Abstract
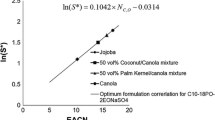
In this work, the impacts of extended surfactant structure (number of polypropylene oxide PO groups and branching nature of the hydrocarbon chain) on microemulsion formation and IFT values were examined with triglyceride oils. The results show that branching of the hydrocarbon tail of extended surfactants lowers optimum salinity and IFT values. The results also show that for the surfactants studied ultralow IFTs and microemulsion formation with vegetable oils can be achieved using extended surfactants with at least eight PO groups.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamilton RJ, Bhati A (1987) Recent advances in chemistry and technology of fats and oils. Elsevier Applied Science, New York
Knothe G (2006) Biodiesel and vegetable oil fuels: then and now. Inform 17:729–731
Baumann H, Buehler M, Fochem H, Hirsinger F, Zoebelein H, Falbe J (1988) Natural fats and oils—renewable raw materials for the chemical industry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 27:41–62
Kalustian P (1984) Pharmaceutical and cosmetic uses of palm and lauric products. J Am Oil Chem Soc 62:77–79
Crandall L (2003) Surfactant trends in personal-care products. Inform 14:270–271
McClements DJ (2005) Food emulsions: principles, practices, and techniques, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Do LD, Sabatini DA (2010) Aqueous extended-surfactant based method for vegetable oil extraction: proof of concept. J Am Oil Chem Soc. doi:10.1007/s11746-010-1603-0
Phan TT, Witthayapanyanon A, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2010) Microemulsion-based vegetable oil detergency using an extended surfactant. J Surfact Deterg 13:313–319
Salager JL, Anton RE, Sabatini DA, Harwell JH, Acosta EJ, Tolosa LI (2005) Enhancing solubilization in microemulsions–state of the art and current trends. J Surfact Deterg 8:3–21
Winsor PA (1948) Solvent properties of amphiphilic compounds. Trans Faradays Soc 44:736
Bourrel M, Schecter R (1988) Microemulsions and related systems. Marcel Dekker, New York
Rosen MJ (2004) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena. Wiley, New Jersey
Alander J, Warnheim T (1989) Model microemulsions containing vegetable oils part 1: nonionic surfactant systems. J Am Oil Chem Soc 66:1656–1660
Alander J, Warnheim T (1989) Model microemulsions containing vegetable oils 2. Ionic surfactant systems. J Am Oil Chem Soc 66:1661–1665
Tungsubutra T, Miller CA (1994) Effect of secondary alcohol ethoxylates on behavior of triolein-water-surfactant systems. J Am Oil Chem Soc 71:65–73
Miñana-Pérez M, Graciaa A, Lachaise J, Salager JL (1995) Solubilization of polar oils with extended surfactants. Colloids Surf A 100:217–224
von Corswant C, Soderman O (1997) Microemulsions based on soybean phosphatidylcholine and triglycerides. Phase Behav Microstruct Langmuir 13:5061–5070
Huang L, Lips A, Co CC (2004) Microemulsification of triglyceride sebum and the role of interfacial structure on bicontinuous phase behavior. Langmuir 20:3559–3563
Komesvarakul N, Sanders MD, Acosta EJ, Faller JF, Mentlik T, Fisher LB, Nicoll G, Sabatini DA, Scamehorn JF (2006) Microemulsions of triglyceride-based oils: the effects of co-oil and salinity on phase diagram. J Cosmet Sci 55:309–325
Engelskirchen S, Elsner N, Sottmann T, Strey R (2007) Triacylglycerol microemulsions stabilized by alkyl ethoxylate surfactants-a basic study. phase behavior, interfacial tension and microstructure. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:114–121
Garrett PR, Carr D, Giles D, Pierre-Louis G, Staples E, Miller CA, Chen BH (2008) Solubilisation of triolein by microemulsions containing C12E4/hexadecane/water: equilibrium and dynamics. J Colloid Interface Sci 325:508–515
Witthayapanyanon A, Acosta EJ, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2006) Formulation of ultralow interfacial tension systems using extended surfactants. J Surf Deterg 9:331–339
Do LD, Witthayapanyanon A, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2009) Environmentally friendly vegetable oil microemulsions using extended-surfactants and linkers. J Surf Deterg 12:91–99
Phan TT, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2010) Effects of triglyceride molecular structure on optimum formulation of surfactant-oil-water systems. J Surf Deterg 13:189–194
Velasquez J, Scorzza C, Vejar F, Forgiarini MA, Anton ER, Salager JL (2010) Effect of temperature and other variables on the optimum formulation of anionic extended surfactant–alkane–brine systems. J Surfact Deterg 13:69–73
Forgiarini MA, Scorzza C, Velasquez J, Vejar F, Zambrano E, Salager JL (2010) Influence of the mixed propoxy/ethoxy spacer arrangement order and of the ionic head group nature on the adsorption and aggregation of extended surfactants. J Surfact Deterg 13:451–458
Klaus A, Tiddy JTG, Touraud D, Schramm A, Stuhler G, Drechsler M, Kunz W (2010) Phase behavior of an extended surfactant in water and a detailed characterization of the dilute and semidilute phases. Langmuir 26:5435–5443
Aoudia M, Wade WH, Weerasooriya V (1995) Optimum microemulsions formulated with propoxylated guerbet alcohol and propoxylated tridecyl alcohol sodium sulfates. J Dispers Sci Technol 16:115–135
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Geoff Russell and Victoria Stolarski, Sasol North America (Lake Charles, LA) for providing the extended surfactant samples. Funding for this work was provided by industrial sponsors of the Institute of Applied Surfactant Research at the University of Oklahoma: Akzo Nobel, Clorox, Conoco-Philips, Church and Dwight, Dow Chemical, Ecolab, Haliburton, Huntsman, Oxiteno, Procter & Gamble, Sasol North America, S.C. Johnson & Son, Shell Chemical; and by the Sun Oil Company Endowed Chair (David A. Sabatini).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, T.T., Attaphong, C. & Sabatini, D.A. Effect of Extended Surfactant Structure on Interfacial Tension and Microemulsion Formation with Triglycerides. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88, 1223–1228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-011-1784-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-011-1784-1