Abstract
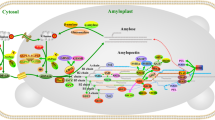
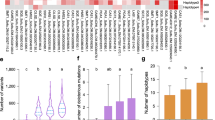
Transitory starch metabolism is a nonlinear and highly regulated process. It originated very early in the evolution of chloroplast-containing cells and is largely based on a mosaic of genes derived from either the eukaryotic host cell or the prokaryotic endosymbiont. Initially located in the cytoplasm, starch metabolism was rewired into plastids in Chloroplastida. Relocation was accompanied by gene duplications that occurred in most starch-related gene families and resulted in subfunctionalization of the respective gene products. Starch-related isozymes were then evolutionary conserved by constraints such as internal starch structure, posttranslational protein import into plastids and interactions with other starch-related proteins. 25 starch-related genes in 26 accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana were sequenced to assess intraspecific diversity, phylogenetic relationships, and modes of selection. Furthermore, sequences derived from additional 80 accessions that are publicly available were analyzed. Diversity varies significantly among the starch-related genes. Starch synthases and phosphorylases exhibit highest nucleotide diversities, while pyrophosphatases and debranching enzymes are most conserved. The gene trees are most compatible with a scenario of extensive recombination, perhaps in a Pleistocene refugium. Most genes are under purifying selection, but disruptive selection was inferred for a few genes/substitutiones. To study transcript levels, leaves were harvested throughout the light period. By quantifying the transcript levels and by analyzing the sequence of the respective accessions, we were able to estimate whether transcript levels are mainly determined by genetic (i.e., accession dependent) or physiological (i.e., time dependent) parameters. We also identified polymorphic sites that putatively affect pattern or the level of transcripts.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that SS sequence data for 26 accessions and transcript data for middle of the light period (MOL) for 6 accessions are taken from a previous study (Schwarte et al. 2013) and are included here to provide a comprehensive coverage of genes and transcripts underlying starch metabolism.
References
Abbott RJ, Gomes MF (1989) Population genetic structure and the outcrossing rate of Arabidopsis thaliana. Heredity 62:411–418
Akey JM, Eberle MA, Rieder MJ, Carlson CS, Shriver MD, Nickerson DA, Kruglyak L (2004) Population history and natural selection shape patterns of genetic variation in 132 genes. PLoS Biol 2:e286
Albrecht T, Koch A, Lode A, Greve B, Schneider-Mergener J, Steup M (2001) Plastidic (Pho1-type) phosphorylase isoforms in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plants: expression analysis and immunochemical characterization. Planta 213:602–613
Andriotis VME, Pike MJ, Schwarz SL, Rawsthorne S, Wang TL, Smith AM (2012) Altered starch turnover in the maternal plant has major effects on Arabidopsis fruit growth and seed composition. Plant Physiol 160:1175–1186
Bailey CD, Carr TG, Harris SA, Hughes CE (2003) Characterization of angiosperm nrDNA polymorphism, paralogy, and pseudogenes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:435–455
Ball SG (2012) Evolution of the starch pathway. In: Tetlow IJ (ed) Essential reviews in experimental biology 5. Starch: origins, structure and metabolism, 1st edn. Society for Experimental Biology, London, pp 29–54
Ball SG, Colleoni C, Cenci U, Raj JN, Tirtiaux C (2011) The evolution of glycogen and starch metabolism in eukaryotes gives molecular clues to understand the establishment of plastid endosymbiosis. J Exp Bot 62:1776–1801
Ball SG, Subtil A, Bhattacharya D, Moustafa A, Weber APM, Gehre L, Colleoni C, Arias M-C, Cenci U, Dauvillée D (2013) Metabolic effectors secreted by bacterial pathogens: essential facilitators of plastid endosymbiosis? Plant Cell 25:7–21
Ballicora MA, Iglesias AA, Preiss J (2004) ADP-Glucose pyrophosphorylase: a regulatory enzyme for plant starch synthesis. Photosynth Res 79:1–24
Bertoft E (2013) On the building block and backbone concepts of amylopectin structure. Cereal Chem 90:294–311
Blanc G, Hokamp K, Wolfe KH (2003) A recent polyploidy superimposed on older large-scale duplications in the Arabidopsis genome. Genome Res 13:137–144
Cao J, Schneeberger K, Ossowski S, Günther T, Bender S, Fitz J, Koenig D, Lanz C, Stegle O, Lippert C, Wang X, Ott F, Müller J, Alonso-Blanco C, Borgwardt K, Schmid KJ, Weigel D (2011) Whole-genome sequencing of multiple Arabidopsis thaliana populations. Nat Genet 43:956–963
Casas-Mollano JA, Lao NT, Kavanagh TA (2006) Intron-regulated expression of SUVH3, an Arabidopsis Su(var)3-9 homologue. J Exp Bot 57:3301–3311
Cenci U, Chabi M, Ducatez M, Tirtiaux C, Nirmal-Raj J, Utsumi Y, Kobayashi D, Sasaki S, Suzuki E, Nakamura Y, Putaux JL, Roussel X, Durand-Terrasson A, Bhattacharya D, Vercoutter-Edouart AS, Maes E, Cecilia Arias M, Palcic M, Sim L, Ball SG, Colleoni C (2013) Convergent evolution of polysaccharide debranching defines a common mechanism for starch accumulation in Cyanobacteria and plants. Plant Cell 25:3961–3975
Cenci U, Nitschke F, Steup M, Minassian BA, Colleoni C, Ball SG (2014) Transition from glycogen to starch metabolism in Archaeplastida. Trends Plant Sci 19:18–28
Chaw SM, Chang CC, Chen HL, Li WH (2004) Dating the monocot-dicot divergence and the origin of core eudicots using whole chloroplast genomes. J Mol Evol 58:424–441
Cheng J, Khan MA, Qiu W-M, Li J, Zhou H, Zhang Q, Guo W, Zhu T, Peng J, Sun F, Li S, Korban SS, Han Y (2012) Diversification of genes encoding granule-bound starch synthase in monocots and dicots is marked by multiple genome-wide duplication events. PLoS ONE 7:e30088
Clauss MJ, Koch MA (2006) Poorly known relatives of Arabidopsis thaliana. Trends Plant Sci 11:449–459
Cork JM, Purugganan MD (2005) High-diversity genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Genetics 170:1897–1911
Crevillén P, Ballicora MA, Mérida A, Preiss J, Romero JM (2003) The different large subunit isoforms of Arabidopsis thaliana ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase confer distinct kinetic and regulatory properties to the heterotetrameric enzyme. J Biol Chem 278:28508–28515
Crevillén P, Ventriglia T, Pinto F, Orea A, Mérida A, Romero JM (2005) Differential pattern of expression and sugar regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase-encoding genes. J Biol Chem 280:8143–8149
Crumpton-Taylor M, Pike M, Lu K-J, Hylton CM, Feil R, Eicke S, Lunn JE, Zeeman SC, Smith AM (2013) Starch synthase 4 is essential for coordination of starch granule formation with chloroplast division during Arabidopsis leaf expansion. New Phytol 200:1064–1075
Delatte T, Trevisan M, Parker ML, Zeeman SC (2005) Arabidopsis mutants Atisa1 and Atisa2 have identical phenotypes and lack the same multimeric isoamylase, which influences the branch point distribution of amylopectin during starch synthesis. Plant J 41:815–830
Delph LF, Kelly JK (2014) On the importance of balancing selection in plants. New Phytol 201:45–56
Delvallé D, Dumez S, Wattebled F, Roldán I, Planchot V, Berbezy P, Colonna P, Vyas D, Chatterjee M, Ball S, Mérida A, D’Hulst C (2005) Soluble starch synthase I: a major determinant for the synthesis of amylopectin in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant J 43:398–412
Deschamps P, Colleoni C, Nakamura Y, Suzuki E, Putaux JL, Buléon A, Haebel S, Ritte G, Steup M, Falcón LI, Moreira D, Löffelhardt W, Raj JN, Planck C, d’Hulst C, Dauvillée D, Ball S (2007) Metabolic symbiosis and the birth of the plant kingdom. Mol Biol Evol 25:536–548
Deschamps P, Haferkamp I, d’Hulst C, Neuhaus HE, Ball SG (2008) The relocation of starch metabolism to chloroplasts: when, why and how. Trends Plant Sci 13:574–582
Dumez S, Wattebled F, Dauvillee D, Delvalle D, Planchot V, Ball SG, D’Hulst C (2006) Mutants of Arabidopsis lacking starch branching enzyme II substitute plastidial starch synthesis by cytoplasmic maltose accumulation. Plant Cell 18:2694–2709
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, von Heijne G (1999) ChloroP, a neural network-based method for predicting chloroplast transit peptides and their cleavage sites. Protein Sci 8:978–984
Emes MJ and Tetlow IJ (2012) The role of heteromeric protein complexes in starch synthesis. In: Tetlow IJ (ed) Essential reviews in experimental biology 5. Starch: origins, structure and metabolism, 1st edn. Society for Experimental Biology, London, pp 255-278
Facon M, Lin Q, Azzaz AM, Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Myers AM, Putaux J-L, Roussel X, D’Hulst C, Wattebled F (2013) Distinct functional properties of isoamylase-type starch debranching enzymes in monocot and dicot leaves. Plant Physiol 163:1363–1375
Fay JC, Wu CI (2000) Hitchhiking under positive Darwinian selection. Genetics 155:1405–1413
Freeling M (2009) Bias in plant gene content following different sorts of duplication: tandem, whole-genome, segmental, or by transposition. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:433–453
Fu YX, Li WH (1993) Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations. Genetics 133:693–709
Fujita N, Satoh R, Hayashi A, Kodama M, Itoh R, Aihara S, Nakamura Y (2011) Starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm requires the presence of either starch synthase I or IIIa. J Exp Bot 62:4819–4831
Gan X, Stegle O, Behr J, Steffen JG, Drewe P, Hildebrand KL, Lyngsoe R, Schultheiss SJ, Osborne EJ, Sreedharan VT, Kahles A, Bohnert R, Jean G, Derwent P, Kersey P, Belfield EJ, Harberd NP, Kemen E, Toomajian C, Kover PX, Clark RM, Rätsch G, Mott R (2011) Multiple reference genomes and transcriptomes for Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 477:419–423
Georgelis N, Braun EL, Shaw JR, Hannah LC (2007) The two AGPase subunits evolve at different rates in angiosperms, yet they are equally sensitive to activity-altering amino acid changes when expressed in bacteria. Plant Cell 19:1458–1472
Graf A, Smith AM (2011) Starch and the clock: the dark side of plant productivity. Trends Plant Sci 16:169–175
Grigoriev IV, Nordberg H, Shabalov I, Aerts A, Cantor M, Goodstein D, Kuo A, Minovitsky S, Nikitin R, Ohm RA, Otillar R, Poliakov A, Ratnere I, Riley R, Smirnova T, Rokhsar D, Dubchak I (2012) The genome portal of the department of energy joint genome institute. Nucleic Acids Res 40(Database issue):D26–D32
Hädrich N, Hendriks JH, Kötting O, Arrivault S, Feil R, Zeeman SC, Gibon Y, Schulze WX, Stitt M, Lunn JE (2012) Mutagenesis of cysteine 81 prevents dimerization of the APS1 subunit of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and alters diurnal starch turnover in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant J 70:231–242
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Series 41:95–98
Hennen-Bierwagen TA, James MG, Myers AM (2012) Involvement of debranching enzymes in starch biosynthesis. In: Tetlow IJ (ed) Essential reviews in experimental biology 5. Starch: origins, structure and metabolism, 1st edn. Society for Experimental Biology, London, pp 179–215
Hir HL, Nott A, Moore MJ (2003) How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci 28:215–220
Hu TT, Pattyn P, Bakker EG, Cao J, Cheng JF, Clark RM, Fahlgren N, Fawcett JA, Grimwood J, Gundlach H, Haberer G, Hollister JD, Ossowski S, Ottilar RP, Salamov AA, Schneeberger K, Spannagl M, Wang X, Yang L, Nasrallah ME, Bergelson J, Carrington JC, Gaut BS, Schmutz J, Mayer KF, Van de Peer Y, Grigoriev IV, Nordborg M, Weigel D, Guo YL (2011) The Arabidopsis lyrata genome sequence and the basis of rapid genome size change. Nat Genet 43:476–481
Jespersen HM, MacGregor EA, Henrissat B, Sierks MR, Svensson B (1993) Starch- and glycogen-debranching and branching enzymes: prediction of structural features of the catalytic (beta/alpha)8-barrel domain and evolutionary relationship to other amylolytic enzymes. J Protein Chem 12:791–805
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Tanabe M (2012) KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D109–D114
Keeling PL, Myers AM (2010) Biochemistry and genetics of starch synthesis. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:271–303
Kizirian D, Donnelly MA (2004) The criterion of reciprocal monophyly and classification of nested diversity at the species level. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:1072–1076
Kubo A, Rahman S, Utsumi Y, Li Z, Mukai Y, Yamamoto M, Ugaki M, Harada K, Satoh H, Konik-Rose C, Morell M, Nakamura Y (2005) Complementation of sugary-1 phenotype in rice endosperm with the wheat isoamylase1 gene supports a direct role for isoamylase1 in amylopectin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 137:43–56
Kubo A, Colleoni C, Dinges JR, Lin Q, Lappe RR, Rivenbark JG, Meyer AJ, Ball SG, James MG, Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Myers AM (2010) Functions of heteromeric and homomeric isoamylase-type starch-debranching enzymes in developing maize endosperm. Plant Physiol 153:956–969
Kuittinen H, Aguadé M (2000) Nucleotide variation at the CHALCONE ISOMERASE locus in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 155:863–872
Kuittinen H, de Haan AA, Vogl C, Oikarinen S, Leppälä J, Koch M, Mitchell-Olds T, Langley CH, Savolainen O (2004) Comparing the linkage maps of the close relatives Arabidopsis lyrata and A. thaliana. Genetics 168:1575–1584
Lattanzi FA, Ostler U, Wild M, Morvan-Bertrand A, Decau M-L, Lehmeier CA, Meuriot F, Prud’homme M-P, Schäufele R, Schnyder H (2012) Fluxes in central carbohydrate metabolism of source leaves in a fructan-storing C3 grass: rapid turnover and futile cycling of sucrose in continuous light under contrasting nitrogen nutrition status. J Exp Bot 63:2363–2375
Li L, Ilarslan H, James MG, Myers AM, Wurtele ES (2007) Genome wide co-expression among the starch debranching enzyme genes AtISA1, AtISA2, and AtISA3 in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 58:3323–3342
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Lin TP, Caspar T, Somerville C, Preiss J (1988) Isolation and characterization of a starchless mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh lacking ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase activity. Plant Physiol 86:1131–1135
Lu Y, Steichen JM, Yao J, Sharkey TD (2006) The role of cytosolic alpha-glucan phosphorylase in maltose metabolism and the comparison of amylomaltase in Arabidopsis and Escherichia coli. Plant Physiol 142:878–889
Lynch M, Conery JS (2000) The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicated genes. Science 290:1151–1155
Meyer K, Stecca KL, Ewell-Hicks K, Allen SM, Everard JD (2012) Oil and protein accumulation in developing seeds is influenced by the expression of a cytosolic pyrophosphatase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 159:1221–1234
Moyroud E, Minguet EG, Ott F, Yant L, Posé D, Monniaux M, Blanchet S, Bastien O, Thévenon E, Weigel D, Schmid M, Parcy F (2011) Prediction of regulatory interactions from genome sequences using a biophysical model for the Arabidopsis LEAFY transcription factor. Plant Cell 23:1293–1306
Nakano K, Fukui T (1986) The complete amino acid sequence of potato a-glucan phosphorylase. J Biol Chem 261:8230–8236
Navarro-De la Sancha E, Coello-Coutiño MP, Valencia-Turcotte LG, Hernández-Domínguez EE, Trejo-Yepes G, Rodríguez-Sotres R (2007) Characterization of two soluble inorganic pyrophosphatases from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci 172:796–807
Nordborg M, Hu TT, Ishino Y, Jhaveri J, Toomajian C, Zheng H, Bakker E, Calabrese P, Gladstone J, Goyal R, Jakobsson M, Kim S, Morozov Y, Padhukasahasram B, Plagnol V, Rosenberg NA, Shah C, Wall JD, Wang J, Zhao K, Kalbfleisch T, Schulz V, Kreitman M, Bergelson J (2005) The pattern of polymorphism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Biol 3:e196
Nougué O, Corbi J, Ball SG, Manicacci D, Tenaillon MI (2014) Molecular evolution accompanying functional divergence of duplicated genes along the plant starch biosynthesis pathway. BMC Evol Biol 14:103
Osorio S, Nunes-Nesi A, Stratmann M, Fernie AR (2013) Pyrophosphate levels strongly influence ascorbate and starch content in tomato fruit. Front Plant Sci 4:308
Ossowski S, Schneeberger K, Lucas-Lledó JI, Warthmann N, Clark RM, Shaw RG, Weigel D, Lynch M (2010) The rate and molecular spectrum of spontaneous mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 327:92–94
Paparelli E, Parlanti S, Gonzali S, Novi G, Mariotti L, Ceccarelli N, van Dongen JT, Kölling K, Zeeman SC, Perata P (2013) Nighttime sugar starvation orchestrates gibberelline biosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3760–3769
Pyl E-T, Piques M, Ivakov A, Schulze W, Ishihara H, Stitt M, Sulpice R (2012) Metabolism and growth in Arabidopsis depend on the daytime temperature but are temperature-compensated against cool nights. Plant Cell 24:2443–24469
Ragel P, Streb S, Feil R, Sahwrawy M, Annunziata MG, Lunn JE, Zeeman S, Mérida Á (2013) Loss of starch granule initiation has a deleterious effect on the growth of Arabidopsis plants due to an accumulation of ADP-glucose. Plant Physiol 163:75–85
Ramos-Onsins SE, Rozas J (2002) Statistical properties of new neutrality tests against population growth. Mol Biol Evol 19:2092–2100
Rathore RS, Garg N, Garg S, Kumar A (2009) Starch phosphorylase: role in starch metabolism and biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 29:214–224
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5:69–76
Roldán I, Wattebled F, Lucas MM, Delvallé D, Planchot V, Jimenez S, Perez R, Ball S, D’Hulst C, Merida A (2007) The phenotype of soluble starch synthase IV defective mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests a novel function of elongation enzymes in the control of starch granule formation. Plant J 49:492–504
Salomé PA, Bomblies K, Fitz J, Laitinen RA, Warthmann N, Yant L, Weigel D (2012) The recombination landscape in Arabidopsis thaliana F2 populations. Heredity 108:447–455
Schulze S, Mant A, Kossmann J, Lloyd JR (2004) Identification of an Arabidopsis inorganic pyrophosphatase capable of being imported into chloroplasts. FEBS Lett 565:101–105
Schwarte S, Tiedemann R (2011) A gene duplication/loss event in the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) small subunit gene family among accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biol Evol 28:1861–1876
Schwarte S, Brust H, Steup M, Tiedemann R (2013) Intraspecific sequence variation and differential expression in starch synthase genes of Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Res Notes 6:84
Scialdone A, Mugford ST, Feike D, Skeffington A, Borrill P, Graf A, Smith AM, Howard M (2013) Arabidopsis plants perform arithmetic division to prevent starvation at night. Elife 2:e00669
Sharbel TF, Haubold B, Mitchell-Olds T (2000) Genetic isolation by distance in Arabidopsis thaliana: biogeography and postglacial colonization of Europe. Mol Ecol 9:2109–2118
Sim L, Beeren SR, Findinier J, Dauvillée D, Ball S, Henriksen A, Palcic MM (2014) Crystal structure of the Chlamydomonas starch debranching isoamylase ISA1 reveals insights into the mechanism of branch trimming and complex assembly. J Biol Chem 289:22991–23003
Sonnewald U, Kossmann J (2013) Starches - from current models to genetic engineering. Plant Biotechnol J 11:223–232
Spasovski V, Tosic N, Nikcevic G, Stojiljkovic M, Zukic B, Radmilovic M, Karan-Djurasevic T, Srzentic SS, Colovic M, Pavlovic S (2013) The influence of novel transcriptional regulatory element in intron 14 on the expression of Janus kinase 2 gene in myeloproliferative neoplasms. J Appl Genetics 54:21–26
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Stein L (2001) Genome annotation: from sequence to biology. Nat Rev Genet 2:493–503
Streb S, Eicke S, Zeeman SC (2012) The simultaneous abolition of three starch hydrolases blocks transient starch breakdown in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 287:41745–41756
Sulpice R, Pyl ET, Ishihara H, Trenkamp S, Steinfath M, Witucka-Wall H, Gibon Y, Usadel B, Poree F, Piques MC, Von Korff M, Steinhauser MC, Keurentjes JJ, Guenther M, Hoehne M, Selbig J, Fernie AR, Altmann T, Stitt M (2009) Starch as a major integrator in the regulation of plant growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:10348–10353
Sulpice R, Flis A, Ivakov AA, Apelt F, Krohn N, Encke B, Abel C, Feil R, Stitt M (2014) Arabidopsis coordinates the diurnal regulation of carbon allocation and growth across a wide range of photoperiods. Mol Plant 7:137–155
Sundberg M, Pfister B, Fulton D, Bischof S, Delatte T, Eicke S, Stettler M, Smith SM, Streb S, Zeeman SC (2013) The heteromultimeric debranching enzyme involved in starch synthesis in Arabidopsis requires both isoamylase1 and isoamylase2 subunits for complex stability and activity. PLoS One 8:e75223
Svensson B (1994) Protein engineering in the alpha-amylase family: catalytic mechanism, substrate specificity, and stability. Plant Mol Biol 25:141–157
Szydlowski N, Ragel P, Hennen-Bierwagen TA, Planchot V, Myers M, Mérida Á, D’Hulst C, Wattebled F (2011) Integrated functions among multiple starch synthases determine both amylopectin chain length and branch linkage location in Arabidopsis leaf starch. J Exp Bot 62:4547–4559
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Tenorio G, Orea A, Romero JM, Mérida A (2003) Oscillation of mRNA level and activity of granule-bound starch synthase I in Arabidopsis leaves during the day/night cycle. Plant Mol Biol 51:949–958
Tetlow IJ, Wait R, Lu Z, Akkasaeng R, Bowsher CG, Esposito S, Kosar-Hashemi B, Morell MK, Emes MJ (2004) Protein phosphorylation in amyloplasts regulates starch branching enzyme activity and protein-protein interactions. Plant Cell 16:694–708
Tetlow IJ, Beisel KG, Cameron S, Makhmoudova A, Liu F, Bresolin NS, Wait R, Morell MK, Emes JE (2008) Analysis of protein complexes in wheat amyloplasts reveals functional interactions among starch biosynthetic enzymes. Plant Physiol 146:1878–1891
Tomlinson K, Denyer K (2003) Starch synthesis in cereal grains. Adv Bot Res 40:1–61
Utsumi Y, Nakamura Y (2006) Structural and enzymatic characterization of the isoamylase1 homo-oligomer and the isoamylase1-isoamylase2 hetero-oligomer from rice endosperm. Planta 225:75–87
Utsumi Y, Utsumi C, Sawada T, Fujita N, Nakamura Y (2011) Functional diversity of isoamylase oligomers: the ISA1 homo-oligomer is essential for amylopectin biosynthesis in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol 156:61–77
Ventriglia T, Kuhn ML, Ruiz MT, Ribeiro-Pedro M, Valverde F, Ballicora MA, Preiss J, Romero JM (2008) Two Arabidopsis ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunits (APL1 and APL2) are catalytic. Plant Physiol 148:65–76
Vijn I, Smeekens S (1999) Fructan: more than a reserve carbohydrate? Plant Physiol 120:351–359
Wattebled F, Dong Y, Dumez S, Delvallé D, Planchot V, Berbezy P, Vyas D, Colonna P, Chatterjee M, Ball S, D’Hulst C (2005) Mutants of Arabidopsis lacking a chloroplastic isoamylase accumulate phytoglycogen and an abnormal form of amylopectin. Plant Physiol 138:184–195
Wattebled F, Planchot V, Dong Y, Szydlowski N, Pontoire B, Devin A, Ball S, D’Hulst C (2008) Further evidence for the mandatory nature of polysaccharide debranching for the aggregation of semicrystalline starch and for overlapping functions of debranching enzymes in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Physiol 148:1309–1323
Weigel D, Mott R (2009) The 1001 genomes project for Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol 10:107
Wolfe KH, Gouy M, Yang YW, Sharp PM, Li WH (1989) Date of the monocot-dicot divergence estimated from chloroplast DNA sequence data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:6201–6205
Yan HB, Pan XX, Jiang HW, Wu GJ (2009) Comparison of the starch synthesis genes between maize and rice: copies, chromosome location and expression divergence. Theor Appl Genet 119:815–825
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Bio Sci 13:555–556
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AMK (2000) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Yilmaz A, Mejia-Guerra MK, Kurz K, Liang X, Welch L, Grotewold E (2011) AGRIS: the Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an update. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Database issue):D1118–D1122
Zeeman SC, Thorneycroft D, Schupp N, Chapple A, Weck M, Dunstan H, Haldimann P, Bechtold N, Smith AM, Smith SM (2004) Plastidial alpha-glucan phosphorylase is not required for starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves but has a role in the tolerance of abiotic stress. Plant Physiol 135:849–858
Zeeman SC, Kossmann J, Smith AM (2010) Starch: its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modifications in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:209–234
Zhang X, Myers AM, James MG (2005) Mutations affecting starch synthase III in Arabidopsis alter leaf starch structure and increase the rate of starch synthesis. Plant Physiol 138:663–674
Zhang X, Szydlowski N, Delvallé D, D’Hulst C, James MG, Myers AM (2008) Overlapping functions of the starch synthases SSII and SSIII in amylopectin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 8:96
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Thomas Altmann for providing plant seeds and Michael Lenhard for providing access to Realtime PCR equipment. Financial support by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) within the GoFORSYS initiative and by the University of Potsdam is gratefully acknowledged. MS thanks the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, Potsdam-Golm, and the University of Guelph for generously permitting the use of the library. We would like to thank the anonymous reviewer for very useful comments and suggestions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11103_2015_293_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Fig. S1 Duplications of chromosomal segments and the position of starch-related genes in the A. thaliana genome The chromosomes of A. thaliana (I to V) are shown as grey horizontal bars. The occurrence and positions of segmental duplications (similar sequences; various colors) were taken from Stein (2001; Fig. 3). Duplications occurred within and across chromosomes and could be either unidirectional or inverted (twisted bars). Chromosome length (given in megabases [Mb]) was modified according to TAIR 10.0. Starch-related genes are evenly distributed across the genome. The positions of the genes are given above each chromosome. (PDF 117 kb)
11103_2015_293_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
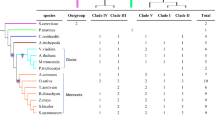
Fig. S2 Phylogenetic trees of the combined data set of A. thaliana. Rooted maximum likelihood trees among accessions of A. thaliana and A. lyrata as an outgroup based on gene sequences (including introns). The combined data set consists of 105 accessions comprising 26 accessions from our data set and 80 accessions from the 1001 Genome Project (Cao et al. 2011). Accessions that are used for Realtime PCR analyses are highlighted in the same color as in Figs. 3–8. (PDF 7940 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarte, S., Wegner, F., Havenstein, K. et al. Sequence variation, differential expression, and divergent evolution in starch-related genes among accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Mol Biol 87, 489–519 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0293-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0293-2