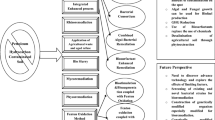
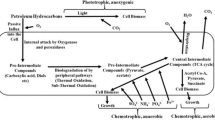
Abstract
There is an upsurge in industrial production to meet the rising demands of the rapidly growing population globally. The enormous energy demand of the growing economies still depends upon petroleum. It has also resulted in environmental pollution due to the release of petroleum origin pollutants. Soil and aquifers, especially in the direct impact zones of petroleum refineries, are the worst hit. The integrated concept of bioremediation and resource recovery offers a sustainable solution to mitigate environmental pollution. It involves biodegradation, a benign utilization of toxic wastes, and the recycling of natural resources. Bioremediation is considered an integral contributor to the emerging concepts of bio-economy and sustainable development goals. This review article aims to provide an updated overview of bioremediation involving petroleum-based contaminants. Microbial degradation is discussed as a promising strategy for petroleum refinery effluent and sludge treatment. The review also provides an insight into resource reuse and recovery as a holistic approach towards sustainable refinery waste treatment. Furthermore, the integrated technologies that deserve in-depth exploration for future study in the refinery sector are highlighted in the present study.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 March 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01072-x
References
Patel SKS, Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2016) Integrative approach for producing hydrogen and polyhydroxyalkanoate from mixed wastes of biological origin. Indian J Microbiol 56:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-016-0595-3
Patel SKS, Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2017) Dark-fermentative biological hydrogen production from mixed biowastes using defined mixed cultures. Indian J Microbiol 57:171–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-017-0643-7
Patel SKS, Ray S, Prakash J, Wee JH, Kim S-Y, Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2019) Co-digestion of biowastes to enhance biological hydrogen process by defined mixed bacterial cultures. Indian J Microbiol 59:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-018-00777-8
Patel SKS, Kondaveeti S, Otari SV, Pagolu RT, Jeong SH, Kim SC, Cho BK, Kang YC, Lee J-K (2018) Repeated batch methanol production from a simulated biogas mixture using immobilized Methylocystis bryophila. Energy 145:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.142
Imam A, Suman SK, Ghosh D, Kanaujia PK (2019) Analytical approaches used in monitoring the bioremediation of hydrocarbons in petroleum-contaminated soil and sludge. TrAC—Trends Anal Chem 118:50–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.023
Patel SKS, Jeon MS, Gupta RK, Jeon Y, Kalia VC, Kim SC, Cho BK, Kim DR, Lee J-K (2019) Hierarchical macroporous particles for efficient whole-cell immobilization: application in bioconversion of greenhouse gases to methanol. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:18968–18977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03420
Patel SKS, Shanmugam R, Kalia VC, Lee J-K (2020) Methanol production by polymer-encapsulated methanotrophs from simulated biogas in the presence of methane vector. Bioresour Technol 304:123022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123022
Patel SKS, Selvaraj C, Mardina P, Jeong J-H, Kalia VC, Kang YC, Lee J-K (2016) Enhancement of methanol production from synthetic gas mixture by Methylosinus sporium through covalent immobilization. Appl Energy 171:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.022
Patel SKS, Kumar V, Mardina P, Li J, Lestari R, Kalia VC, Lee JK (2018) Methanol production from simulated biogas mixtures by co-immobilized Methylomonas methanica and Methylocella tundrae. Bioresour Technol 263:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.096
Patel SKS, Gupta RK, Das D, Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2020) Continuous biohydrogen production from poplar biomass hydrolysate by a defined bacterial mixture immobilized on lignocellulosic materials under non-sterile conditions. J Clean Prod 287:125037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125037
Board M, Board OS, Council NR (2003) Oil in the sea III: inputs, fates, and effects. national academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/10388
Saito L, Rosen MR, Roesner L, Howard N (2010) Improving estimates of oil pollution to the sea from land-based sources. Mar Pollut Bull 60:990–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.02.003
Sun P, Elgowainy A, Wang M, Han J, Henderson RJ (2018) Estimation of US refinery water consumption and allocation to refinery products. Fuel 221:542–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.07.089
Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2020) Mapping microbial capacities for bioremediation: genes to genomics. Indian J Microbiol 60:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00842-w
Bhardwaj P, Singh KR, Jadeja NB, Phale PS, Kapley A (2020) Atrazine Bioremediation and its influence on soil microbial diversity by metagenomics analysis. Indian J Microbiol 60:388–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-020-00877-4
Musa NM, Suleiman ADI (2015) Bioremediation of petroleum refinery wastewater effluent via augmented native microbes. J Emerg Trends Eng Appl Sci 6:1–6
Isaac P, Martínez FL, Bourguignon N, Sanchez LA, Ferrero MA (2015) Improved PAHs removal performance by a defined bacterial consortium of indigenous Pseudomonas and actinobacteria from Patagonia, Argentina. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 101:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.03.014
Jamal MT, Pugazhendi A (2018) Degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons and treatment of refinery wastewater under saline condition by a halophilic bacterial consortium enriched from marine environment (Red Sea), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Biotech 8:276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1296-x
Haleyur N, Shahsavari E, Jain SS, Koshlaf E, Ravindran VB, Morrison PD, Osborn AM, Ball AS (2019) Influence of bioaugmentation and biostimulation on PAH degradation in aged contaminated soils: response and dynamics of the bacterial community. J Environ Manage 238:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.115
Raper E, Stephenson T, Anderson DR, Fisher R, Soares A (2018) Industrial wastewater treatment through bioaugmentation. Process Saf Environ Prot 118:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.06.035
Herrero M, Stuckey DC (2015) Bioaugmentation and its application in wastewater treatment: a review. Chemosphere 140:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.10.033
Low A, Zhao S, Rogers MJ, Zemb O, Lee M, He J, Manefield M (2019) Isolation, characterization and bioaugmentation of an acidotolerant 1,2-dichloroethane respiring Desulfitobacterium species from a low pH aquifer. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 95:fiz055. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiz055
Roy A, Dutta A, Pal S, Gupta A, Sarkar J, Chatterjee A, Saha A, Sarkar P, Sar P, Kazy SK (2018) Biostimulation and bioaugmentation of native microbial community accelerated bioremediation of oil refinery sludge. Bioresour Technol 253:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.004
Sarkar J, Kazy SK, Gupta A, Dutta A, Mohapatra B, Roy A, Bera P, Mitra A, Sar P (2016) Biostimulation of indigenous microbial community for bioremediation of petroleum refinery sludge. Front Microbiol 7:1407. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01407
Sun Y, Chen W, Wang Y, Guo J, Zhang H, Hu X (2021) Nutrient depletion is the main limiting factor in the crude oil bioaugmentation process. J Environ Sci 100:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.07.025
Borah D, Yadav RNS (2017) Bioremediation of petroleum based contaminants with biosurfactant produced by a newly isolated petroleum oil degrading bacterial strain. Egypt J Pet 26:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2016.02.005
Marchut-Mikolajczyk O, Drożdżyński P, Pietrzyk D, Antczak T (2018) Biosurfactant production and hydrocarbon degradation activity of endophytic bacteria isolated from Chelidonium majus L. Microb Cell Fact 17:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1017-5
Gharibzadeh F, Kalantary RR, Nasseri S, Esrafill A, Azari A (2016) Reuse of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminated soil washing effluent by bioaugmentation/biostimulation process. Sep Purif Technol 168:248–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.05.022
Zhang Z, Lo IMC (2015) Biostimulation of petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated marine sediment with co-substrate: involved metabolic process and microbial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:5683–5696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6420-9
Varjani S, Upasani VN (2019) Comparing bioremediation approaches for agricultural soil affected with petroleum crude: a case study. Indian J Microbiol 59:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00814-0
Chen M, Xu P, Zeng G, Yang C, Huang D, Zhang J (2015) Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol Adv 33:745–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.05.003
Kästner M, Miltner A (2016) Application of compost for effective bioremediation of organic contaminants and pollutants in soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:3433–3449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7378-y
Xu P, Lai C, Zeng G, Huang D, Chen M, Song B, Peng X, Wan J, Hu L, Duan A, Tang W (2018) Enhanced bioremediation of 4-nonylphenol and cadmium co-contaminated sediment by composting with Phanerochaete chrysosporium inocula. Bioresour Technol 250:625–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.069
Leech C, Tighe MK, Pereg L, Winter G, McMillan M, Esmaeili A, Wilson SC (2020) Bioaccessibility constrains the co-composting bioremediation of field aged PAH contaminated soils. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 149:104922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.104922
Abtahi H, Parhamfar M, Saeedi R, Villasenor J, Sartaj M, Kumar V, Coulon F, Parhamfar M, Didehdar M, Seifi H, Koolivand A (2020) Effect of competition between petroleum-degrading bacteria and indigenous compost microorganisms on the efficiency of petroleum sludge bioremediation: field application of mineral-based culture in the composting process. J Environ Manage 258:110013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.110013
Koolivand A, Rajaei MS, Ghanadzadeh MJ, Saeedi R, Abtahi H, Godini K (2017) Bioremediation of storage tank bottom sludge by using a two-stage composting system: effect of mixing ratio and nutrients addition. Bioresour Technol 235:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.100
Patel SKS, Choi SH, Kang YC, Lee J-K (2016) Large-scale aerosol-assisted synthesis of biofriendly Fe2O3 yolk–shell particles: a promising support for enzyme immobilization. Nanoscale 8:6728–6738. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR00346J
Patel SKS, Choi H, Lee J-K (2019) Multi-metal based inorganic-protein hybrid system for enzyme immobilization. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:13633–13638. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02583
Patel SKS, Gupta RK, Kim S-Y, Kim I-W, Kalia VC, Lee J-K (2020) Rhus vernicifera laccase immobilization on magnetic nanoparticles to improve stability and its potential application in Bisphenol A Degradation. Indian J Microbiol 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-020-00912-4
Okino-Delgado CH, Zanutto-Elgui MR, do Prado DZ, Pereira MS, Fleuria LF (2019) Enzymatic bioremediation: current status, challenges of obtaining process, and applications. In: Microbial metabolism of xenobiotic compounds. Springer, pp 79–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7462-3_4
Patel SKS, Choi SH, Kang YC, Lee J-K (2017) Eco-friendly composite of Fe3O4-reduced graphene oxide particles for efficient enzyme immobilization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2213–2222. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b05165
Patel SKS, Otari SV, Li J, Kim DP, Kim SC, Cho B-K, Kalia VC, Kang YC, Lee J-K (2018) Synthesis of cross-linked protein-metal hybrid nanoflowers and its application in repeated batch decolorization of synthetic dyes. J Hazard Mater 347:442–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.003
Kumar V, Shahi SK, Singh S (2018) Bioremediation: an eco-sustainable approach for restoration of contaminated sites. In: Microbial bioprospecting for sustainable development. Springer, pp 115–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0053-0_6
Zhang S, Ning Y, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Yang X, Wu K, Yang S, La G, Sun X, Li X (2015) Contrasting characteristics of anthracene and pyrene degradation by wood rot fungus Pycnoporus sanguineus H1. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 105:228–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.09.012
Suganthi SH, Murshid S, Sriram S, Ramani K (2018) Enhanced biodegradation of hydrocarbons in petroleum tank bottom oil sludge and characterization of biocatalysts and biosurfactants. J Environ Manage 220:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.120
Agrawal N, Verma P, Shahi SK (2018) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons ( phenanthrene and pyrene ) by the ligninolytic fungi Ganoderma lucidum isolated from the hardwood stump. Bioresour Bioprocess. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-018-0197-5
Apriceno A, Bucci R, Girelli AM (2017) Immobilization of laccase from Trametes versicolor on chitosan macrobeads for anthracene degradation. Anal Lett 50:2308–2322. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2017.1282504
Patel SKS, Singh RK, Kumar A, Jeong JH, Jeong SH, Kalia VC, Kim I-W, Lee J-K (2017) Biological methanol production by immobilized Methylocella tundrae using simulated biohythane as a feed. Bioresour Technol 241:922–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.160
Prakash J, Sharma R, Patel SKS, Kim IW, Kalia VC (2018) Bio-hydrogen production by co-digestion of domestic wastewater and biodiesel industry effluent. PLoS ONE 13:e0199059. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199059
Patel SKS, Gupta RK, Kondaveeti S, Otari SV, Kumar A, Kalia VC, Lee J-K (2020) Conversion of biogas to methanol by methanotrophs immobilized on chemically modified chitosan. Bioresour Technol 315:123791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123791
Patel SKS, Kalia VC, Joo JB, Kang YC, Lee J-K (2020) Biotransformation of methane into methanol by methanotrophs immobilized on coconut coir. Bioresour Technol 297:122433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122433
Banerjee A, Ghoshal AK (2016) Biodegradation of real petroleum wastewater by immobilized hyper phenol-tolerant strains of Bacillus cereus in a fluidized bed bioreactor. Biotech 6:137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0447-1
Costa AS, Romão LPC, Araújo BR, Lucas SCO, Maciel STA, Wisniewski A, Alexandre MR (2012) Bioresource Technology Environmental strategies to remove volatile aromatic fractions ( BTEX ) from petroleum industry wastewater using biomass. Bioresour Technol 105:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.096
Imam A, Suman SK, Singh R, Vempatapu BP, Ray A, Kanaujia PK (2020) Application of laccase immobilized rice straw biochar for anthracene degradation. Environ Pollut 11582 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115827
Akhbarizadeh R, Moore F, Mowla D, Keshavarzi B (2018) Improved waste-sourced biocomposite for simultaneous removal of crude oil and heavy metals from synthetic and real oilfield-produced water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:31407–31420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3136-2
Kondaveeti S, Kim I-W, Otari S, Patel SKS, Pagolu R, Losetty V, Kalia VC, Lee J-K (2019) Co-generation of hydrogen and electricity from biodiesel process effluents. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:27285–27296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.08.258
Patel SKS, Kumar P, Singh M, Lee J-K, Kalia, (2015) Integrative approach to produce hydrogen and polyhydroxybutyrate from biowaste using defined bacterial cultures. Bioresour Technol 176:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.138
Patel SKS, Gupta RK, Kalia VC, Lee J-K (2021) Integrating anaerobic digestion of potato peels to methanol production by methanotrophs immobilized on banana leaves. Bioresour Technol 323:124550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124550
Guo X, Zhan Y, Chen C, Sun S, Zhao L, Guo S (2015) Simultaneous bioelectricity generation and biodegradability improvement of refinery wastewater using microbial fuel cell technology. Desalin Water Treat 53:2740–2745. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.931535
Mohanakrishna G, Abu-Reesh IM, Kondaveeti S, AI-Raoush RI, He Z, (2018) Enhanced treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater by short-term applied voltage in single chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 253:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.005
Nasirpour N, Mousavi SM, Shojaosadati SA (2015) Biodegradation potential of hydrocarbons in petroleum refinery effluents using a continuous anaerobic-aerobic hybrid system. Korean J Chem Eng 32:874–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0307-9
Hallenbeck PC, Ghosh D, Skonieczny MT, Yargeau V (2009) Microbiological and engineering aspects of biohydrogen production. Indian J Microbiol 49:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-009-0010-4
Purohit HJ (2019) Aligning microbial biodiversity for valorization of biowastes: conception to perception. Indian J Microbiol 59:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00826-w
Kondaveeti S, Patel SKS, Pagolu R, Li J, Kalia VC, Choi M-S, Lee J-K (2019) Conversion of simulated biogas to electricity: sequential operation of methanotrophic reactor effluents in microbial fuel cell. Energy 189:116309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116309
Rehman K, Imran A, Amin I, Afzal M (2019) Enhancement of oil field-produced wastewater remediation by bacterially-augmented floating treatment wetlands. Chemosphere 217:576–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.041
Sudarsan JS, Annadurai R, Subramani S, George RB (2016) Petrochemical wastewater treatment using constructed wetland technique. Pollut Res 35:727–732
Agarry SE, Oghenejoboh KM, Latinwo GK, Owabor CN (2020) Biotreatment of petroleum refinery wastewater in vertical surface-flow constructed wetland vegetated with Eichhornia crassipes: lab-scale experimental and kinetic modelling. Environ Technol 41:1793–1813. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1549106
Mustapha HI, Van Bruggen JJA, Lens PNL (2018) Fate of heavy metals in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating secondary treated petroleum refinery wastewater in Kaduna, Nigeria. Int J Phytoremediation 20:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1337062
Sudarsan JS, Subramani S, Rajan RJ, Shah I, Nithiyananantham S (2018) Simulation of constructed wetland in treating wastewater using fuzzy logic technique. JPhCS 1000:12137. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1000/1/012137
Yang Q, Wu Z, Liu L, Zhang F, Liang S (2016) Treatment of oil wastewater and electricity generation by integrating constructed wetland with microbial fuel cell. Materials (Basel) 9:885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9110885
Wei M, Rakoczy J, Vogt C, Harnisch F, Schumann R, Richnow HH (2015) Enhancement and monitoring of pollutant removal in a constructed wetland by microbial electrochemical technology. Bioresour Technol 196:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.07.111
Sarkar J, Roy A, Sar P, Kazy SK (2020) Accelerated bioremediation of petroleum refinery sludge through biostimulation and bioaugmentation of native microbiome. In: Emerging technologies in environmental bioremediation. Elsevier, pp 23–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819860-5.00002-X
Rajmohan KS, Chandrasekaran R, Varjani S (2020) A Review on occurrence of pesticides in environment and current technologies for their remediation and management. Indian J Microbiol 60:125–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00841-x
Liu C, Zhang Y, Sun S, Huang L, Yu L, Liu X, Lai R, Luo Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Z (2018) Oil recovery from tank bottom sludge using rhamnolipids. J Pet Sci Eng 170:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.031
Vemic M, Bordas F, Guibaud G, Lens PNL, Van-Hullebusch EDV (2017) Leaching and recovery of molybdenum from spent catalysts. In: Sustainable heavy metal remediation. Springer, New York, pp 207–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61146-4_7
Srichandan H, Singh S, Blight K, Pathak A, Kim DJ, Lee S, Lee SW (2015) An integrated sequential biological leaching process for enhanced recovery of metals from decoked spent petroleum refinery catalyst: a comparative study. Int J Miner Process 134:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2014.11.002
Srichandan H, Singh S, Pathak A, Kim DJ, Lee S-W, Heyes G (2014) Bioleaching of metals from spent refinery petroleum catalyst using moderately thermophilic bacteria: effect of particle size. J Environ Sci Heal Part A 49:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2014.882211
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, under the project OLP-1094. INSPIRE fellowship of the first author from Department of Science and Technology, India is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations of competing interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised as affiliation 3 had incorrect information.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Imam, A., Kanaujia, P.K., Ray, A. et al. Removal of Petroleum Contaminants Through Bioremediation with Integrated Concepts of Resource Recovery: A Review. Indian J Microbiol 61, 250–261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00928-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00928-4