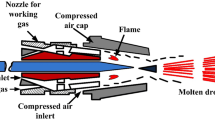
Abstract
Slurry and cavitation erosion often limits the durability of many fluid machines such as hydroturbines, pumps, and propellers. Despite good resistance against slurry erosion, thermal spray coatings generally exhibit poor resistance against cavitation erosion. The performance of thermal spray coatings under cavitation erosion is limited by the presence of defects such as pores, splat boundaries, and limited adhesion with the substrate. In the present work, we performed post-processing of the WC-10Co-4Cr and Ni coatings deposited using the detonation gun process. For post-processing, microwave technique was used owing to its capability for atomic-level heating. The microstructural characterization of the as-sprayed and post-processed coatings showed significant homogenization for the latter. Compared to the typical lamellar structure of as-sprayed, the processed samples exhibited a columnar structure with metallurgical bonding with the substrate. The mechanical properties of the coatings were significantly improved after post-processing owing to the elimination of splat boundaries and pores which significantly enhanced the cavitation and slurry erosion resistance. Post-processed coatings showed at least ten times higher resistance to cavitation erosion. The slurry erosion resistance of the coatings also improved up to three times depending upon the impingement angle. A significant difference in the erosion mechanism was also observed after post-processing.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhao, M. Maurer, F. Fischer, R. Dicks, and E. Lugscheider, Influence of Spray Parameters on the Particle in-Flight Properties and the Properties of HVOF Coating of WC-CoCr, Wear, 2004, 257, p 41-46
Y. Wu, S. Hong, J. Zhang, Z. He, W. Guo, Q. Wang, and G. Li, Microstructure and Cavitation Erosion Behavior of WC–Co–Cr Coating on 1Cr18Ni9Ti Stainless Steel by HVOF Thermal Spraying, Int. J. Refract Metal Hard Mater., 2012, 32, p 21-26
C.P. Bergmann and J. Vicenzi, Protection Against Erosive Wear Using Thermal Sprayed Cermet: A Review, Protection Against Erosive Wear Using Thermal Sprayed Cermet, Springer, New York, 2011, p 1-77
Q. Wang, Z. Tang, and L. Cha, Cavitation and Sand Slurry Erosion Resistances of WC-10Co-4Cr Coatings, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 2435-2443
S. Hong, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, Y. Zheng, Y. Qin, W. Gao, and G. Li, Cavitation Erosion Behavior and Mechanism of HVOF Sprayed WC-10Co-4Cr Coating in 3.5 wt% NaCl Solution, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2015, 68, p 151-159
X. Ding, X.-D. Cheng, C. Li, X. Yu, Z.-X. Ding, and C.-Q. Yuan, Microstructure and Performance of Multi-dimensional WC-CoCr Coating Sprayed by HVOF, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, 96, p 1-9
K. Lo, F. Cheng, C. Kwok, and H. Man, Improvement of Cavitation Erosion Resistance of AISI, 316 Stainless Steel by Laser Surface Alloying Using Fine WC Powder, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 165, p 258-267
J. Murthy, D. Rao, and B. Venkataraman, Effect of Grinding on the Erosion Behaviour of a WC–Co–Cr Coating Deposited by HVOF and Detonation Gun Spray Processes, Wear, 2001, 249, p 592-600
S. Hong, Y. Wu, B. Wang, Y. Zheng, W. Gao, and G. Li, High-Velocity Oxygen-Fuel Spray Parameter Optimization of Nanostructured WC–10Co–4Cr Coatings and Sliding Wear Behavior of the Optimized Coating, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 286-291
J. Murthy and B. Venkataraman, Abrasive Wear Behaviour of WC–CoCr and Cr3C2–20 (NiCr) Deposited by HVOF and Detonation Spray Processes, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200, p 2642-2652
S. Bhandari, H. Singh, H. Kumar, and V. Rastogi, Slurry Erosion Performance Study of Detonation Gun-Sprayed WC-10Co-4Cr Coatings on CF8M Steel Under Hydro-Accelerated Conditions, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2012, 21, p 1054-1064
S. Cui, Q. Miao, W. Liang, B. Huang, Z. Ding, and B. Chen, Slurry Erosion Behavior of F6NM Stainless Steel and High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel-Sprayed WC-10Co-4Cr Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2017, 26, p 473-482
D. Shetty, I. Wright, P. Mincer, and A. Clauer, Indentation Fracture of WC-Co Cermets, J. Mater. Sci., 1985, 20, p 1873-1882
A. Babu, H. Arora, H. Singh, H. Grewal, Microwave Synthesized Composite Claddings with Enhanced Cavitation Erosion Resistance, Wear, (2019).
D. Guo, F. Li, J. Wang, and J. Sun, Effects of Post-coating Processing on Structure and Erosive Wear Characteristics of Flame and Plasma Spray Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 1995, 73, p 73-78
C. Huang, X. Yan, W. Li, W. Wang, C. Verdy, M. Planche, H. Liao, and G. Montavon, Post-spray Modification of Cold-Sprayed Ni-Ti Coatings by High-Temperature Vacuum Annealing and Friction Stir Processing, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 451, p 56-66
G. Xie, X. Lin, K. Wang, X. Mo, D. Zhang, and P. Lin, Corrosion Characteristics of Plasma-Sprayed Ni-Coated WC Coatings Comparison with Different Post-treatment, Corros. Sci., 2007, 49, p 662-671
F. Wang, G.-N. Luo, J. Huang, and Y. Liu, Properties Improvement of Atmospheric Plasma Sprayed Tungsten Coating by Annealing, surf. coat. technol., 2019, 358, p 276-281
S. Saeidi, K. Voisey, and D. McCartney, The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Oxidation Behavior of HVOF and VPS CoNiCrAlY Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18, p 209-216
L. Lelait, S. Alperine, C. Diot, and M. Mevrel, Thermal Barrier Coatings: Microstructural Investigation After Annealing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1989, 120, p 475-482
Y. Yuanzheng, Z. Youlan, L. Zhengyi, and C. Yuzhi, Laser Remelting of Plasma Sprayed Al2O3 Ceramic Coatings and Subsequent Wear Resistance, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 291, p 168-172
P. Cheang, K. Khor, L. Teoh, and S. Tam, Pulsed Laser Treatment of Plasma-Sprayed Hydroxyapatite Coatings, Biomaterials, 1996, 17, p 1901-1904
R.B. Nair, H.S. Arora, P. Mandal, S. Das, H.S. Grewal, High‐Performance Microwave‐Derived Multi‐Principal Element Alloy Coatings for Tribological Application. Adv. Eng. Mater., (2018) 1800163.
R.B. Nair, H. Arora, and H. Grewal, Microwave Synthesized Complex Concentrated Alloy Coatings: Plausible Solution to Cavitation Induced Erosion-Corrosion, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2019, 50, p 114-125
S. Kaushal, D. Gupta, and H. Bhowmick, On Surface Modification of Austenitic Stainless Steel Using Microwave Processed Ni/Cr3C2 Composite Cladding, Surf. Eng., 2018, 34, p 809-817
A. Babu, H. Arora, S.N. Behera, M. Sharma, and H. Grewal, Towards Highly Durable Bimodal Composite Claddings Using Microwave Processing, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 349, p 655-666
C.D. Prasad, S. Joladarashi, M. Ramesh, M. Srinath, and B. Channabasappa, Influence of Microwave Hybrid Heating on the Sliding Wear Behaviour of HVOF Sprayed CoMoCrSi Coating, Mater. Res. Express, 2018, 5, p 086519
C.B. Ponton and R.D. Rawlings, Vickers Indentation Fracture Toughness Test Part 1 Review of Literature and Formulation of Standardised Indentation Toughness Equations, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1989, 5, p 865-872
R. Nair, K. Selvam, H. Arora, S. Mukherjee, H. Singh, and H. Grewal, Slurry Erosion Behavior of High Entropy Alloys, Wear, 2017, 386, p 230-238
H.S. Grewal, S. Bhandari, and H. Singh, Parametric Study of Slurry-Erosion of Hydroturbine Steels with and without Detonation Gun Spray Coatings Using Taguchi Technique, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43, p 3387-3401
A.S. Kurlov and A.I. Gusev, Tungsten Carbides: Structure, Properties and Application in Hardmetals, Springer, New York, 2013
R.J.K. Wood, B.G. Mellor, and M.L. Binfield, Sand Erosion Performance of Detonation Gun Applied Tungsten Carbide/Cobalt-Chromium Coatings, Wear, 1997, 211, p 70-83
D. Thakur, B. Ramamoorthy, and L. Vijayaraghavan, Influence of different post treatments on tungsten carbide–cobalt inserts, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, p 4403-4406
S. Zafar and A.K. Sharma, Abrasive and Erosive Wear Behaviour of Nanometric WC–12Co Microwave Clads, Wear, 2016, 346, p 29-45
W.N. Sharpe Jr, A. McAleavey, Tensile Properties of LIGA Nickel, Materials and Device Characterization in Micromachining, International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1998, pp. 130-137.
H. Grewal, A. Agrawal, H. Singh, and B.A. Shollock, Slurry Erosion Performance of Ni-Al2O3 Based Thermal-Sprayed Coatings: Effect of Angle of Impingement, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2014, 23, p 389-401
Y. Wang, J. Han, H. Wu, B. Yang, and X. Wang, Effect of Sigma Phase Precipitation on the Mechanical and Wear Properties of Z3CN20. 09M Cast Duplex Stainless Steel, Nucl. Eng. Des., 2013, 259, p 1-7
D. Wheeler and R. Wood, Erosion of Hard Surface Coatings for Use in Offshore Gate Valves, Wear, 2005, 258, p 526-536
A.V. Levy and W. Buqian, Erosion of Hard Material Coating Systems, Wear, 1988, 121, p 325-346
I. Hutchings, Wear by Particulates, Chem. Eng. Sci., 1987, 42, p 869-878
P.H. Shipway and I.M. Hutchings, The Rôle of Particle Properties in the Erosion of Brittle Materials, Wear, 1996, 193, p 105-113
H. Feller and Y. Kharrazi, Cavitation Erosion of Metals and Alloys, Wear, 1984, 93, p 249-260
W. Yuping, L. Pinghua, C. Chenglin, W. Zehua, C. Ming, and H. Junhua, Cavitation Erosion Characteristics of a Fe–Cr–Si–B–Mn Coating Fabricated by High Velocity Oxy-Fuel (HVOF) Thermal Spray, Mater. Lett., 2007, 61, p 1867-1872
W. Tomlinson, N. Kalitsounakis, and G. Vekinis, Cavitation Erosion of Aluminas, Ceram. Int., 1999, 25, p 331-338
C. Jiang, Y. Xing, J. Hao, and X. Song, Effects of Heat-Treatment on Crystallization and Wear Property of Plasma Sprayed Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings, J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2013, 28, p 643-646
G. Liu, Y. An, J. Chen, G. Hou, and J. Chen, Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Sliding Wear of Thermally Sprayed Fe-Based Metallic Glass Coatings, Tribol. Lett., 2012, 46, p 131-138
G.J. Li, J. Li, and X. Luo, Effects of High Temperature Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Clad NiCrBSi/WC Coatings on Titanium Alloy Substrate, Mater. Charact., 2014, 98, p 83-92
H. Pokhmurska, B. Wielage, T. Lampke, T. Grund, M. Student, and N. Chervinska, Post-treatment of Thermal Spray Coatings on Magnesium, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2008, 202, p 4515-4524
J. Lin, Z. Wang, P. Lin, J. Cheng, X. Zhang, and S. Hong, Effects of Post Annealing on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Cavitation Erosion Behavior of Arc-sprayed FeNiCrBSiNbW Coatings, Mater. Des., 2015, 65, p 1035-1040
Z. Zheng, Y. Zheng, W. Sun, and J. Wang, Effect of Heat Treatment on the Structure, Cavitation Erosion and Erosion–Corrosion Behavior of Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings, Tribol. Int., 2015, 90, p 393-403
Acknowledgments
H S Grewal thankfully acknowledges the financial assistance provided by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Science & Engineering Research Board (SERB), India, under the project title “Microwave Derived Bi-modal Composite Coatings For Encountering Erosion-Related Problems” (File No. ECR/2015/000106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, A., Arora, H.S. & Grewal, H.S. Microwave-Assisted Post-processing of Detonation Gun-Sprayed Coatings for Better Slurry and Cavitation Erosion Resistance. J Therm Spray Tech 28, 1565–1578 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-019-00914-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-019-00914-9