Abstract
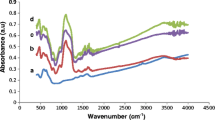
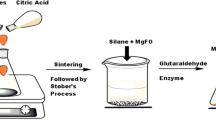
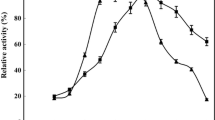
Enzymes play a pivotal role in catalyzing diverse reactions. However, their instability upon repetitive/prolonged use, as well as their inhibition by high substrates and product concentration, remains an area of concern. In this study, porcine pancreatic α-amylase was immobilized on magnetic Fe2O3 nanoparticles (Fe2O3-NPs) in order to hydrolyze starch. The magnetic nanoparticle bound enzymes retained 94% of their initial enzyme activity. X-ray diffraction and atomic force microscopy analyses showed that the prepared matrix had advantageous microenvironment and a large surface area for binding significant amounts of protein. Functional groups present in enzyme and support were monitored by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Immobilized enzyme exhibited lowered pH optimum (pH 6.0) to a greater degree than its soluble counterpart (pH 7.0). Optimum temperature for the immobilized enzyme shifted towards higher temperatures. The immobilized enzyme was significantly more resistant to inactivation caused by various metal ions and chemical denaturants. Immobilized α-amylase hydrolyzed 92% starch in a batch process, after 8 h at 40°C; while the free enzyme could hydrolyze only 73% starch under similar experimental conditions. A reusability experiment demonstrated that the immobilized enzyme retained 83% of its original activity even after its 8th repeated use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bordbar, A. K., K. Omidiyan, and R. Hosseinzadeh (2005) Study on interaction of α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis with cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide. Colloid. Surf. B: Bioint. 40: 67–71.
Abd El-Ghaffar, M. A. and M. S. Hashem (2009) Immobilization of α-amylase onto chitosan and its amino acid condensation adducts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 112: 805–814.
Akoh, C. C., S. W. Chang, G. C. Lee, and J. F. Shaw (2008) Biocatalysis for the production of industrial products and functional foods from rice and other agricultural produce. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56: 10445–104451.
Husain, Q. (2010) β Galactosidases and their potential applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 30: 41–62.
Husain, Q. (2006) Potential applications of the oxidoreductive enzymes in the decolorization and detoxification of textile and other synthetic dyes from polluted water: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 26: 201–221.
Mateo, C., O. Abian, R. Fernandez-Lafuente, and J. M. Guisan (2000) Increase in conformational stability of enzymes immobilized on epoxy-activated supports by favoring additional multipoint covalent attachment. Enz. Microb. Technol. 26: 509–515.
Chen, B., M. E. Miller, and R. A. Gross (2007) Effects of porous polystyrene resin parameters on Candida antarctica lipase B adsorption, distribution, and polyester synthesis activity. Langmuir 23: 6467–6474.
Kim, M. I., J. Kim, J. Lee, and H. Jia (2007) Crosslinked enzyme aggregates in hierarchically-ordered mesoporous silica: A simple and effective method for enzyme stabilization. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 96: 210–218.
Safarik, I. and M. Safarikova (2009) Magnetic nano and microparticles in biotechnology. Chem. Pap. 63: 497–505.
Safarikova, M., L. Ptackova, I. Kibrikova, and I. Safarık (2005) Biosorption of water-soluble dyes on magnetically modified Saccharomyces cerevisiae subsp. uvarum cells. Chemosphere 59: 831–835.
Namdeo, M. and S. K. Bajpai (2009) Immobilization of α-amylase onto cellulose-coated magnetite (CCM) nanoparticles and preliminary starch degradation study. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 59: 134–139.
Raming, T. P., A. J. Winnubst, C. M. van Kats, and A. P. Philipse (2002) The synthesis and magnetic properties of nanosized hematite (α-Fe2O3) particles. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 249: 346–350.
Bernfield, P. (1955) Amylases α and β. pp. 149–158. In: S. P. Colowick and N. O. Kaplan (eds.). Methods in enzymol. Academic press, NY.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Iyer, P. V. and L. Ananthanarayan (2008) Enzyme stability and stabilization-aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Proc. Biochem. 43: 1019–132.
Kennedy, J. F. and M. Paterson (1993) Application of cellulosic fast flow column filters to protein immobilization and recovery. Polym. Int. 32: 71–81.
Hasirci, N., S. Aksoy, and H. Tumturk (2006) Activation of poly (dimmer acid-co-alkyl polyamine) particles for covalent immobilization of α-amylase. Reac. Func. Polym. 66: 1546–1551.
Mallikarjuna, N. N., S. K. Manohar, P. V. Kulkarni, A. Venkataraman, and T. M. Aminabhavi (2005) Novel high dielectric constant nanocomposites of polyaniline dispersed with Γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 97: 1868–1874.
Weng, L., L. Zhang, D. Ruan, L. Shi, and J. Xu (2004) Thermal gelation of cellulose in a NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. Langmuir 20: 2086–2093.
Konwarh, R., N. Karak, S. K. Rai, and A. K. Mukherjee (2009) Polymer-assisted iron oxide magnetic nanoparticle immobilized keratinase. Nanotechnol. 20: 225107–225117.
Scaramuzzo, F. A., R. Salvati, B. Paci, A. Generosi, V. Rossi-Albertini, A. Latini, and M. Barteri (2009) Nanoscale in situ morphological study of proteins immobilized on gold thin films. J. Phys. Chem. B. 113: 15895–15899.
Saal, K., V. Sammelselg, A. Lohmus, E. Kuusk, G. Raidaru, T. Rinken, and A. Rinken (2002) Characterization of glucose oxidase immobilization onto mica carrier by atomic force microscopy and kinetic studies. Biomol. Eng. 19: 195–199.
Lei, C. H., Y. Shin, J. Liu, and E. J. Ackerman (2002) Entrapping enzyme in a functionalized nanoporous support. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124: 11242–11243.
Jackson, M. and H. H. Mantsch (1995) The use and misuse of FTIR spectroscopy in the determination of protein structure. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30: 95–120.
Krimm, S. and J. Bandekar (1986) Vibrational spectroscopy and conformation of peptides, polypeptides and proteins. Adv. Protein Chem. 38: 181–364.
Roig, M. G, A. Slade, and J. F. Kennedy (1993) α-Amylase immobilized on plastic supports: Stabilities, pH and temperature profiles and kinetic parameters. Biomat. Artif. Cells Immob. Biotechnol. 21: 487–525.
Bayramoglu, G., M. Yilmaz, and M. Y. Arica (2004) Immobilization of thermostable α-amylase onto reactive membranes: Kinetics characterization and application to continuous starch hydrolysis. Food Chem. 84: 591–599.
Arica, M. Y., V. Hasirci, and N. G. Alaeddinoglu (1995) Covalent immobilization of α-amylase onto pHEMA microspheres: Preparation and application to fixed bed reactor. Biomaterials 16: 761–768.
Magri, M. L., M. V. Miranda, and O. Cascone (2005) Immobilization of soybean seed coat peroxidase on polyaniline: Synthesis optimization and catalytic properties. Biocatal. Biotrans. 23: 339–346.
Lee, P. M., K. H. Lee, and S. Y. Siaw (1993) Covalent immobilization of aminoacrylase to alginate for L-phenylalanine production. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 58: 65–70.
Ramesh, M. V. and B. K. Lonsane (1990) Effect of metal salts and protein modifying agents on activity of thermostable α-amylase produced by Bacillus lichiniformis M27 under solid state fermentation. Chem. Microb. Technol. Lebensm. 12: 129–136.
Lo, H., L. Lin, H. Chen, W. Hsu, and C. Chang (2001) Enzymatic properties of a SDS-resistant Bacillus sp. TS-23 α-amylase produced by recombinant Escherichia coli. Proc. Biochem. 36: 743–750.
Makhatadze, G. I. and P. L. Privalov (1992) Protein interactions with urea and guanidinium chloride. A calorimetric study. J. Mol. Biol. 226: 491–505.
Zhou, H. X. (2004) Protein folding and binding in confined spaces and in crowded solutions. J. Mol. Recognit. 17: 368–375.
Tanriseven, A. and S. Dogan (2002) A novel method for the immobilization of β-galactosidase. Proc. Biochem. 38: 27–30.
Yagar, H., F. Ertan, and B. Balkan (2008) Comparison of some properties of free and immobilized α-amylase by Aspergillus sclerotiorum in calcium alginate gel beads. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 38: 13–23.
Shewale, S. D. and A. B. Pandit (2007) Hydrolysis of soluble starch using Bacillus licheniformis α-amylase immobilized on superporous CELBEADS. Carbohyd. Res. 342: 997–1008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.J., Husain, Q. & Azam, A. Immobilization of porcine pancreatic α-amylase on magnetic Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Applications to the hydrolysis of starch. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 377–384 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0105-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0105-8