Abstract
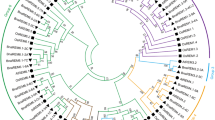
Starch is one of two crucial products of photosynthetic carbon-assimilation and mainly functions as the unit of energy storage in most crops such as rice, maize and sorghum, whereas interestingly in sugarcane that unit of energy storage is sucrose. Mature sugarcane stalk tissue has a very large apoplastic volume and contains nearly 700 mM sucrose—which is among the highest recorded sucrose concentrations in plant tissue. We identified 9 genes of starch synthases (SSs) related to the starch synthesis pathway in the genome of S. spontaneum. Based on gene structure and phylogenetic analysis, SSs genes were clustered into five clades and were relatively conserved. In S. spontaneum, the SS is a very ancient gene family, in which, SSIIIa and SSIIIb originated from the ρ-whole genome duplications (WGDs), SSIIb and SsIIc originated from gene duplication after the split of monocots and dicots; GBSSI and GBSSII in Clade V and SSIIa in Clade II were retained from the ε-WGD, and the remaining two SSs (SSI and SSIV) were retained from the very ancient gene duplication event about 355–389 million year ago (Mya). In addition, we found all SS genes were under the influence of strong purification with a Ka/Ks ratio of less than 0.5 in S. spontaneum. In the 5 families, SSIIIa, SSIIb and GBSSII had relatively predominant expression levels in all the examined tissues from the two Saccharum species, indicating the three genes were the fundamental members in the non-storage tissues, leaf or stem, which is in agreement with previous studies. Interestingly, the expression levels of SSs in stems showed significantly higher values in S. spontenum than in S. officinarum at pre-mature and mature stages. These results were negatively correlated with the sucrose levels between the two Saccharum species. At the pre-mature and mature stages, the sucrose contents in stems from S. officinarum were much higher than in stems from S. spontenum, suggesting that SSs involved in the differential of carbohydrate metabolism between the two Saccharum species. Besides, the expression of SSs displayed a clearly consistent trend in line with normal distribution under the diurnal rhythms of S. spontaneum. Moreover, the expression pattern of SSIIIa, SSIIb and GBSSII displayed a clearly consistent trend in both Saccharum species and in maize, rice, which was in accordance with photosynthetic intensity across leaf gradients. This result suggested the functional constraints for the SSs gene family in Gramineae. Our results are valuable for further functional analysis of SSs genes and provided the foundation for carbohydrate metabolism in sugarcane.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball S, Colleoni C, Cenci U, Raj JN, Tirtiaux C (2011) The evolution of glycogen and starch metabolism in eukaryotes gives molecular clues to understand the establishment of plastid endosymbiosis. J Exp Bot 62. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq411
Batra R et al (2017) Comparative Analysis of AGPase Genes and Encoded Proteins in Eight Monocots and Three Dicots with Emphasis on Wheat. Front Plant Sci 8:19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00019
Bläsing OE, Stitt M (2005) Sugars and circadian regulation make major contributions to the global regulation of diurnal gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:3257
Bonnett GD (2013) Developmental Stages (Phenology). In: Sugarcane: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Functional Biology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, pp 35–53. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118771280.ch3
Campbell BC et al (2016) Domestication and the storage starch biosynthesis pathway: signatures of selection from a whole sorghum genome sequencing strategy. Plant Biotechnol J 14:2240–2253. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12578
Cheng J et al (2012) Diversification of genes encoding granule-bound starch synthase in monocots and dicots is marked by multiple genome-wide duplication events. PLoS One 7:e30088. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030088
D’Hont A (2005) Unraveling the genome structure of polyploids using FISH and GISH; examples of sugarcane and banana. Cytogenetic and Genome Research 109:27–33
Deschamps P et al (2008) Metabolic symbiosis and the birth of the plant kingdom. Mol Biol Evol 25. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm280
Dian W, Jiang H, Wu P (2005) Evolution and expression analysis of starch synthase III and IV in rice. J Exp Bot 56:623–632. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri065
Edger PP, Pires JC (2009) Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes. Chromosome Research An International Journal on the Molecular Supramolecular & Evolutionary Aspects of Chromosome Biology 17:699
Feike D et al (2016) The Starch Granule-Associated Protein EARLY STARVATION1 Is Required for the Control of Starch Degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana Leaves. Plant Cell 28:1472–1489. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00011
Finn RD et al (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D222
Grivet L, Glaszmann J-C, D'Hont A (2003) Molecular evidence for sugarcane evolution and domestication. Paper presented at the Molecular Biology Workshop, Montpellier, France, 2003-04-07 / 2003-04-11
Guindon S, Gascuel O, Rannala B (2003) A Simple, Fast, and Accurate Algorithm to Estimate Large Phylogenies by Maximum Likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150390235520
Hirose T, Terao T (2004) A comprehensive expression analysis of the starch synthase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 220:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1314-6
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296
Hu W et al (2018) New insights into the evolution and functional divergence of the SWEET family in Saccharum based on comparative genomics. BMC Plant Biol 18:270. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1495-y
Ingkasuwan P et al (2012) Inferring transcriptional gene regulation network of starch metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves using graphical Gaussian model. BMC Syst Biol 6:100–100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-6-100
Jiao Y, Li J, Tang H, Paterson AH (2014) Integrated syntenic and phylogenomic analyses reveal an ancient genome duplication in monocots. Plant Cell 26:2792–2802
Jiao Y et al (2011) Ancestral polyploidy in seed plants and angiosperms. Nature 473:97
Kumar Behera K, Sahoo S (2009) Rapid In vitro Micro propagation of Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L. cv- Nayana) Through Callus Culture vol 7
Leterrier M, Holappa LD, Broglie KE, Beckles DM (2008) Cloning, characterisation and comparative analysis of a starch synthase IV gene in wheat: functional and evolutionary implications. BMC Plant Biol 8:98. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-8-98
Li P et al (2010a) The developmental dynamics of the maize leaf transcriptome. Nat Genet 42:1060
Li P et al (2010b) The developmental dynamics of the maize leaf transcriptome. Nat Genet 42:1060–1067. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.703
Lloyd JR, Kossmann J (2015) Transitory and storage starch metabolism: two sides of the same coin? Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.11.026
Matsumoto T et al (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Ming R et al (2015a) The pineapple genome and the evolution of CAM photosynthesis. Nat Genet 47:1435
Ming R et al (2015b) The pineapple genome and the evolution of CAM photosynthesis. Nat Genet 47:1435–1442. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3435
Moore PH, Paterson AH, Tew T (2013) Sugarcane: The Crop, the Plant, and Domestication. In: Sugarcane: Physiology, Biochemistry, and Functional Biology. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, pp 1–17. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118771280.ch1
Muller LM, von Korff M, Davis SJ (2014) Connections between circadian clocks and carbon metabolism reveal species-specific effects on growth control. J Exp Bot 65:2915–2923. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru117
Nougué O, Corbi J, Ball SG, Manicacci D, Tenaillon MI (2014) Molecular evolution accompanying functional divergence of duplicated genes along the plant starch biosynthesis pathway. BMC Evol Biol 14:103–103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-14-103
Pan X, Yan H, Li M, Wu G, Jiang H (2011) Evolution of the Genes Encoding Starch Synthase in Sorghum and Common Wheat. Molecular Plant Breeding. https://doi.org/10.5376/mpb.2011.02.0009
Paterson AH et al (2009) The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature 457:551 doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07723. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature07723#supplementary-information
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pfister B, Zeeman SC (2016) Formation of starch in plant cells. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences: CMLS 73:2781–2807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2250-x
Piperidis G, Piperidis N, D’Hont A (2010) Molecular cytogenetic investigation of chromosome composition and transmission in sugarcane. Mol Gen Genomics 284:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0546-3
Preiss J (2004) Plant starch synthesis:3–56 doi:10.1533/9781855739093.1.3
Schnable PS et al (2009) The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326:1112–1115
Schwarte S, Wegner F, Havenstein K, Groth D, Steup M, Tiedemann R (2015) Sequence variation, differential expression, and divergent evolution in starch-related genes among accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 87:489–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0293-2
Seaton DD, Ebenhoh O, Millar AJ, Pokhilko A (2014) Regulatory principles and experimental approaches to the circadian control of starch turnover. J R Soc Interface 11:20130979. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2013.0979
Skeffington AW, Graf A, Duxbury Z, Gruissem W, Smith AM (2014) Glucan, Water Dikinase Exerts Little Control over Starch Degradation in Arabidopsis Leaves at Night. Plant Physiol 165:866–879. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.237016
Smith AM, Stitt M (2007) Coordination of carbon supply and plant growth. Plant Cell Environ 30:1126–1149. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01708.x
Stitt M, Zeeman SC (2012) Starch turnover: pathways, regulation and role in growth. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15:282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2012.03.016
Streb S, Zeeman SC (2012) Starch metabolism in Arabidopsis. The Arabidopsis book 10:e0160. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0160
Sulpice R et al (2009) Starch as a major integrator in the regulation of plant growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10348–10353. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903478106
Sweetlove LJ, Burrell MM, ap Rees T (1996) Starch metabolism in tubers of transgenic potato (Solanum tuberosum) with increased ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase. Biochem J 320:493–498
Tao Y et al (2017) Whole-Genome Analysis of Candidate genes Associated with Seed Size and Weight in Sorghum bicolor Reveals Signatures of Artificial Selection and Insights into Parallel Domestication in Cereal Crops. Front Plant Sci 8:1237. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01237
Valdez HA, Busi MV, Wayllace NZ, Parisi G, Ugalde RA, Gomez-casati DF (2008) Role of the N-Terminal starch-binding domains in the kinetic properties of Starch Synthase III from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochemistry 47. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi702418h
Vrinten PL, Nakamura T (2000) Wheat Granule-Bound Starch Synthase I and II Are Encoded by Separate Genes That Are Expressed in Different Tissues. Plant Physiol 122:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.1.255
Wang DP, Wan HL, Song Z, Yu J (2009) γ -MYN: a new algorithm for estimating Ka and Ks with consideration of variable substitution rates. Biol Direct 4:1–18
Wang J, Nayak S, Koch K, Ming R (2013) Carbon partitioning in sugarcane (Saccharum species). Front Plant Sci 4:201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00201
Wang L et al (2014) Comparative analyses of C(4) and C(3) photosynthesis in developing leaves of maize and rice. Nat Biotechnol 32:1158–1165. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3019
Yan L, Wei S, Wu Y, Hu R, Li H, Yang W, Xie Q (2015) High-Efficiency Genome Editing in Arabidopsis Using YAO Promoter-Driven CRISPR/Cas9 System. Mol Plant 8:1820–1823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.10.004
Zeeman SC, Kossmann J, Smith AM (2010) Starch: its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:209–234. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112301
Zhang J et al (2018) Allele-defined genome of the autopolyploid sugarcane Saccharum spontaneum L. Nat Genet 50:1565–1573. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0237-2
Zhang J, Zhou M, Walsh J, Zhu L, Chen Y, Ming R (2014) Sugarcane Genetics and Genomics. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Hoboken
Zhang Q, Hu W, Zhu F, Wang L, Yu Q, Ming R, Zhang J (2016) Structure, phylogeny, allelic haplotypes and expression of sucrose transporter gene families in Saccharum. BMC Genomics 17:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2419-6
Zhang X, Szydlowski N, Delvalle D, D'Hulst C, James MG, Myers AM (2008) Overlapping functions of the starch synthases SSII and SSIII in amylopectin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 8:96. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-8-96
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by grants from the 863 program (2013AA100604), NSFC (31201260, 31760413 and 31660420), Science and Technology Major Project of Guangxi (AA17202025) and Fujian Provincial Department of Education (No. JA12082). We are grateful for editing the language of Irene Lavagi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jisen Zhang designed the experiments. Jisen Zhang and Panpan Ma conceived the study. Panpan Ma, Yuan Yuan, Qiaochu Shen, Qing Jiang, Xiuting Hua, Qing Zhang, Muqing Zhang, Ray Ming performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Panpan Ma and Jisen Zhang wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Philippe Lashermes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
Comparison of the allelic characteristics of the starch synthetases genes in S. spontaneum. The identity value is the similarity of protein sequences in sugarcane aligned to corresponding orthologs in sorghum. (DOCX 16 kb)
Fig. S1
The calculation of substitution rates of homologues of starch synthetases genes between S.spontaneum and S. bicolor. (PNG 174 kb)
Fig. S2
The comparison of allelic gene structure of starch synthetases in S. spontaneum. Gene structure starts from translation start sites to stop sites. Diagram is drawn to scale. Exons are represented by boxes and introns as lines. (PNG 1236 kb)
Fig. S3
The expression of SpSSIIa, SoSSIIa, and SoGBSSII in different tissues by qRT-PCR. JY, leaf roll; ZY: leaf; J6: stem 6; J9: stem 9. The expression values from the RNA-seq database are marked by the blue bar based on FPKM values on the left hand side, and expression levels from qRT-PCR experiments are marked by orange dashed line using the scale on the right hand side based on the relative values to value of stem 9 in S. spontaneum and stem 15 in S. officinarum, relatively. (PNG 290 kb)
Fig. S4
The starch content of leaf and stem in seedling from sorghum and three Saccharum species. (PNG 173 kb)
Additional file 1
The gene information of starch synthases from different species collected based on previous studies, including 4 dicots, 6 monocots, A. trichopoda and 3 outgroup species. (XLSX 110 kb)
Additional file 2
The gene sequence information of nine starch synthases and their alleles in S. spontaneum. (FASTA 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, P., Yuan, Y., Shen, Q. et al. Evolution and Expression Analysis of Starch Synthase Gene Families in Saccharum spontaneum. Tropical Plant Biol. 12, 158–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-019-09225-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-019-09225-3