 mA·cm−2, it can operate without degradation for 30 h. This study not only offers a cost-effective solution for water splitting but also provides a new strategy for developing various catalytic nanostructures by changing the metal–organic framework precursors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morales-Guio, C. G.; Stern, L. A.; Hu, X. L. Nanostructured hydrotreating catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6555–6569.
Zou, X. X.; Zhang, Y. Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5148–5180.
Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen- and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2060–2086.
Faber, M. S.; Jin, S. Earth-abundant inorganic electrocatalysts and their nanostructures for energy conversion applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3519–3542.
Greeley, J.; Jaramillo, T. F.; Bonde, J.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J. K. Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 909–913.
Walter, M. G.; Warren, E. L.; McKone, J. R.; Boettcher, S. W.; Mi, Q. X.; Santori, E. A.; Lewis, N. S. Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446–6473.
Skúlason, E.; Karlberg, G. S.; Rossmeisl, J.; Bligaard, T.; Greeley, J.; Jónsson, H.; Nørskov, J. K. Density functional theory calculations for the hydrogen evolution reaction in an electrochemical double layer on the Pt(111) electrode. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 3241–3250.
Lee, Y.; Suntivich, J.; May, K. J.; Perry, E. E.; Shao-Horn, Y. Synthesis and activities of rutile IrO2 and RuO2 nanoparticles for oxygen evolution in acid and alkaline solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 399–404.
Ledendecker, M.; Krick Calderón, S.; Papp, C.; Steinrück, H. P.; Antonietti, M.; Shalom, M. The synthesis of nano-structured Ni5P4 films and their use as a non-noble bifunctional electrocatalyst for full water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 12538–12542.
Dai, L. M.; Xue, Y. H.; Qu, L. T.; Choi, H.-J.; Baek, J.-B. Metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4823–4892.
Zhu, W. X.; Yue, X. Y.; Zhang, W. T.; Yu, S. X.; Zhang, Y. H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. L. Nickel sulfide microsphere film on Ni foam as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1486–1489.
Ran, J. R.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J. G.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Earth-abundant cocatalysts for semiconductor-based photocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7787–7812.
Kaeffer, N.; Chavarot-Kerlidou, M.; Artero, V. Hydrogen evolution catalyzed by cobalt diimine–dioxime complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1286–1295.
Merki, D.; Hu, X. L. Recent developments of molybdenum and tungsten sulfides as hydrogen evolution catalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3878–3888.
Sun, C. C.; Yang, J.; Dai, Z. Y.; Wang, X. W.; Zhang, Y. F.; Li, L. Q.; Chen, P.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. C. Nanowires assembled from MnCo2O4@C nanoparticles for water splitting and all-solid-state supercapacitor. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1300–1309.
Zhu, J. X.; Sakaushi, K.; Clavel, G.; Shalom, M.; Antonietti, M.; Fellinger, T.-P. A general salt-templating method to fabricate vertically aligned graphitic carbon nanosheets and their metal carbide hybrids for superior lithium ion batteries and water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5480–5485.
Kong, D. S.; Cha, J. J.; Wang, H. T.; Lee, H. R.; Cui, Y. First-row transition metal dichalcogenide catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3553–3558.
Suntivich, J.; May, K. J.; Gasteiger, H. A.; Goodenough, J. B.; Shao-Horn, Y. A perovskite oxide optimized for oxygen evolution catalysis from molecular orbital principles. Science 2011, 334, 1383–1385.
Liu, Y. W.; Cheng, H.; Lyu, M. J.; Fan, S. J.; Liu, Q. H.; Zhang, W. S.; Zhi, Y. D.; Wang, C. M.; Xiao, C.; Wei, S. Q. et al. Low overpotential in vacancy-rich ultrathin CoSe2 nanosheets for water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15670–15675.
Zhu, Q. L.; Xu, Q. Metal–organic framework composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5468–5512.
Li, H. L.; Eddaoudi, M.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal–organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279.
Murray, L. J.; Dincă, M.; Long, J. R. Hydrogen storage in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1294–1314.
Lee, J.; Farha, O. K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K. A.; Nguyen, S. T.; Hupp, J. T. Metal–organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459.
Jiang, H.-L.; Akita, T.; Ishida, T.; Haruta, M.; Xu, Q. Synergistic catalysis of Au@ Ag core−shell nanoparticles stabilized on metal−organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1304–1306.
Hu, Z. C.; Deibert, B. J.; Li, J. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5815–5840.
Zhang, M.; Feng, G. X.; Song, Z. G.; Zhou, Y.-P.; Chao, H.-Y.; Yuan, D. Q.; Tan, T. T. Y.; Guo, Z. G.; Hu, Z. G.; Tang, B. Z. et al. Two-dimensional metal–organic framework with wide channels and responsive turn-on fluorescence for the chemical sensing of volatile organic compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7241–7244.
He, C. B.; Liu, D. M.; Lin, W. B. Nanomedicine applications of hybrid nanomaterials built from metal-ligand coordination bonds: Nanoscale metal–organic frameworks and nanoscale coordination polymers. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11079–11108.
Xia, W.; Mahmood, A.; Zou, R. Q.; Xu, Q. Metal–organic frameworks and their derived nanostructures for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1837–1866.
Li, S.-L.; Xu, Q. Metal–organic frameworks as platforms for clean energy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1656–1683.
Zhang, L.; Wu, H. B.; Madhavi, S.; Hng, H. H.; Lou, X. W. Formation of Fe2O3 microboxes with hierarchical shell structures from metal–organic frameworks and their lithium storage properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17388–17391.
Hou, Y.; Li, J. Y.; Wen, Z. H.; Cui, S. M.; Yuan, C.; Chen, J. H. Co3O4 nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped porous carbon dodecahedrons with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium storage and water splitting. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 1–8.
Hou, Y.; Wen, Z. H.; Cui, S. M.; Ci, S. Q.; Mao, S.; Chen, J. H. An advanced nitrogen-doped graphene/cobalt-embedded porous carbon polyhedron hybrid for efficient catalysis of oxygen reduction and water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 872–882.
Wu, H. B.; Xia, B. Y.; Yu, L.; Yu, X. Y.; Lou, X. W. Porous molybdenum carbide nano-octahedrons synthesized via confined carburization in metal–organic frameworks for efficient hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6512–6519.
You, B.; Jiang, N.; Sheng, M. L.; Gul, S.; Yano, J.; Sun, Y. J. High-performance overall water splitting electrocatalysts derived from cobalt-based metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7636–7642.
Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. F.; Chen, G.; Chen, D.; Zhou, C. W.; Shen, G. Z. Hierarchical three-dimensional ZnCo2O4 nanowire arrays/carbon cloth anodes for a novel class of high-performance flexible lithium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3005–3011.
Sun, C. C.; Yang, J.; Rui, X. H.; Zhang, W. N.; Yan, Q. Y.; Chen, P.; Huo, F. W.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. C. MOFdirected templating synthesis of a porous multicomponent dodecahedron with hollow interiors for enhanced lithiumion battery anodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8483–8488.
Shi, Q.; Chen, Z. F.; Song, Z. W.; Li, J. P.; Dong, J. X. Synthesis of ZIF-8 and ZIF-67 by steam-assisted conversion and an investigation of their tribological behaviors. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 672–675.
Cabán-Acevedo, M.; Faber, M. S.; Tan, Y. Z.; Hamers, R. J.; Jin, S. Synthesis and properties of semiconducting iron pyrite (FeS2) nanowires. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1977–1982.
Feng, Y. J.; He, T.; Alonso-Vante, N. Oxygen reduction reaction on carbon-supported CoSe2 nanoparticles in an acidic medium. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 5252–5256.
Xu, Y. F.; Gao, M. R.; Zheng, Y. R.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S. H. Nickel/nickel(II) oxide nanoparticles anchored onto cobalt(IV) diselenide nanobelts for the electrochemical production of hydrogen. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8546–8550.
Van der Heide, H.; Hemmel, R.; Van Bruggen, C. F.; Haas, C. X-ray photoelectron spectra of 3d transition metal pyrites. J. Solid State Chem. 1980, 33, 17–25.
Liu, T. T.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Luo, Y. L.; Sun, X. P. An amorphous CoSe film behaves as an active and stable full water-splitting electrocatalyst under strongly alkaline conditions. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16683–16686.
Kong, D. S.; Wang, H. T.; Lu, Z. Y.; Cui, Y. CoSe2 nanoparticles grown on carbon fiber paper: An efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4897–4900.
Zhang, H. X.; Yang, B.; Wu, X. L.; Li, Z. J.; Lei, L. C.; Zhang, X. W. Polymorphic CoSe2 with mixed orthorhombic and cubic phases for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015, 7, 1772–1779.
Liang, Y. Y.; Li, Y. G.; Wang, H. L.; Zhou, J. G.; Wang, J.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. J. Co3O4 nanocrystals on graphene as a synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 780–786.
Liu, X. J.; Chang, Z.; Luo, L.; Xu, T. H.; Lei, X. D.; Liu, J. F.; Sun, X. M. Hierarchical ZnxCo3–x O4 nanoarrays with high activity for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 1889–1895.
Cui, X. J.; Ren, P. J.; Deng, D. H.; Deng, J.; Bao, X. H. Single layer graphene encapsulating non-precious metals as high-performance electrocatalysts for water oxidation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 123–129.
Zou, X. X.; Huang, X. X.; Goswami, A.; Silva, R.; Sathe, B. R.; Mikmeková, E.; Asefa, T. Cobalt-embedded nitrogen-rich carbon nanotubes efficiently catalyze hydrogen evolution reaction at all pH values. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 4461–4465.
Duan, J. J.; Chen, S.; Chambers, B. A.; Andersson, G. G.; Qiao, S. Z. 3D WS2 nanolayers@heteroatom-doped graphene films as hydrogen evolution catalyst electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4234–4241.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Self-supported nanoporous cobalt phosphide nanowire arrays: An efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0–14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7587–7590.
Pentland, N.; Bockris, J. O. M.; Sheldon, E. Hydrogen evolution reaction on copper, gold, molybdenum, palladium, rhodium, and iron: Mechanism and measurement technique under high purity conditions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1957, 104, 182–194.
de Chialvo, M. R. G.; Chialvo, A. C. Hydrogen evolution reaction: Analysis of the Volmer-Heyrovsky-Tafel mechanism with a generalized adsorption model. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 372, 209–223.
Ma, T. Y.; Dai, S.; Qiao, S. Z. Self-supported electrocatalysts for advanced energy conversion processes. Mater. Today, in press, DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.10.012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Dong, Q., Yang, J. et al. Metal–organic framework derived CoSe2 nanoparticles anchored on carbon fibers as bifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. Nano Res. 9, 2234–2243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1110-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1110-1