Abstract
The sustainable development of human society in today’s high-tech world depends on some form of eco-friendly energy source because existing technologies cannot keep up with the rapid population expansion and the vast amounts of wastewater that result from human activity. A green technology called a microbial fuel cell (MFC) focuses on using biodegradable trash as a substrate to harness the power of bacteria to produce bioenergy. Production of bioenergy and wastewater treatment are the two main uses of MFC. MFCs have also been used in biosensors, water desalination, polluted soil remediation, and the manufacture of chemicals like methane and formate. MFC-based biosensors have gained a lot of attention in the last few decades due to their straightforward operating principle and long-term viability, with a wide range of applications including bioenergy production, treatment of industrial and domestic wastewater, biological oxygen demand, toxicity detection, microbial activity detection, and air quality monitoring, etc. This review focuses on several MFC types and their functions, including the detection of microbial activity.
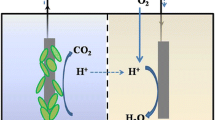
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- DO :
-
Dissolved oxygen
- BOD :
-
Biochemical oxygen demand
- COD :
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- AG :
-
Activated graphite
- CB :
-
Carbon brush
- CC :
-
Carbon cloth
- CF :
-
Carbon fiber
- CP :
-
Carbon paper
- CR :
-
Carbon rod
- GF :
-
Graphite felt
- GG :
-
Graphite gravel
- GP :
-
Graphite plate
- GR :
-
Graphite rod
- SPEEK :
-
Sulfonated poly ether ketone
- AC :
-
Activated carbon
- SCE :
-
Saturated calomel electrode
- Pt. :
-
Platinum
- TWWM :
-
Titanium woven wire mesh
- ENIG :
-
Electro less nickel immersion gold
- AEM :
-
Anion exchange membrane
- CEM :
-
Cation exchange membrane
- PEM :
-
Proton exchange membrane
- PF :
-
Porous filter
- SDS :
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- VFA :
-
Volatile fatty acids
- MMFCs :
-
Microfluidic microbial fuel cells
- SAV :
-
Surface area-to-volume
- PDMS :
-
Polydimethylsiloxane
- PTFE :
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- GAL :
-
-D-galactosidase
- GUS :
-
B-d-glucuronidase
References
Abbas, S. Z., Wang, J.-Y., Wang, H., Wang, J.-X., Wang, Y.-T., & Yong, Y.-C. (2022). Recent advances in soil microbial fuel cells based self-powered biosensor. Chemosphere, 303, 135036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135036
Ahmed, S. F., Mofijur, M., Islam, N., Parisa, T. A., Rafa, N., Bokhari, A., et al. (2022). Insights into the development of microbial fuel cells for generating biohydrogen, bioelectricity, and treating wastewater. Energy, 254, 124163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124163
Apollon, W., Luna-Maldonado, A. I., Vidales-Contreras, J. A., Rodríguez-Fuentes, H., Gómez-Leyva, J. F., & Kamaraj, S.-K. (2022). Application of microbial fuel cells and other bioelectrochemical systems: A comparative study. Microbial Fuel Cells: Emerging Trends in Electrochemical Applications. https://doi.org/10.1088/978-0-7503-4791-4ch14
Dwivedi, K. A., Huang, S.-J., Wang, C.-T., & Kumar, S. (2022). Fundamental understanding of microbial fuel cell technology: recent development and challenges. Chemosphere, 288, 132446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132446
Imoro, A. Z., Acheampong, N. A., Oware, S., Okrah, H., Coulibaly, V. T., Ali, A. G., et al. (2022). The potential benefits of microbial fuel cells in the context of the sustainable development goals. In: Ahmad, A., Mohamad Ibrahim, M. N., Yaqoob, A. A., Mohd Setapar, S. H., (Eds.), Microbial fuel cells for environmental remediation (pp. 167–82). Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2681-5_9.
Massaglia, G., & Quaglio, M. (2022). 3D composite PDMS/MWCNTs aerogel as high-performing anodes in microbial fuel cells. Nanomaterials, 12, 4335. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234335
Prathiba, S., Kumar, P. S., & Vo, D.-V.N. (2022). Recent advancements in microbial fuel cells: a review on its electron transfer mechanisms, microbial community, types of substrates and design for bio-electrochemical treatment. Chemosphere, 286, 131856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131856
Suganya, P., Divya Navamani, J., Lavanya, A., Mrinal, R. (2022). Design and development of microbial fuel cells based low power energy harvesting mechanism for ecological monitoring and farming of agricultural applications. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers 2350112. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126623501128
Touqeer, T., Miran, W., Mumtaz, M. W., Mukhtar, H. (2022). Design and configuration of microbial fuel cells. In: Ahmad, A., Mohamad Ibrahim, M. N., Yaqoob, A. A., Mohd Setapar, S. H (Eds), Microbial fuel cells for environmental remediation (pp. 25–39). Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2681-5_3
Dharmalingam, S., Kugarajah, V., Elumalai, V. (2022). Chapter 2 - Proton exchange membrane for microbial fuel cells. In: Kaur, G (Ed), PEM Fuel Cells (pp. 25–53). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823708-3.00011-0
Mahmoud, R. H., Gomaa, O. M., & Hassan, R. Y. A. (2022). Bio-electrochemical frameworks governing microbial fuel cell performance: technical bottlenecks and proposed solutions. RSC Advances, 12, 5749–64. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA08487A
Li, S., Zhao, Z., Li, B., Wei, T., Jiang, H., & Yan, Z. (2022). Supercapacitors accumulating energy harvesting from stacked sediment microbial fuel cells and boosting input power for power management systems. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 47, 10689–10700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.11.081
Ma, J., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Guo, Q., Hu, T., Xiao, H., et al. (2023). Progress on anodic modification materials and future development directions in microbial fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources., 556, 232486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232486
Shabangu, K. P., Bakare, B. F., & Bwapwa, J. K. (2022). Microbial fuel cells for electrical energy: Outlook on scaling-up and application possibilities towards South African energy grid. Sustainability, 14, 14268. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114268
Nishaa, V., Spoorthi, B. V., Soumya, T. B., Meda, U. S., & Desai, V. S. (2022). Powering implantable medical devices with biological fuel cells. ECS Transactions, 107, 19197. https://doi.org/10.1149/10701.19197ecst
Žalnėravičius, R., Paškevičius, A., Samukaitė-Bubnienė, U., Ramanavičius, S., Vilkienė, M., Mockevičienė, I., et al. (2022). Microbial fuel cell based on nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium anhuiense bacteria. Biosensors, 12, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020113
Coy-Aceves, L. E., & Corona-Vasquez, B. (2022). Bibliometric analysis of artificial intelligence algorithms used for microbial fuel cell research. Water Practice and Technology, 17, 2071–2082. https://doi.org/10.2166/wpt.2022.116
Dwivedi, K. A., Huang, S.-J., & Wang, C.-T. (2022). Integration of various technology-based approaches for enhancing the performance of microbial fuel cell technology: a review. Chemosphere., 287, 132248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132248
Kolajo, O. O., Pandit, C., Thapa, B. S., Pandit, S., Mathuriya, A. S., Gupta, P. K., et al. (2022). Impact of cathode biofouling in microbial fuel cells and mitigation techniques. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 43, 102408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102408
Moqsud, M. A. (2022). Introduction to microbial fuel cell technology. Microbial Fuel Cells: Emerging Trends in Electrochemical Applications. https://doi.org/10.1088/978-0-7503-4791-4ch1
Ren, Z., Ji, G., Liu, H., Yang, M., Xu, S., Ye, M., et al. (2022). Accelerated start-up and improved performance of wastewater microbial fuel cells in four circuit modes: role of anodic potential. Journal of Power Sources, 535, 231403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.231403
ul Haque, S., Nasar, A., Duteanu, N., Pandey, S., Inamuddin. (2023). Carbon based-nanomaterials used in biofuel cells – a review. Fuel, 331:125634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125634
ul Haque S, Yasir M, Cosnier S. Recent advancements in the field of flexible/wearable enzyme fuel cells. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2022;214:114545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114545.
Wang, J., He, N., Fei, J., Ma, Z., Ji, Z., Chen, Z., et al. (2022). Flexible and wearable fuel cells: a review of configurations and applications. Journal of Power Sources, 551, 232190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232190
You, J., Gajda, I., Greenman, J., & Ieropoulos, I. A. (2022). Integration of cost-efficient carbon electrodes into the development of microbial fuel cells. In F. Borghi, F. Soavi, & P. Milani (Eds.), Nanoporous carbons for soft and flexible energy devices (pp. 43–57). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81827-2_3
Shao, Y., Wang, J., Wu, H., Liu, J., Aksay, I. A., & Lin, Y. (2010). Graphene based electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis, 22, 1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200900571
Chen, Z., Niu, Y., Zhao, S., Khan, A., Ling, Z., Chen, Y., et al. (2016). A novel biosensor for p-nitrophenol based on an aerobic anode microbial fuel cell. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 85, 860–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.06.007
Biofuel cell based on bacteria of the genus - ProQuest n.d. https://www.proquest.com/docview/2158431855 (Accessed 4 Mar 2022).
Yang, G.-X., Sun, Y.-M., Kong, X.-Y., Zhen, F., Li, Y., Li, L.-H., et al. (2013). Factors affecting the performance of a single-chamber microbial fuel cell-type biological oxygen demand sensor. Water Science and Technology, 68, 1914–1919. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.415
Chang, I. S., Jang, J. K., Gil, G. C., Kim, M., Kim, H. J., Cho, B. W., et al. (2004). Continuous determination of biochemical oxygen demand using microbial fuel cell type biosensor. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 19, 607–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0956-5663(03)00272-0
Ayyaru, S., & Dharmalingam, S. (2014). Enhanced response of microbial fuel cell using sulfonated poly ether ether ketone membrane as a biochemical oxygen demand sensor. Analytica Chimica Acta, 818, 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.01.059
Modin, O., & Wilén, B.-M. (2012). A novel bioelectrochemical BOD sensor operating with voltage input. Water Research, 46, 6113–6120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.08.042
Pasternak, G., Greenman, J., & Ieropoulos, I. (2017). Self-powered, autonomous biological oxygen demand biosensor for online water quality monitoring. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 244, 815–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.019
Di Lorenzo, M., Thomson, A. R., Schneider, K., Cameron, P. J., & Ieropoulos, I. (2014). A small-scale air-cathode microbial fuel cell for on-line monitoring of water quality. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 62, 182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.050
Xu, L., Zhao, Y., Fan, C., Fan, Z., & Zhao, F. (2017). First study to explore the feasibility of applying microbial fuel cells into constructed wetlands for COD monitoring. Bioresource Technology, 243, 846–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.179
Kretzschmar, J., Koch, C., Liebetrau, J., Mertig, M., Harnisch, F. (2016). Electroactive biofilms as sensor for volatile fatty acids: cross sensitivity, response dynamics, latency and stability. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.097
Jin, X., Li, X., Zhao, N., Angelidaki, I., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Bio-electrolytic sensor for rapid monitoring of volatile fatty acids in anaerobic digestion process. Water Research, 111, 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.12.045
Zhang, Y., & Angelidaki, I. (2012). A simple and rapid method for monitoring dissolved oxygen in water with a submersible microbial fuel cell (SBMFC). Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 38, 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.05.032
Song, N., Yan, Z., Xu, H., Yao, Z., Wang, C., Chen, M., et al. (2019). Development of a sediment microbial fuel cell-based biosensor for simultaneous online monitoring of dissolved oxygen concentrations along various depths in lake water. Science of the Total Environment, 673, 272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.032
Zhou, T., Han, H., Liu, P., Xiong, J., Tian, F., & Li, X. (2017). Microbial fuels cell-based biosensor for toxicity detection: A review. Sensors (Basel), 17, 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102230
Kim, M., Sik Hyun, M., Gadd, G. M., & Joo, K. H. (2007). A novel biomonitoring system using microbial fuel cells. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 9, 1323–1328. https://doi.org/10.1039/b713114c
(PDF) Microbial Fuel Cell-Based Biosensors n.d. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334653412_Microbial_Fuel_Cell-Based_Biosensors (Accessed 4 Mar 2022).
Schneider, G., Czeller, M., Rostás, V., & Kovács, T. (2015). Microbial fuel cell-based diagnostic platform to reveal antibacterial effect of beta-lactam antibiotics. Enyzme and Microbial Technology, 73–74, 59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2015.04.004
Jiang, Y., Liang, P., Liu, P., Wang, D., Miao, B., & Huang, X. (2017). A novel microbial fuel cell sensor with biocathode sensing element. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 94, 344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.052
Zhang, Y., & Angelidaki, I. (2011). Submersible microbial fuel cell sensor for monitoring microbial activity and BOD in groundwater: Focusing on impact of anodic biofilm on sensor applicability. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108, 2339–2347. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23204
Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2020). Oxygen is the high-energy molecule powering complex multicellular life: Fundamental corrections to traditional bioenergetics. ACS Omega, 5, 2221–2233. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03352
Rewatkar, P., & Goel, S. (2020). 3D printed bioelectrodes for enzymatic biofuel cell: Simple, rapid, optimized and enhanced approach. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 19, 4–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2019.2941196
Khaled, F., Ondel, O., & Allard, B. (2016). Microbial fuel cells as power supply of a low-power temperature sensor. Journal of Power Sources, 306, 354–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.12.040
Singh, A., & Yakhmi, J. (2014). Microbial fuel cells – applications for generation of electrical power and beyond. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 42, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.3109/1040841X.2014.905513
Water quality monitoring in developing countries; can microbial fuel cells be the answer? - PubMed n.d. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26193327/ (Accessed 9 Mar 2022)
Elmekawy, A., Sandipam, S., Vanbroekhoven, K., De Wever, H., & Pant, D. (2014). Bioelectro-catalytic valorization of dark fermentation effluents by acetate oxidizing bacteria in bioelectrochemical system (BES). Journal of Power Sources, 262, 183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.03.111
Di Lorenzo, M., Curtis, T. P., Head, I. M., & Scott, K. (2009). A single-chamber microbial fuel cell as a biosensor for wastewaters. Water Research, 43, 3145–3154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.01.005
Rabaey, K., & Verstraete, W. (2005). Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends in Biotechnology, 23, 291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.04.008
Du, Z., Li, H., & Gu, T. (2007). A state of the art review on microbial fuel cells: A promising technology for wastewater treatment and bioenergy. Biotechnology Advances, 25, 464–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.05.004
Perumal, V., & Hashim, U. (2014). Advances in biosensors: Principle, architecture and applications. Journal of Applied Biomedicine, 12, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jab.2013.02.001
Clauwaert, P., Aelterman, P., Pham, T., Schamphelaire, L., Carballa, M., Rabaey, K., et al. (2008). Minimizing losses in bio-electrochemical systems: The road to applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 79, 901–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1522-2
Yaqoob, A. A., Khatoon, A., Mohd Setapar, S. H., Umar, K., Parveen, T., Mohamad Ibrahim, M. N., et al. (2020). Outlook on the role of microbial fuel cells in remediation of environmental pollutants with electricity generation. Catalysts, 10, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080819
Kjeang, E., Djilali, N., & Sinton, D. (2009). Microfluidic fuel cells: A review. Journal of Power Sources, 186, 353–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.10.011
Ho, B., & Kjeang, E. (2011). Microfluidic fuel cell systems. Open. Engineering, 1, 123–131. https://doi.org/10.2478/s13531-011-0012-y
Safdar, M., Jänis, J., & Sánchez, S. (2016). Microfluidic fuel cells for energy generation. Lab on a Chip, 16, 2754–2758. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6LC90070D
Ren, H., Lee, H. S., & Chae, J. (2012). Miniaturizing microbial fuel cells for potential portable power sources: Promises and challenges. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 13, 353–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-0986-7
Micro- and nanoscale fluid mechanics: transport in microfluidic devices. SiloPub 2018. https://silo.pub/micro-and-nanoscale-fluid-mechanics-transport-in-microfluidic-devices.html (Accessed 9 Mar 2022).
Alrifaiy, A., Lindahl, O. A., & Ramser, K. (2012). Polymer-based microfluidic devices for pharmacy, biology and tissue engineering. Polymers, 4, 1349–1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym4031349
Weibel, D. B., Diluzio, W. R., & Whitesides, G. M. (2007). Microfabrication meets microbiology. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 5, 209–218. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1616
Xia, Y., & Whitesides, G. M. (1998). Soft lithography. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition in English), 37, 550–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980316)37:5%3c550::AID-ANIE550%3e3.0.CO;2-G
Jiang, H., Ali, M. A., Xu, Z., Halverson, L. J., & Dong, L. (2017). Integrated microfluidic flow-through microbial fuel cells. Science and Reports, 7, 41208. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41208
Chiao, M., Lam, K. B., & Lin, L. (2006). Micromachined microbial and photosynthetic fuel cells. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 16, 2547–2553. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/16/12/005
Luo, X., Xie, W., Wang, R., Wu, X., Yu, L., & Qiao, Y. (2018). Fast start-up microfluidic microbial fuel cells with serpentine microchannel. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 2816. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02816
Lim, K. G., & Palmore, G. T. R. (2007). Microfluidic biofuel cells: The influence of electrode diffusion layer on performance. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 22, 941–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.04.019
Wu, R., Ye, D., Chen, R., Zhang, B., Zhu, X., Guo, H. et al. (2019). A membraneless microfluidic fuel cell with continuous multistream flow through cotton threads. International Journal of Energy Research, 44. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5085
Fraiwan, A., Adusumilli, S. P., Han, D., Steckl, A. J., Call, D. F., Westgate, C. R., et al. (2014). Microbial power-generating capabilities on micro-/nano-structured anodes in micro-sized microbial fuel cells. Fuel Cells, 14, 801–809. https://doi.org/10.1002/fuce.201400041
Amirdehi, M. A., Khodaparastasgarabad, N., Landari, H., Zarabadi, M. P., Miled, A., & Greener, J. (2020). A high performance membraneless microfluidic microbial fuel cell for stable, long-term benchtop operation under strong flow. ChemElectroChem, 7, 2227–2235. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202000040
Saadi, M., Pezard, J., Haddour, N., Erouel, M., Vogel, T., Khirouni, K. (2020). Stainless steel coated with carbon nanofiber/PDMS composite as anodes in microbial fuel cells. Materials Research Express, 7. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6c99.
Togo, M., Takamura, A., Asai, T., Kaji, H., & Nishizawa, M. (2007). An enzyme-based microfluidic biofuel cell using vitamin K3-mediated glucose oxidation. Electrochimica Acta, 52, 4669–4674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.01.067
Déctor, A., Dector, D., Moreno, A., On-Torres, S., An-Valencia, M., Arriaga, L. G., et al. (2016). Glucose microfluidic fuel cell using air as oxidant. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 41, 23394–23400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.238
Ammam, M., & Fransaer, J. (2012). Glucose/O2 biofuel cell based on enzymes, redox mediators, and multiple-walled carbon nanotubes deposited by AC-electrophoresis then stabilized by electropolymerized polypyrrole. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 109, 1601–1609. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24438
Arjun, A. M., Vimal, M., & Sandhyarani, N. (2019). A hybrid hydrogel separated biofuel cell with a novel enzymatic anode and glucose tolerant cathode. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44, 27056–27066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.08.131
Selloum, D., Tingry, S., Techer, V., Renaud, L., Innocent, C., & Zouaoui, A. (2014). Optimized electrode arrangement and activation of bioelectrodes activity by carbon nanoparticles for efficient ethanol microfluidic biofuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 269, 834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.07.052
Tang, J., Yan, X., Engelbrekt, C., Ulstrup, J., Magner, E., Xiao, X., et al. (2020). Development of graphene-based enzymatic biofuel cells: a minireview. Bioelectrochemistry., 134, 107537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107537
Li, X., Li, D., Zhang, Y., Lv, P., Feng, Q., & Wei, Q. (2020). Encapsulation of enzyme by metal-organic framework for single-enzymatic biofuel cell-based self-powered biosensor. Nano Energy, 68, 104308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104308
Desmaële, D., Nguyen-Boisse, T. T., Renaud, L., & Tingry, S. (2016). Integration of cantilevered porous electrodes into microfluidic co-laminar enzymatic biofuel cells: Toward higher enzyme loadings for enhanced performance. Microelectronic Engineering, 165, 23–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2016.08.008
Escalona-Villalpando, R. A., Reid, R. C., Milton, R. D., Arriaga, L. G., Minteer, S. D., & Ledesma-García, J. (2017). Improving the performance of lactate/oxygen biofuel cells using a microfluidic design. Journal of Power Sources, 342, 546–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.12.082
Pramanik, H., & Rathoure, A. K. (2017). Electrooxidation study of NaBH4 in a membraneless microfluidic fuel cell with air breathing cathode for portable power application. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 8, 5340–5350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.11.143
Ji, J., Ro, S., & Kwon, Y. (2020). Membraneless biofuel cells using new cathodic catalyst including hemin bonded with amine functionalized carbon nanotube and glucose oxidase sandwiched by poly(dimethyl-diallylammonium chloride). Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 87, 242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.04.010
Togo, M., Takamura, A., Asai, T., Kaji, H., & Nishizawa, M. (2008). Structural studies of enzyme-based microfluidic biofuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 178, 53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.12.052
Siu, C.-P.-B., & Chiao, M. (2009). A microfabricated PDMS microbial fuel cell. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 17, 1329–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2008.2006816
Banerjee, R., Jeevan Kumar, P., Mehendale, N., Sevda, S., & Garlapati, V. K. (2019). Intervention of microfluidics in biofuel and bioenergy sectors: technological considerations and future prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 101, 548–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.11.040
Kulkarni, T., & Slaughter, G. (2015). Enzymatic glucose biofuel cell and its application. Journal of Biochips & Tissue Chips, 5, 1000111. https://doi.org/10.4172/21530777.1000111
Luz, R. A. S., Pereira, A. R., de Souza, J. C. P., Sales, F. C. P. F., & Crespilho, F. N. (2014). Enzyme biofuel cells: Thermodynamics, kinetics and challenges in applicability. ChemElectroChem, 1, 1751–1777. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201402141
Zebda, A., Innocent, C., Renaud, L., Cretin, M., Pichot, F., Ferrigno. R, et al. (2011). Enzyme-based microfluidic biofuel cell to generate micropower. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/17190.
Miyake, T., Oike, M., Yoshino, S., Yatagawa, Y., Haneda, K., & Nishizawa, M. (2010). Automatic, sequential power generation for prolonging the net lifetime of a miniature biofuel cell stack. Lab on a Chip, 10, 2574–2578. https://doi.org/10.1039/C004322B
Zebda, A., Renaud, L., Cretin, M., Innocent, C., Ferrigno, R., & Tingry, S. (2010). Membraneless microchannel glucose biofuel cell with improved electrical performances. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 149, 44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.06.032
Kim, T., & Han, J.-I. (2013). Fast detection and quantification of Escherichia coli using the base principle of the microbial fuel cell. Journal of Environmental Management, 130, 267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.08.051
Patel, A., Mahboubi, A., Horváth, I. S., Taherzadeh, M. J., Rova, U., Christakopoulos, P, et al. (2021). Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) generated by anaerobic digestion serve as feedstock for freshwater and marine oleaginous microorganisms to produce biodiesel and added-value compounds. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12.
Nieto-Taype, M. A., Garcia-Ortega, X., Albiol, J., Montesinos-Seguí, J. L., Valero, F. (2020). Continuous cultivation as a tool toward the rational bioprocess development with Pichia pastoris cell factory. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 8.
Understanding Graphene Batteries. AZoNanoCom 2016. https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=4326 (Accessed 10 Mar 2022).
Kaur, A., Ibrahim, S., Pickett, C., Michie, I., Dinsdale, R., Guwy, A., et al. (2014). Anode modification to improve the performance of a microbial fuel cell volatile fatty acid biosensor. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 201, 266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.04.062
Jiang, Y., Liang, P., Liu, P.-P., Miao, B., Bian, Y., Zhang, H. (2017). Enhancement of the sensitivity of microbial fuel cell sensor by transient-state operation. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 3. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00346J.
Nagel, B., Dellweg, H., & Gierasch, L. M. (1992). Glossary for chemists of terms used in biotechnology (IUPAC Recommendations 1992). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 64, 143–168. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199264010143
Karube, I., Matsunaga, T., Mitsuda, S., & Suzuki, S. (1977). Microbial electrode BOD sensors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 19, 1535–1547. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260191010
Yang, Z., Suzuki, H., Sasaki, S., & Karube, I. (1996). Disposable sensor for biochemical oxygen demand. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 46, 10–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050776
Tan, T. C., Li, F., Neoh, K. G., & Lee, Y. K. (1992). Microbial membrane-modified dissolved oxygen probe for rapid biochemical oxygen demand measurement. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 8, 167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4005(92)80175-W
Kim, B. H., Chang, I. S., Cheol Gil, G., Park, H. S., & Kim, H. J. (2003). Novel BOD (biological oxygen demand) sensor using mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biotechnology Letters, 25, 541–545. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022891231369
Liu, J., & Mattiasson, B. (2002). Microbial BOD sensors for wastewater analysis. Water Research, 36, 3786–3802. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(02)00101-x
Feng, Y., Barr, W., & Harper, W. F. (2013). Neural network processing of microbial fuel cell signals for the identification of chemicals present in water. Journal of Environmental Management, 120, 84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.01.018
Melhuish, C., Ieropoulos, I., Greenman, J., & Horsfield, I. (2006). Energetically autonomous robots: Food for thought. Autonomous Robots, 21, 187–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-006-6574-5
Peixoto, L., Min, B., Martins, G., Brito, A. G., Kroff, P., Parpot, P., et al. (2011). In situ microbial fuel cell-based biosensor for organic carbon. Bioelectrochemistry, 81, 99–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2011.02.002
Hsieh, M.-C., Cheng, C.-Y., Liu, M.-H., & Chung, Y.-C. (2015). Effects of operating parameters on measurements of biochemical oxygen demand using a mediatorless microbial fuel cell biosensor. Sensors (Basel), 16, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010035
Torres, C. I., Marcus, A. K., Parameswaran, P., & Rittmann, B. E. (2008). Kinetic experiments for evaluating the Nernst-Monod model for anode-respiring bacteria (ARB) in a biofilm anode. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 6593–6597. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800970w
Tardy, G., Lóránt, B., Gyalai-Korpos, M., Bakos, V., Simpson, D., & Goryanin, I. (2021). Microbial fuel cell biosensor for the determination of biochemical oxygen demand of wastewater samples containing readily and slowly biodegradable organics. Biotechnology Letters, 43, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03050-5
Kim, B. H., Park, H. S., Kim, H. J., Kim, G. T., Chang, I. S., Lee, J., et al. (2004). Enrichment of microbial community generating electricity using a fuel-cell-type electrochemical cell. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 63, 672–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1412-6
Sun, J., Kingori, G., Si, R., Zhai, D.-D., Liao, Z.-H., Sun, D.-Z., et al. (2015). Microbial fuel cell-based biosensors for environmental monitoring: A review. Water Science and Technology, 71, 801–809. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.035
Bowler, M. W., Montgomery, M. G., Leslie, A. G. W., & Walker, J. E. (2006). How azide inhibits ATP hydrolysis by the F-ATPases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A, 103, 8646–8649. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602915103
Harvey, J., Hardy, S. C., & Ashford, M. L. (1999). Dual actions of the metabolic inhibitor, sodium azide on K(ATP) channel currents in the rat CRI-G1 insulinoma cell line. British Journal of Pharmacology, 126, 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0702267
Petrie, B., Barden, R., & Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. (2015). A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Research, 72, 3–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.053
Choi, S. H., & Gu, M. B. (2003). Toxicity biomonitoring of degradation byproducts using freeze-dried recombinant bioluminescent bacteria. Analytica Chimica Acta, 481, 229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00091-6
Yang, H., Zhou, M., Liu, M., Yang, W., & Gu, T. (2015). Microbial fuel cells for biosensor applications. Biotechnology Letters, 37, 2357–2364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1929-7
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. (2012). Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Experientia Supplementum, 101, 133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Giller, K. E., Witter, E., & Mcgrath, S. P. (1998). Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 30, 1389–1414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00270-8
Yu, D., Bai, L., Zhai, J., Wang, Y., & Dong, S. (2017). Toxicity detection in water containing heavy metal ions with a self-powered microbial fuel cell-based biosensor. Talanta, 168, 210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.03.048
Xu, Z., Liu, B., Dong, Q., Lei, Y., Li, Y., Ren, J., et al. (2015). Flat microliter membrane-based microbial fuel cell as “on-line sticker sensor” for self-supported in situ monitoring of wastewater shocks. Bioresource Technology, 197, 244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.081
Cheung, K. H., & Gu, J.-D. (2007). Mechanism of hexavalent chromium detoxification by microorganisms and bioremediation application potential: A review. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 59, 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.05.002
Wang, G.-H., Cheng, C.-Y., Liu, M.-H., Chen, T.-Y., Hsieh, M.-C., & Chung, Y.-C. (2016). Utility of Ochrobactrum anthropi YC152 in a microbial fuel cell as an early warning device for hexavalent chromium determination. Sensors (Basel), 16, E1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081272
Wu, L.-C., Tsai, T.-H., Liu, M.-H., Kuo, J.-L., Chang, Y.-C., & Chung, Y.-C. (2017). A green microbial fuel cell-based biosensor for in situ chromium (VI) measurement in electroplating wastewater. Sensors (Basel), 17, E2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112461
Tran, P. H. N., Luong, T. T. T., Nguyen, T. T. T., Nguyen, H. Q., Duong, H. V., Kim, B. H., et al. (2015). Possibility of using a lithotrophic iron-oxidizing microbial fuel cell as a biosensor for detecting iron and manganese in water samples. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 17, 1806–1815. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EM00099H
Zhao, S., Liu, P., Niu, Y., Chen, Z., Khan, A., Zhang, P., et al. (2018). A novel early warning system based on a sediment microbial fuel cell for in situ and real time hexavalent chromium detection in industrial wastewater. Sensors, 18, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020642
Wu, S., Han, C., Liu, L., Zhong, W. (2018). A novel sediment microbial fuel cell based sensor for on-line and in situ monitoring copper shock in water. Electroanalysis, 30. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800424
Prévoteau, A., Clauwaert, P., Kerckhof, F.-M., & Rabaey, K. (2019). Oxygen-reducing microbial cathodes monitoring toxic shocks in tap water. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 132, 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.037
Kraemer, S. A., Ramachandran, A., & Perron, G. G. (2019). Antibiotic pollution in the environment: From microbial ecology to public policy. Microorganisms, 7, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7060180
Wu, W., Lesnik, K. L., Xu, S., Wang, L., & Liu, H. (2014). Impact of tobramycin on the performance of microbial fuel cell. Microbial Cell Factories, 13, 91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-014-0091-6
Chouler, J., & Di Lorenzo, M. (2015). Water quality monitoring in developing countries; can microbial fuel cells be the answer? Biosensors (Basel), 5, 450–470. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5030450
Zeng, L., Li, X., Shi, Y., Qi, Y., Huang, D., Tadé, M., et al. (2017). FePO4 based single chamber air-cathode microbial fuel cell for online monitoring levofloxacin. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 91, 367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.021
Yang, W., Wei, X., Fraiwan, A., Coogan, C., Lee, H., Choi, S. (2015). Fast and sensitive water quality assessment: a μL-scale microbial fuel cell-based biosensor integrated with an air-bubble trap and electrochemical sensing functionality. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.12.002.
Chouler, J., Cruz-Izquierdo, Á., Rengaraj, S., Scott, J. L., & Di Lorenzo, M. (2018). A screen-printed paper microbial fuel cell biosensor for detection of toxic compounds in water. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 102, 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.11.018
Shen, Y. J., Lefebvre, O., Tan, Z., & Ng, H. Y. (2012). Microbial fuel-cell-based toxicity sensor for fast monitoring of acidic toxicity. Water Science and Technology, 65, 1223–1228. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.957
Jiang, Y., Liang, P., Liu, P.-P., Yan, X., Bian, Y. (2016). A cathode-shared microbial fuel cell senor array for water alert system. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.050.
De Schamphelaire, L., Van den Bossche, L., Dang, H. S., Höfte, M., Boon, N., Rabaey, K., et al. (2008). Microbial fuel cells generating electricity from rhizodeposits of rice plants. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 3053–3058. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071938w
Li, T., Wang, X., Zhou, Q., Liao, C., Zhou, L., Wan, L., et al. (2018). Swift acid rain sensing by synergistic rhizospheric bioelectrochemical responses. ACS Sens, 3, 1424–1430. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b00401
Abrevaya, X. C., Sacco, N. J., Bonetto, M. C., Hilding-Ohlsson, A., & Cortón, E. (2015). Analytical applications of microbial fuel cells. Part II: Toxicity, microbial activity and quantification, single analyte detection and other uses. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 63, 591–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.053
Miller, L. G., & Oremland, R. S. (2008). Electricity generation by anaerobic bacteria and anoxic sediments from hypersaline soda lakes. Extremophiles, 12, 837–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-008-0191-5
Abrevaya, X. C., Mauas, P. J. D., & Cortón, E. (2010). Microbial fuel cells applied to the metabolically based detection of extraterrestrial life. Astrobiology, 10, 965–971. https://doi.org/10.1089/ast.2009.0460
Liu, Z., Liu, J., Zhang, S., Xing, X.-H., & Su, Z. (2011). Microbial fuel cell based biosensor for in situ monitoring of anaerobic digestion process. Bioresource Technology, 102, 10221–10229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.08.053
Kim, I., Chae, K.-J., Choi, M.-J., Verstraete, W., Kim, I. S., Chae, K.-J., Choi, M.-J., & Verstraete, W. (2008). Microbial fuel cells: recent advances, bacterial communities and application beyond electricity generation. Environmental Engineering Research, 13, 51–65. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2008.13.2.051
Le, C., Zha, Y., Li, Y., Sun, D., Lu, H., & Yin, B. (2010). Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environmental Management, 45, 662–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-010-9440-3
Yang, M. (2011). A current global view of environmental and occupational cancers. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part C, Environmental Carcinogenesis & Ecotoxicology Reviews, 29, 223–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2011.601848
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All the authors have their consent to participate.
Consent to Publish
All the authors have their consent to publish their work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Varshney, A., Sharma, L., pandit, C. et al. Microbial Fuel Cell–Based Biosensors and Applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 3508–3531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04397-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04397-x