Abstract
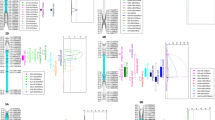
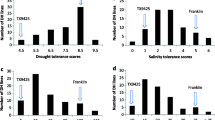
For discovering the quantitative trait loci (QTLs) contributing to early seedling growth and drought tolerance during germination, conditional and unconditional analyses of 12 traits of wheat seedlings: coleoptile length, seedling height, longest root length, root number, seedling fresh weight, stem and leaves fresh weight, root fresh weight, seedling dry weight, stem and leaves dry weight, root dry weight, root to shoot fresh weight ratio, root-to-shoot dry weight ratio, were conducted under two water conditions using two F8:9 recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations. The results of unconditional analysis are as follows: 88 QTLs accounting for 3.33–77.01% of the phenotypic variations were detected on chromosomes 1A, 1B, 1D, 2A, 2B, 2D, 3A, 3B, 4A, 4B, 4D, 5A, 5B, 5D, 6A, 6B, 6D, 7A, 7B and 7D. Among these QTLs, 19 were main-effect QTLs with a contribution rate greater than 10%. The results of the conditional QTL analysis of 12 traits under osmotic stress on normal water conditions were as follows: altogether 22 QTLs concerned with drought tolerance were detected on chromosomes 1B, 2A, 2B, 3B, 4A, 5D, 6A, 6D, 7B, and 7D. Of these QTLs, six were main-effect QTLs. These 22 QTLs were all special loci directly concerned with drought tolerance and most of them could not be detected by unconditional analysis. The finding of these QTLs has an important significance for fine-mapping technique, map-based cloning, and molecular marker-assisted selection of early seedling traits, such as growth and drought tolerance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhosein I., Miyuki N., Shuhei N., Kenji K., Masaya F., Hitoshi M. and Yutaka O. 2012 Novel QTLs for growth angle of seminal roots in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Soil 354, 395–405.
Almansouri M., Kinet J. M. and Lutts S. 2001 Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on germination in durum wheat (Triticumdurum Desf). Plant Soil 231, 243–254.
Anderson J. A., Stack R. W., Liu S., Waldron B. L., Fjeld A. D., Coyne C. et al. 2001 DNA markers for fusarium head blight tolerance QTL in two wheat populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102, 1164–1168.
Atchley W. R. and Zhu J. 1997 Developmental quantitative genetics: conditional epigenetic Variability and growth in mice. Genetics 147, 765–776.
Atefeh N., Alireza E., Jaime A., Teixeirada S. and Reza M. 2011 Assessment of yield, yield-related traits and drought tolerance of durum wheat genotypes (Triticum turjidum var. durum Desf.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 5, 8–16.
Austin D. F. and Lee M. 1998 Detection of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and yield components in maize across generations in stress and nonstress environments. Crop Sci. 38, 1296–1308.
Bálint A., Röder M. S., Hell R., Galiba G., and Börner A. 2007 Mapping of QTL affecting copper tolerance and the Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn concentrations in the shoots of wheat seedlings. Biol. Plant. 51, 129–134.
Beavis W. B. 1998 QTL analyses: power, precision, and accuracy. In Molecular dissection of complex traits (ed. A. H. Patterson). CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA.
Blum A. 1996 Crop responses to drought and the interpretation of adaptation. Plant Growth Regul. 20, 135–148.
Blum A., Sinmena B. and Ziv O. 1980 An evaluation of seed and seedling drought tolerance screening tests in wheat. Euphytica 29, 727–736.
Borner A., Schumann E., Fürste A., Cöster H., Leithold B., Röder M. S. et al. 2002 Mapping of quantitative trait loci determining agronomic important characters in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 105, 921–936.
Buckler E. S., Holland J. B., Acharya C. B., Brown P. J., Browne C, Ersoz E. et al. 2009 The genetic architecture of maize flowering time. Science 325, 714–718.
Cao G., Zhu J., He C., Gao Y., Yan J. and Wu P. 2001 Impact of epistasis and QTL×environment interaction on the developmental behavior of plant height in rice (Oryza sativa L.) height in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103, 153–160.
Cattivelli L., Baldi P., Crosatti C., Fonzo N. D., Faccioli P., Grossi M. et al. 2002 Chromosome regions and stress-related sequences involved in resistance to abiotic stress in Triticeae. Plant Mol. Biol. 48, 649–665.
Courtois B., Ahmadi N., Khowaja F., Price A. H., Rami J. F., Frouin J. et al. 2009 Rice root genetic architecture: meta analysis from a drought QTL database. Rice 2, 115–128.
Collard B. C. Y., Jahufer M. Z. Z., Brouwer J. B. and Pang E. C. K. 2005 An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 142, 169–196.
Cui K. H., Peng S. B., Xing Y. Z., Yu S. B., Xu C. G. and Zhang Q. 2003 Molecular dissection of the genetic relationships of source, sink and transport tissue with yield traits in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106, 649–658.
Cui F., Li J., Ding A. M., Zhao C. H., Wang L., Wang X. Q. et al. 2011 Conditional QTL mapping for plant height with respect to the length of the spike and internode in two mapping populations of wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 122, 1517–1536.
Cui F, Ding A. M., Li J., Zhao C. H., Wang L., Wang X. Q. et al. 2012 QTL detection of seven spike-related traits and their genetic correlations in wheat using two related RIL populations. Euphytica 186, 177–192.
Dhanda S. S., Sethi G. S. and Behl R. K. 2004 Indices of drought tolerance in wheat genotypes at early stages of plant growth. Agron. Crop Sci. 190, 6–12.
Faris J. D. and Friesen T. L. 2005 Identification of quantitative trait loci for race-nonspecific tolerance to tan spot in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 111, 386–392.
Galiba G., Pecchioni N., Vágújfalvi A., Francia E., Tóth B., Barabaschi D. et al. 2005 Localization of QTL and candidate genes involved in the regulation of frost tolerance in cereals. In In the wake of the double helix: from the green revolution to the gene revolution (ed. R. Tuberosa, R. L. Phillips and M. D. Gale), pp. 253. Avenue Media, Bologna, Italy.
Guo L. B., Xing Y. Z., Mei H. W., Xu C. G., Shi C. H., Wu P. and Luo L. J. 2005 Dissection of component QTL expression in yield formation in rice. Plant Breed. 124, 127–132.
Jiang H., Jiang L., Guo L., Gao Z. Y., Zeng D., Zhu L. et al. 2008 Conditional and unconditional mapping of quantitative trait loci underlying plant height and tiller number in rice. Prog. Nat. Sci. 12, 1539–1547.
Hamada A., Nitta M., Nasuda S., Kato K., Fujita M., Matsunaka H. et al. 2012 Novel QTLs for growth angle of seminal roots in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Plant Soil 354, 395–405.
Hao Z. F., Chang X. P., Guo X. J., Jing R. L., Li R. Z. and Jia J. Z. 2003 QTL mapping for drought tolerance at stages of germination and seedling in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using a DH population. Agric. Sci. China 9, 943–949.
Kumar N., Kulwal P. L., Balyan H. S. and Gupta P. K. 2007 QTL mapping for yield and yield contributing traits in two mapping populations of bread wheat. Mol. Breed. 19, 163–177.
Kumar S., Sehgal S. K., Kumar U., Prasad P. V. V., Joshi A. K. and Gill B. S. 2012 Genomic characterization of drought tolerance related traits in spring wheat. Euphytica 186, 265–276.
Lander E. S. and Botstein D. 1989 Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121, 185–199.
Landjeva S., Neumann K., Lohwasser U. and Borner A. 2008 Molecular mapping of genomic regions associated with wheat seedling growth under osmotic stress. Biol. Plant. 52, 259–266.
Landjeva S., Lohwasser U. and Börner A. 2010 Genetic mapping within the wheat D genome reveals QTL for germination, seed vigour and longevity, and early seedling growth. Euphytica 171, 129–143.
Li H. H., Ye G. Y. and Wang J. K. 2007 A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175, 361–374.
Liu G. F., Yang J., Xu H. M., Hayat Y. and Zhu J. 2008 Genetic analysis of grain yield conditioned on its component traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 59, 189–195.
Liu X. L., Li R. Z., Chang X. P. and Jing R. L. 2013 Mapping QTLs for seedling root traits in a doubled haploid wheat population under different water regimes. Euphytica 189, 51–66.
Lohwasser U., Röder M. S. and Börner A. 2005 QTL mapping of the domestication traits pre-harvest sprouting and dormancy in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 143, 247–249.
Luigi C., Paolo B., Cristina C., Natale D. F., Primetta F., Maria G. et al. 2002 Chromosome regions and stress-related sequences involved in tolerance to abiotic stress in Triticeae. Plant Mol. Biol. 48, 649–665.
Ma Z. Q., Zhao D. M., Zhang C. Q., Zhang Z. Z., Xue S. L., Lin F. et al. 2007 Molecular genetic analysis of five spike-related traits in wheat using RIL and immortalized F2 populations. Mol. Genet. Genomics 277, 31–42.
Matsui T., Inanaga S., Sugimoto Y. and Nakata N. 1998 Chromosomal location of genes controlling final coleoptile length in wheat using chromosome substitution lines. Wheat Inf. Serv. 87, 22–26.
Mujtaba S. M., Khanzada B., Ali M., Naqvi M. H., Mughal S., Alam S. M. et al. 2005 The effect of polyethylene glycol on seed germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes lines. Wheat Inf. Serv. 99, 58–60.
Nelson J. C., van Deynze A. E., Autrique E., Sorrells M. E., Lu Y. H., Merlino M. et al. 1995 Molecullar mapping of wheat: Homologous group 2. Genome 38, 517–524.
Nelson J. C., Singh R. P., Autrique J. E. and Sorrells M. E. 1997 Mapping genes conferring and suppressing leaf rust tolerance in wheat. Crop Sci. 37, 1928–1935.
Perretant M. R., Cadalen T., Charmet G., Sourdille P., Nicolas P., Boeuf C. et al. 2000 QTL analysis of bread-making quality in wheat using a doubled haploid population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 100, 1167–1175.
Rebetzke G. J., Appels R., Morrison A. D., Richerds R. A., McDonald G., Ellis M. H. et al. 2001 Quantitative trait loci on chromosome 4B for coleoptile length and early vigour in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 52, 1221–1234.
Rebetzke G. J., Ellis M. H., Bonnett D. G. R. and Richards R. A. 2007 Molecular mapping of genes for coleoptile growth inbread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 114, 1173–1183.
Schmolke M., Zimmermann G., Buerstmayr H., Schweizer G., Miedaner T., Korzun V. et al. 2005 Molecular mapping of Fusarium head blight tolerance in the winter wheat population Dream/Lynx. Theor. Appl. Genet. 111, 747–756.
Simón M. R., Ayala F. M., Cordo C. A., Röder M. S. and Börner A. 2004 Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci determining tolerance to Septoria tritici blotch caused by Mycosphaerella graminicola in wheat. Euphytica 138, 41–48.
Sio-Se Mardeh A., Ahmadi A., Poustini K. and Mohammadi V. 2006 Evaluation of drought resistance indices under various environmental conditions. Field Crops Res. 98, 222–229.
Sourdille P., Perretant M. R., Charmet G., Leroy P., Gautier M. F., Joudrier P. et al. 1996 Linkage between RFLP markers and genes affecting kernel hardness in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 93, 580–586.
Sourdille P., Snape J. W., Cadalen T., Charmet G., Nakata N., Bernard S. et al. 2000 Detection of QTLs for heading time and photoperiod response in wheat using a doubled-haploid population. Genome 43, 487–494.
Spielmeyer W., Hyles J., Joaquim P., Azanza F., Bonnett D., Ellis M. E. et al. 2007 A QTL on chromosome 6A in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) is associated with longer coleoptiles, greater seedling vigour and final plant height. Theor. Appl. Genet. 115, 59–66.
Vales M. I., Schon C. C., Capettini F., Chen X. M., Corey A. E., Mather D. E. et al. 2005 Effect of population size on the estimation of QTL: a test using tolerance to barley stripe rust. Theor. Appl. Genet. 11, 1260–1270.
Wen Y. X. and Zhu J. 2005 Multivariable conditional analysis for complex trait and its components. Acta Genet. Sin. 32, 289–296.
Yan J. Q., Zhu J. and He C. X. 1998a Quantitative trait analysis for the developmental behavior of tiller number in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97, 267–274.
Yan J. Q., Zhu J., He C., Benmoussa M., Wu P. et al. 1998b Molecular dissection of development behavior of plant height in rice. Genetics 150, 1257–1265.
Yonemaru J., Yamamoto T., Fukuoka S., Uga Y., Hori K. and Yano M. 2010 Q-TARO: QTL annotation rice online database. Rice 3, 194–203.
Yue B., Xue W., Xiong L., Yu X., Luo L., Cui K. et al. 2006a Genetic basis of drought resistance at reproductive stage in rice: separation of drought tolerance from drought avoidance. Genetics 172, 1213–1228.
Zeng Z. B. 1993 Theoretical basis for separation of multiple linked gene effects in mapping quantitative trait loci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10972–10976.
Zeng Z. B. 1994 Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136, 1457–1468.
Zhou X. G., Jing R. L., Hao Z. F., Chang X. P. and Zhang Z. B. 2005 Mapping QTL for seedling root traits in common wheat. Sci. Agric. Sin. 38, 1951–1957.
Zhu J. 1995 Analysis of conditional genetic effects and variance components in developmental genetics. Genetics 141, 1633–1639.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Basic Research Programme of China (863 Programme, 2011AA100103) and Creation and Utilization of Agriculture-Biology Resource of Shandong Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Zhang H., Cui F., Wang L., Li J., Ding A., Zhao C., Bao Y., Yang Q. and Wang H. 2013 Conditional and unconditional QTL mapping of drought-tolerance-related traits of wheat seedling using two related RIL populations. J. Genet. 92, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ZHANG, H., CUI, F., WANG, L. et al. Conditional and unconditional QTL mapping of drought-tolerance-related traits of wheat seedling using two related RIL populations. J Genet 92, 213–231 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-013-0253-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-013-0253-z