Abstract
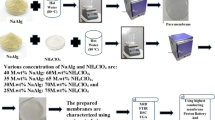
In this present work, a proton-conducting solid biopolymer electrolyte membrane that consists of sodium alginate (SA) incorporated with ammonium formate (NH4HCO2) has been prepared by solution casting technique. Using the highest proton-conducting membrane, electrochemical devices like battery and fuel cell have been constructed. Graphene quantum dot has been used as an additive to highest conducting polymer electrolyte (30 M.wt%SA:70 M.wt%NH4HCO2). The prepared membranes (SA:NH4HCO2) were subjected to various characterization techniques such as XRD, FTIR, DSC, Ac impedance technique, and LSV. On increasing salt concentration, XRD analysis shows that amorphous nature increases. Highest amorphous nature has been found for 30 M.wt%SA:70 M.wt%NH4HCO2. The complex formation between SA and NH4HCO2 has been confirmed by FTIR measurements. The glass transition temperature, Tg, has been measured using DSC (differential scanning calorimetry). 30 M.wt%SA:70 M.wt%NH4HCO2 membrane shows a highest ionic conductivity value of 2.77 × 10−3 S cm−1. The addition of 1.25 ml GQD into the 30 M.wt%SA:70 M.wt%NH4HCO2 biopolymer electrolyte membrane has improved the value of ionic conductivity to 2.01 × 10−2 S cm−1. Transference number analysis reveals that the conductivity is mainly due to the ions in the polymer electrolyte (Wagner’s polarization method). LSV technique is used to measure the electrochemical stability of the biopolymer electrolyte membrane which resulted with 1.90 V (without GQD) and 2.08 V (with GQD). Battery constructed with highest ionic conducting membrane shows an open circuit voltage of 1.77 V (without GQD) and 1.79 V (with GQD). A fuel cell has been constructed using highest conducting biopolymer electrolyte membrane and the open circuit voltages of 707 mV (without GQD) and 778 mV (with GQD) have been measured.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manjuladevi R, Thamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Mangalam R, Premalatha M, Monisha S (2017) Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly (acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. J Solid State Ionics 308:90–100
Fuzlin AF, Saadiah MA, Yao Y, Nagao Y, Samsudin AS (2020) Enhancing proton conductivity of sodium alginate doped with glycolic acid in bio-based polymer electrolytes system. J Polym Res 27(207):1–16
Mazuki NF, Fuzlin AF, Saadiah MA, Samsudin AS (2018) An investigation on the abnormal trend of the conductivity properties of CMC/PVA-doped NH4Cl-based solid biopolymer electrolyte system. Ionics 25:2657–2667
Rasali NMJ, Nagao Y, Samsudin AS (2018) Enhacement on amorphous phase in solid biopolymer electrolyte based alginate doped NH4NO3. Ionics 25:641–654
Deepa M, Sharma N, Agnihotry SA, Singh S, Lal T, Chandra R (2002) Conductivity and viscosity of liquid and gel electrolytes based on LiClO4, LiN(CF3SO2)2 and PMMA. Solid State Ionics 152–153:253–258
Perera K, Dissanayake MAKL (2006) Conductivity variation of the liquid electrolyte, EC:PC:LiCF3SO3 with salt concentration. Sri Lankan J Phys 7:1–5
Zhao D, Fei Z, Ang WH, Dyson PJ (2007) Sulfonium-based ionic liquids incorporating the allyl functionality. Int J Mol Sci 8(4):304–315
Muthupradeepa R, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R, Suryanarayanan V (2017) Sulfonium cation based ionic liquid incorporated polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Polym Bull 74(5):1677–1691
Fisher AS, Khalid MB, Widstrom M, Kofinas P (2011) Soild polymer electrolytes with sulfur based ionic liquid for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 196(22):9767–9773
Kim HJ, Boysen DA, Newhouse JM, Spatocco BL, Chung B, Burke PJ, Bradwell DJ, Jiang K, Tomaszowska AA, Wang K, Wei WF, Ortiz LA, Barriga SA, Poizeau SM, Sadoway DR (2013) Liquid metal batteries: past, present and future. Chem Rev 113(3):2075–2099
Rasali NMJ, Samsudin AS (2018) Characterization on ionic conductivity of Solid Bio-Polymer Electrolytes system based Alginate Doped Ammonium Nitrate via Impedance Spectroscopy. AIP conference proceeding 2030(020224):1–8
Murata K, Izuchi S, Yoshihisa Y (2000) An overview of the research and development of solid polymer electrolyte batteries. J Electrochem Ica Acta 45(8–9):1501–1508
Kima S, Hwang EJ, Jung Y, Han M, Park SJ (2007) Ionic conductivity of polymeric nanocomposite electrolytes based on poly(ethylene oxide) and organo-clay materials. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng Aspects 313–314:216–219
Aziz SB, Brza MA, Saed SR, Hamsan MH, Kadir MFZ (2020) Ion association as a main shortcoming in polymer blend electrolytes based on GS:PS incorporated with various amounts of ammonium tetrafluoroborate. J Mater Res Technol 9(3):5410–5421
Aziz SB (2013) Li+ion conduction mechanism in poly (g-caprolactone) based polymer electrolyte. Iran polym J 22:877–883
Liu YH, Zhu LQ, Shi Yi, Wan Q (2014) Proton conducting sodium alginate electrolyte laterally coupled low- voltage oxide – based transistors. Appl Phys Lett 104(133504):1–5
Gao H, Lian K (2014) Proton –conducting polymer electrolytes and their applications in solid supercapacitors a review. J RSC Adv 4:33091–33113
Fuzlin AF, Nagao Y, Misnon II, Samsudin AS (2020) Studies on structural and ionic transport in biopolymer electrolytes based alginate – libr. Ionics 26:1923–1938
Singh R, Polu AR, Bhattacharya B, Rhee HW, Varlikli C, Singh PK (2016) Perspective for solid biopolymer electrolytes in dye sensitized solar cell and battery application. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 65:1098–1117
Kurupati S, Gunturi SS, Nadella KJ, Erothu H (2019) Novel solid polymer electrolyte based on PMMA: CH3COOLi effect of salt concentration on optical and conductivity studies. Polym Bull 76:5463–5481
Wang J, Song S, Muchakayala R, Hu X, Liu R (2017) Structural, electrical and electrochemical properties of PVA-based biodegradable gel polymer electrolyte membrances for Mg-ion battery applications. Ionics 23:1759–1769
Kingslin Mary Genova F, Selvasekarapandian S, Vijaya N, Sivadevi S, Premalatha M, Karthikeyan S (2017) Lithium-ion conducting polymer electrolytes blend based on PVA-PAN doped with lithium triflate. Ionics 23:2727–2734
Karthika P, Sundaresan B (2018) AC impedance, surface & TGA/DTA Analysis of PVC-LiNO3-CdO. Mech Mater Sci Eng J 14:1–5
Sarangika HNM, Dissanayake MAKL, Senadeera GKR, Rathnayake RRDV, Pitawala HMJC (2017) Polyethylene oxide and ionic liquid-based solid polymer electrolyte for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Ionics 23:2829–2835
Liu J, Wu X, He J, Li J, Lai Y (2017) Preparation and performance of a novel gel polymer electrolyte based on poly (vinylidene fluoride)/grapheme separator for lithium ion battery. Electrochem Acta 235:500–507
Jia W, Li Z, Wu Z, Wang L, Wu B, Wang Y, Cao Y, Li J (2018) Graphene oxide as a filler impove the performance of PAN-LiClO4 flexible solid polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 315:7–13
Kulkarni Vishaka S, Butte Kishor D, Rathod Sudha S (2012) Natural polymers – a comprehensive review. J Pharm Biomed Sci 3(4):1597–1613
Selvalakshmi S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2018) Effect of ethylene carbonate plasticizer on agar-agar: NH4Br-based solid polymer electrolytes. Ionics 24:2209–2217
Meera Naachiyar R, Ragam M, Selvasekarapandian S, Vengadesh Krishna M, Buvaneshwari P (2021) Development of biopolymer electrolyte membrane using Gellan gum biopolymer incorporated with NH4SCN for electrochemical application. Ionics 27:3415–3429
Andrimanantoanina H, Rinaudo M (2010) Relationship between the molecular structure of alginates and their gelation in acidic conditions. Polym Int 59:1531–1541
Draget KI, Skjak-Braek G, Christensen BE, Gaserod O, Smidsrod O (1996) Swelling and partial solubilization of alginic acid gel beads in acidic buffer. Carbohydrate Polym 29(3):209–215
Yeom CK, Lee KH (1998) Characterization of sodium alginate membrane crosslinked with glutaraldehyde in pervaporation separation. J Appl Polym Sci 67:209–219
Veerapur RS, Gudasi KB, Sairam M, Shenoy RV, Netaji M, Raju K, Sreedhar B, Aminabhavi TM (2007) Novel sodium alginate composite membranes prepared by incorporating cobalt(III) complex particles used in pervaporation separation of water–acetic acid mixtures at different temperatures. J Mater Sci 42(12):4406–4417
Oliveira Filho JG, Rodrigues JM, Valadares ACF, Almeida AB, Lima TM, Takeuchi KP (2019) Active food packaging: alginate films with cottonseed protein hydrolysates. Food Hydrocolloids 92:267–275
Chen W, Feng Q, Zhang G, Yang Q, Zhang C (2017) The effect of Sodium Alginate on the flotation separation of scheelite from calcite and fluorite. Miner Eng 113:1–7
Sreekanth Reddy O, Subha MCS, Jithendra T, Madhavi C, Chowdoji Rao K (2020) Curcumin encapsulated dual cross linked Sodim Alginate/ Montmorillonite polymeric composite beads for controlled drug delivery. J Pharm Anal S2095–1779(20):31022–31024
Satheeshbabu BK, Mohamed I (2015) Synthesis and characterization of sodium alginate conjugate and study of effect of conjugation on drug release from matrix tablet. Indian J Pharm Sci 77(5):579–585
Aguero L, Zaldivar-Silva D, Pena L, Dias ML (2017) Alginate microparticles as oral colon drug delivery device. Rev Carbohydr Polym 168:32–43
Reddy PRS, Rao KM, Rao KSVK (2014) Synthesis of Alginate based silver nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Macromol. Res. 22:832–842
Akin A, Isiklan N (2016) Microwave assisted synthesis and characterization of sodium alginate-graft-poly (N, N-dimethylacrylamide). Int J Biol Macromol 82:530–540
Li J, He J, Huang Y (2017) Role of alginate in antibacterial finishing of textiles. Int J Biol Macromol 94:466–473
Bae SB, Nam HC, Park WH (2019) Electrospraying of environmentally sustainable alginate microbeads for cosmetic additives. Int J Biol Macromolecules 133:278–283
Reddy KM, Babu VR, Rao KSVK et al (2007) Use of clays as drug delivery systems: possibilities and limitations. Appl Clay Sci 36:22–36
Prajapati ST, Patel LD, Patel DM (2009) Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation of floating matrix tablets of domperidone. Indian J Pharm Sci 71:19–23
Iwaki YO, Hernandezescalona M, Briones JR, Pawlicka A (2012) Sodium alginate based ionic conducting membranes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 554:221–231
Mohanapriya S, Bhat SD, Sahu AK, Manokaran A, Vijayakumar R, Pitchumani S, Sridhar P, Shukla AK (2010) Sodium alginate based proton exchange membranes as electrolyte for DMFCs. Energy Environ Sci 3:1746–1756
Shaari N, Kamarudin SK (2017) Characterization studies of sodium alginate/sulfonated grapheme oxide based polymer electrolyte membrane for direct methanol fuel cell. Malays J Anal Sci 21:113–118
Hajifathaliha F, Mahboubi A, Nematollahi L, Mohit E, Bolourchian N (2018) Comparison of different cationic polymers efficacy in fabrication of alginate multilayer microcapsules. Asian J Pharm Sci 15:95–103
Park S, Ruoff R (2009) Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat Nanotechnol 4(4):217–224
Dreyer DR, Park S, Bielawski CW, Ruoff RS (2010) The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 39:228–240
Zhu Y, Murali S, Cai W, Li X, Suk JW, Potts JR, Ruoff RS (2010) Graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv Mater 22:3906–3924
Ramanathan T, Abdala AA, Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Herrera-Alonso M, Piner RD, Adamson DH, Schniepp HC, Chen X, Ruoff RS, Nguyen ST, Aksay IA, Prud’homme RK, Brinson LC (2008) Functionalized graphene sheets for polymer nanocomposites. Nanotechnol 3:327–331
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semicrystalline poly(vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer 37:1371–1376
Kanti P, Srigowri K, Madhuri J, Smitha B, Sridhar S (2004) Dehydration of ethanol through blend membranes of chitosan and sodium alginate by pervaporation. Sep Puri Technol 40:259–266
Li P, Dai YN, Zhang JP, Wang AQ, Wei Q (2008) Chitosan-alginate nanoparticles as a novel drug delivary system for nifedipine. Int J Biomed Sci 4(3):221–228
Diana I, Selvin C, Selvasekarapandian S, Vengadesh Krishna M (2021) Investigations on Na-ion conducting electrolyte based on sodium alginate biopolymer for all solid-state sodium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 25:2009–2020
Helmiyati AM (2017) Characterization and properties of Sodium alginate from brown algae used as an ecofriendly superabsorbent. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 188(12019):1–7
Nusrath Unnisa C, Chithra S, Selvasekarapandian S, Monisha S, Nirmala Devi G, Moniha V, Hema M (2018) Development of poly(glycerol suberate) polyester (PGS)-PVA blend polymer electrolytes with NH4SCN and its application. Ionics 24:1979–1993
Ponraj T, Ramalingam A, Selvasekarapandian S, Srikumar SR, Manjuladevi R (2020) Plasticized solid polymer electrolyte based on triblock copolymer poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile-co-methyl methacrylate) for magnesium ion batteries. J Polym Bull 78:35–57
Boukamp BA (1986) A package of impedance admittance data analysis. Solid State Ionics 18–19:136–140
Karthikeyan S, Sikkanthar S, Selvasekarapandian S, Arunkumar D, Nithya H, Iwa Y, Kawamura J (2016) Structural, electrical and electrochemical properties of polyacrylonitrile-ammonium hexaflurophosphate polymer electrolyte system. J Polym Res 23(51):1–10
Wagner JB, Wagner CJ (1957) Electrical conductivity measurements on curprous halides. J Chem Phys 26:1597–1601
Aziz SB, Brza MA, Hamsan HM, Kadir MFZ, Abdulwahid RT (2021) Electrochemical characteristics of solid state doublelayer capacitor constructed from proton conducting chitosan-based polymer blend electrolytes. Polym Bull 78(6):3149–3167
Hamsan MH, Shukur MF, Aziz SB, Yusof YM, Kadir MFZ (2020) Influence of NH4Br as an ionic source on thestructural/electrical properties of dextran-based biopolymer electrolytes and EDLC application. Bull Mater Sci 43(1)
Maheshwari T, Tamilarasan K, Selvasekarapandian S, Chitra R, Kiruthika S (2021) Investigation of blend biopolymer electrolytes based on Dextran-PVA with ammonium thiocyanate. J Solid State Electrochem 25:755–765
Pandey K, Lakshmi N, Chandra S (1998) A rechargeable solid state proton battery with an intercalating cathode and an anode containing a hydrogen storage-material. J Power Sources 76(1):116–123
Monisha S, Mathavan T, Selvesekarapandian S, Beniala AMF, Aristatil G, Manic N, Premalatha M, Vinoth pandi D (2017) Investigation of bio polymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate-ammonium nitrate fpr potential use in electrochemical devices. Carbohyde Polym 157:38–47
Selvalakshmi S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2018) A study of electrochemical devices based on Agar-Agar-NH4I biopolymer electrolytes. AIP Conference Proceedings 1942, 140019:1–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanitha, N., Shanmugapriya, C., Selvasekarapandian, S. et al. Effect of graphene quantum dot on sodium alginate with ammonium formate (NH4HCO2) biopolymer electrolytes for the application of electrochemical devices. Ionics 28, 2731–2749 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04522-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04522-6