Abstract
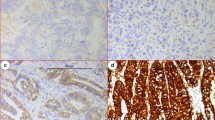
The purpose of this study was to evaluate expression and prognostic impact of Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, proliferation cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), Ki67 and E-cadherin in patients with gastric cancer (GC) by immunohistochemistry. A total of 69 patients were recruited who underwent gastrectomy between 2008 and 2009. We found that expression levels of Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, PCNA, Ki67 and E-cadherin were 26.1, 53.6, 49.3, 52.2, 60.9 and 60.9 %, respectively. Co-expression of more than any two proteins (defined as high-risk group) was detected in 43 of 69 (62.3 %) patients with GC. Only positive expression of Oct4 had relationship with lymphatic invasion (p = 0.013), and positive expression of Ki67 was correlated with T classification (p = 0.011). Furthermore, positive expression of Oct4 (p = 0.043), PCNA (p = 0.035) and Ki67 (p = 0.023) was significantly associated with poor 3-year disease-free survival (DFS). The same result was detected in patients with E-cadherin reduced expression (p = 0.022). But only PCNA positive expression predicted poor overall survival (p = 0.042) in univariate analysis. In addition, 3-year DFS was 20 % in high-risk group and 71 % in low-risk group. The same tendency was found between OS and co-expression of proteins. There was a remarkable difference between DFS or OS and co-expression of more than two proteins (p = 0.000). Multivariate analysis showed that E-cadherin and co-expression were independent prognostic factors of 3-year diseases-free survival. But only co-expression of more than two markers dramatically affected the survival of GC patients. These findings provide evidence that combined evaluation of Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, PCNA, Ki67 and E-cadherin may be a more powerful prognostic factor to predict relapse and distant metastasis for patients with GC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, et al. Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(7):1330–44.
Orditura M, Galizia G, Sforza V, Gambardella V, Fabozzi A, Laterza MM, et al. Treatment of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(7):1635–49.
Xu G, Shen J, Ou Yang X, Sasahara M, Su X. Cancer stem cells: the ‘heartbeat’ of gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48(7):781–97.
Shien K, Toyooka S, Ichimura K, Soh J, Furukawa M, Maki Y, et al. Prognostic impact of cancer stem cell-related markers in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with induction chemoradiotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2012;77(1):162–7.
Wang Z, Oron E, Nelson B, Razis S, Ivanova N. Distinct lineage specification roles for NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(4):440–54.
Ben-Porath I, Thomson MW, Carey VJ, Ge R, Bell GW, Regev A, et al. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat Genet. 2008;40(5):499–507.
Luo W, Li S, Peng B, Ye Y, Deng X, Yao K. Embryonic stem cells markers SOX2, OCT4 and Nanog expression and their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56324.
Hollier BG, Evans K, Mani SA. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: a coalition against cancer therapies. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2009;14(1):29–43.
Steinestel K, Eder S, Schrader AJ, Steinestel J. Clinical significance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Transl Med. 2014;3:17.
He X, Chen Z, Fu T, Jin X, Yu T, Liang Y, et al. Ki-67 is a valuable prognostic predictor of lymphoma but its utility varies in lymphoma subtypes: evidence from a systematic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:153.
Kanaji S, Saito H, Tsujitani S, Matsumoto S, Tatebe S, Kondo A, et al. Expression of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) protein predicts the survival of patients with gastric carcinoma. Oncology. 2006;70(2):126–33.
Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA. Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(2):174–83.
Wang SC. PCNA: a silent housekeeper or a potential therapeutic target? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014;35(4):178–86.
Wang L, Ma J, Liu F, Yu Q, Chu G, Perkins AC, et al. Expression of MUC1 in primary and metastatic human epithelial ovarian cancer and its therapeutic significance. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;105(3):695–702.
Matsuoka J, Yashiro M, Sakurai K, Kubo N, Tanaka H, Muguruma K, et al. Role of the stemness factors sox2, oct3/4, and nanog in gastric carcinoma. J Surg Res. 2012;174(1):130–5.
Hayashi A, Yashima K, Takeda Y, Sasaki S, Kawaguchi K, Harada K, et al. Fhit, E-cadherin, p53, and activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression in endoscopically resected early stage esophageal squamous neoplasia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(11):1752–8.
Mateoiu C, Pirici A, Bogdan F. Immunohistochemical nuclear staining for p53, PCNA, Ki-67 and bcl-2 in different histologic variants of basal cell carcinoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(1 Suppl):315–9.
Bang YJ, Kim YW, Yang HK, Chung HC, Park YK, Lee KH, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): a phase 3 open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;379(9813):315–21.
Jordan CT, Guzman ML, Noble M. Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(12):1253–61.
Chen Z, Xu WR, Qian H, Zhu W, Bu XF, Wang S, et al. Oct4, a novel marker for human gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99(7):414–9.
Lin T, Ding YQ, Li JM. Overexpression of Nanog protein is associated with poor prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Med Oncol. 2012;29(2):878–85.
Zhan YY, He JP, Chen HZ, Wang WJ, Cai JC. Orphan receptor TR3 is essential for the maintenance of stem-like properties in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013;329(1):37–44.
Nishii T, Yashiro M, Shinto O, Sawada T, Ohira M, Hirakawa K. Cancer stem cell-like SP cells have a high adhesion ability to the peritoneum in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(8):1397–402.
Ji W, Jiang Z. Effect of shRNA-mediated inhibition of Nanog gene expression on the behavior of human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2013;6(2):367–74.
Xing X, Tang YB, Yuan G, Wang Y, Wang J, Yang Y, et al. The prognostic value of E-cadherin in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(11):2589–96.
Czyzewska J, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Pryczynicz A, Kemona A, Bandurski R. Immunohistochemical evaluation of Ki-67, PCNA and MCM2 proteins proliferation index (PI) in advanced gastric cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2009;47(2):289–96.
Grossi F, Loprevite M, Chiaramondia M, Ceppa P, Pera C, Ratto GB, et al. Prognostic significance of K-ras, p53, bcl-2, PCNA, CD34 in radically resected non-small cell lung cancers. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39(9):1242–50.
Dworakowska D, Gózdz S, Jassem E, Badzio A, Kobierska G, Urbaniak A, et al. Prognostic relevance of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and p53 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2002;35(1):35–41.
Jin X, Zhu Z, Shi Y. Metastasis mechanism and gene/protein expression in gastric cancer with distant organs metastasis. Bull Cancer. 2014;101(1):E1–12.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all patients for their cooperation. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81470287) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81370661).
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Deng, W., Ma, J. et al. Prognostic evaluation of Nanog, Oct4, Sox2, PCNA, Ki67 and E-cadherin expression in gastric cancer. Med Oncol 32, 433 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0433-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0433-6