Abstract
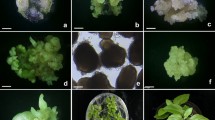
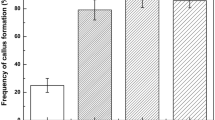
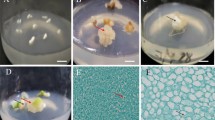
Culture conditions were established for high frequency plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from cell suspension cultures of Nymphoides coreana. Zygotic embryos formed pale-yellow globular structures and calluses at a frequency of 85.6% when cultured on half-strength Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 0.3 mg l−1 of 2,4-D. However, the frequency of pale-yellow globular structures and white callus formation decreased slightly with an increasing concentration of 2,4-D up to 10 mg l−1 with the frequency rate falling to 16.7%. Cell suspension cultures were established from zygotic embryo-derived calluses using half-strength MS medium supplemented with 0.3 mg l−1 of 2,4-D. Upon plating onto half-strength MS basal medium, over 92.3% of cell aggregates gave rise to numerous somatic embryos and developed into plantlets. Regenerated plantlets were successfully transplanted into potting soil and achieved full growth to an adult plant in a growth chamber. The high frequency plant regeneration system for Nymphoides coreana established in this study will be useful for genetic manipulation and cryopreservation of this species.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BA:
-
6-Benzyladenine
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1962)
- NAA:
-
α-Naphthaleneacetic acid
References
Brix H, Schierup HH (1989) The use of aquatic macrophytes in water-pollution control. Ambio 18:100–107
Choi H-K (2007) Menyanthaceae. In: Park C-W (ed) The genera of vascular plants of Korea. Academy, Seoul
Cook CDK (1996) Aquatic plant book. SPB, Amsterdam
Hyun JO (2001) Categorization of the threatened plant species in Korea. PhD thesis. Soonchunhyang University
Jenks MA, Kane ME, McConnell DB (2000) Shoot organogenesis from petiole explants in the aquatic plant Nymphoides indica. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 63:1–8
Kim C, Na HR, Choi H-K (2008) Conservation genetics of endangered Brasenia schreberi based on RAPD and AFLP makers. J Plant Biol 51:260–268
Lee HW, Choung HL, Roh TH, Kwon YH, Kim CH, Hyun JO, Chang IS (2005) Categorization and conservation of the threatened plant species in environmental impact assessment. Korea Environment Institute, Seoul
Min SR, Liu JR, Kim SW (2007) Plant regeneration from zygotic embryo-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Ranunculus kazusensis. Plant Biotechnol Rep 1:57–60
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Oh MJ, Min SR, Liu JR, Kim SW (2007) Plant regeneration from floral stem cultures of Nymphoides indica (L.) O. Kuntze. via somatic embryogenesis. J Plant Biotechnol 34:7–10
Oh MJ, Na HR, Choi HK, Liu JR, Kim SW (2008) High frequency plant regeneration from zygotic embryo derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures of watershield (Brasenia schreberi). Plant Biotechnol Rep 2:87–92
Sarasan V, Cripps R, Ramsay MM, Atherton C, McMichen M, Prendergast G, Rowntree JK (2006) Conservation in vitro of threatened plants–progress in the past decade. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:206–214
Shibayama Y, Kadono Y (2008) Genetic variations in the endangered aquatic plant Nymphoides coreana (Menyanthaceae) in south-western Japan. Plant Species Biol 23:212–216
Yan SZ (1983) Higher water plants of China. Science Press, China (in Chinese)
Yang YH, Kim BC, Kim MH (1990) Phytosociological studies on the vegetation in Chejudo Island. II. Secondary broad-leaved forests. J Basic Sci Cheju Natl Univ 1:37–48
Zimmels Y, Kirzhner F, Roitman S (2004) Use of naturally growing aquatic plants for wastewater purification. Water Environ Res 76:220–230
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from KRIBB Research Initiative Program, and a grant (ABC1000912) to S.W.K. from BioGreen 21 Program funded by the Rural Development Administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, M.J., Na, H.R., Choi, HK. et al. High frequency plant regeneration system for Nymphoides coreana via somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryo-derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4, 125–128 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-010-0126-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-010-0126-3