Abstract
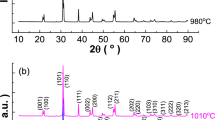
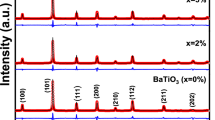
(1 − x)(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-xBi(Cu2/3Nb1/3)O3 [(1 − x)KNN-xBCN, 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.02] lead-free piezoelectric ceramics were prepared by a solid-state reaction method. The effects of BCN addition on the phase transition, microstructure and electrical properties of ceramics were studied. X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy analysis confirmed that the BCN has diffused into KNN to form a solid solution. Both polymorphic phase transition, T O-T, and Curie temperature, T c, gradually decreased with increasing the BCN content. Moreover, the relative permittivity (ε r) was increased greatly and the dielectric loss (tanδ) was almost decreased. Ferroelectric hysteresis loops (P–E) of samples showed that the remnant polarization (P r) was up to a maximum value with 26.52 μm/cm as x = 0.01. The piezoelectric properties of ceramics increased with increasing the x values. When x = 0.005 and 0.01, the ceramics exhibited high piezoelectric constant with 131 pC/N and 105 pC/N over a good piezoelectric stability under 350°C, respectively. These results indicate that BCN addition is an effective way to enhance the properties of KNN ceramics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liu, R.Q. Chu, Z.J. Xu, Y.J. Zhang, Q. Chen, and G.R. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 1463 (2011).
X.L. Chen, F. He, J. Chen, Y.L. Wang, H.F. Zhou, and L. Fang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 2634 (2014).
P. Bharathi and B.R. Varma, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 493 (2014).
H. Ping, P. Henson, and R.W. Johnson, I.E.E.E. Trans. Ind. Electron. 58, 2673 (2011).
H. Wang, X. Zhai, J.W. Xu, C.L. Yuan, and C.R. Zhou, J. Electron. Mater. 24, 2469 (2013).
S.J. Zhang, R. Xia, and T.R. Shrout, J. Electroceram. 19, 251 (2007).
V. Bobnar, M. Hrovat, J. Holc, C. Filipič, A. Levstik, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 105, 954 (2009).
Y. Guo, K. Kakimoto, and H. Ohsato, Solid State Commun. 129, 279 (2004).
V. Bobnar, J. Bernard, and M. Kosec, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 994 (2004).
J. Zhao, H. Du, S. Qu, J. Wang, H. Zhang, Y.M. Yang, and Z. Xu, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3537 (2011).
E.M. Alkoy and M. Papila, Ceram. Int. 36, 1921 (2010).
M.H. Zhang, K. Wang, Y.J. Du, G. Dai, W. Sun, G. Li, D. Hu, H.C. Thong, C. Zhao, X.Q. Xi, Z.X. Yue, and J.F. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 3889 (2017).
F.Z. Yao, K. Wang, W. Jo, K.G. Webber, T.P. Comyn, J.X. Ding, B. Xu, L.Q. Cheng, M.P. Zheng, Y.D. Hou, and J.F. Li, Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 1217 (2016).
Y.M. Li, Z.Y. Shen, F. Wu, T.Z. Pan, Z.M. Wang, and Z.G. Xiao, J. Electron. Mater. 25, 1028 (2014).
K. Kakimoto, K. Akao, Y. Guo, and H. Ohsato, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 7064 (2005).
Y.B. Yao, H.T. Chan, C.L. Mak, and K.H. Wong, Thin Solid Films 537, 156 (2013).
X.L. Chen, G.F. Liu, G.S. Huang, X.X. Li, X. Yan, and H.F. Zhou, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 13126 (2017).
C.W. Ahn, H.I. Hwang, K.S. Lee, B.M. Jin, S. Park, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 49, 095801 (2010).
R. Singh, K. Kambale, A.R. Kulkarni, and C.S. Harendranath, Mater. Chem. Phys. 138, 905 (2013).
R. Wang, R.J. Xie, K. Hanada, K. Matsusaki, H. Bando, and M. Itoh, Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. 202, R57 (2005).
T. Zheng, H.J. Wu, Y. Yuan, X. Lv, Q. Li, T.L. Men, C.L. Zhao, D.Q. Xiao, J.G. Wu, K. Wang, J.F. Li, Y.L. Gu, J.G. Zhua, and S.J. Pennycook, Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 528 (2017).
W.L. Zhu, J.L. Zhu, Y. Meng, M.S. Wang, B. Zhu, et al., J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 44, 505303 (2011).
X.P. Wang, J.G. Wu, D.Q. Xiao, J.G. Zhu, X.J. Cheng, T. Zheng, B.Y. Zhang, X.J. Lou, and X.J. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 2905 (2014).
K. Xu, J. Li, X. Lv, J.G. Wu, X.X. Zhang, D.Q. Xiao, and J.G. Zhu, Adv. Mater. 28, 8519 (2016).
M. Sutapun, C.C. Huang, D.P. Cann, and N. Vittayakorn, J. Alloys Compd. 479, 462 (2009).
H.L. Du, W.C. Zhou, F. Luo, D.M. Zhu, S.B. Qu, Y. Li, and Z.B. Pei, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 034104 (2008).
H.L. Du, W.C. Zhou, F. Luo, D.M. Zhu, S.B. Qu, Y. Li, and Z.B. Pei, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 085416 (2008).
D. Lin, K.W. Kwok, and H.L.W. Chan, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 6778 (2007).
G.Z. Dong, H.Q. Fan, J. Shi, and M. Li, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 1150 (2014).
J.G. Wu, D.Q. Xiao, and J.G. Zhu, Chem. Rev. 115, 2559 (2015).
H.L. Du, W.C. Zhou, F. Luo, D.M. Zhu, S.B. Qu, and Z.B. Pei, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 202907 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Yan, X., Liu, G. et al. (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-Bi(Cu2/3Nb1/3)O3 Lead-free Ceramics: Phase Transition, Enhanced Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 794–799 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5859-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5859-0