Abstract
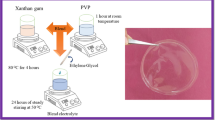
Two water-soluble and biodegradable polymers: xanthan gum (XG) and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) were used to synthesize ecologically friendly solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) matrices. While XG is a natural polymer, PVA is a synthetic one, but both are colorless and form transparent membranes. To obtain ionic conductivity properties, the samples were doped with acetic acid and characterized by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), X-ray diffraction, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and tensile test. The best results of ionic conductivity of 1.97 × 10−4 and 7.41 × 10−4 S/cm at room temperature and 80 °C, respectively, were obtained for the sample containing 55 wt% of acetic acid. Moreover, this electrolyte was found to be predominantly amorphous with transmittance in the visible region of 80% and absorbance values below 0.5 between 240 and 375 nm. Tensile test of this sample, applied up to 18 N of maximum force, resulted in strain of 2322% and Young’s modulus of 0.02 MPa. The obtained results showed that these new eco-friendly materials are promising for use as electrolytes in electrochemical devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baloukas B, Lamarre J-M, Martinu L (2011) Electrochromic interference filters fabricated from dense and porous tungsten oxide films. Sol Energ Mat Sol Cells 95:807–815. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2010.10.026
Sequeira CAC, Santos DMF (eds.) (2010) Polymer Electrolytes - Fundamentals and Applications. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Oxford, UK
Agrawal S, Awadhia A (2004) DSC and conductivity studies on PVA based proton conducting gel electrolytes. B Mater Sci 27:523–527. doi:10.1007/BF02707280
Alves R, Silva MM (2014) The influence of glycerol and formaldehyde in gelatin-based polymer electrolytes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 591:64–73. doi:10.1080/15421406.2013.822739
Granqvist CG (2014) Electrochromics for smart windows: oxide-based thin films and devices. Thin Solid Films 564:1–38. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2014.02.002
Silva VPR, Caliman V, Silva GG (2005) Polímeros com condutividade iônica: desafios fundamentais e potencial tecnológico. Polímeros, Ciência e Technologia 15:249–255. doi:10.1590/S0104-14282005000400008
Guerrini LM, Branciforti MC, Bretas RE, de Oliveira MP (2006) Electrospinning of Aqueous Solution of Poly(vinyl alcohol). Polímeros Ciência e Tecnologia 16:286-293. doi:10.1590/S0104-14282006000400007
Goodship V, Jacobs D (2009) Polyvinyl alcohol: properties and applications. Smithers Rapra Technology, Shrewsbury
Neto MJ, Sentanin F, Esperança JMSS, Medeiros MJ, Pawlicka A, de Zea BV, Silva MM (2015) Gellan gum—ionic liquid membranes for electrochromic device application. Solid State Ionics 274:64–70. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2015.02.011
Rau I, Grote J, Kajzar F, Pawlicka A (2012) DNA—novel nanomaterial for applications in photonics and in electronics. Comptes Rendus Phys 13:853–864. doi:10.1016/j.crhy.2012.09.005
García-Ochoa F, Santos V, Casas J, Gomez E (2000) Xanthan gum: production, recovery, and properties. Biotech Adv 18:549–579. doi:10.1016/S0734-9750(00)00050-1
Casas JA, Santos VE, Garcı́a-Ochoa F (2000) Xanthan gum production under several operational conditions: molecular structure and rheological properties☆. Enz Microb Tech 26:282–291. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00160-X
Machado BAS, Reis JHO, TVB F, Druzian JI (2012) Mapeamento tecnológico da goma xantana sob o enfoque em pedidos de patentes depositados no mundo entre 1970 a 2009. GEINTEC-Gestão, Inovação e Tecnologias 2:154–165. doi:10.7198/S2237-07222012000200006
Lima E, Raphael E, Sentanin F, Rodrigues LC, Ferreira RAS, Carlos LD, Silva MM, Pawlicka A (2012) Photoluminescent polymer electrolyte based on agar and containing europium picrate for electrochemical devices. Mater Sci Eng B 177:488–493. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2012.02.004
Singh A, Narvi S, Dutta P, Pandey N (2006) External stimuli response on a novel chitosan hydrogel crosslinked with formaldehyde. B Mater Sci 29:233–238
Pawlicka A, Sabadini AC, Raphael E, Dragunski DC (2008) Ionic conductivity thermogravimetry measurements of starch-based polymeric electrolytes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 485:804–816. doi:10.1080/15421400801918138
Vieira DF, Avellaneda CO, Pawlicka A (2007) Conductivity study of a gelatin-based polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 53:1404–1408. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.04.034
Pawlicka A, Vieira D, Sabadini RC (2013) Gelatin-HCl biomembranes with ionic-conducting properties. Ionics 19:1723–1731. doi:10.1007/s11581-013-0935-9
Mîndroiu M, Zgârian RG, Kajzar F, Rău I, De Oliveira HCL, Pawlicka A, Tihan GT (2015) DNA-based membranes for potential applications. Ionics 21:1381–1390. doi:10.1007/s11581-014-1293-y
Thayumanasundaram S, Rangasamy VS, Seo JW, Locquet J-P (2017) Electrochemical performance of polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) blend and pyrrolidinium ionic liquid for lithium rechargeable batteries. Electrochim Acta 240:371–378. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2017.04.107
Rajendran S, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R (2003) Effect of salt concentration in poly(vinyl alcohol)-based solid polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 124:225–230. doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00591-3
Lopes LS, Machado GO, Pawlicka A, Donoso JP (2005) Nuclear magnetic resonance and conductivity study of hydroxyethylcellulose based polymer gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 50:3978–3984. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2005.02.056
Dragunski DC, Pawlicka A (2002) Starch based solid polymeric electrolytes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 374:561–568. doi:10.1080/10587250210443
Tretinnikov ON, Zagorskaya SA (2012) Determination of the degree of crystallinity of poly(vinyl alcohol) by FTIR spectroscopy. J Appl Spec 79:521–526. doi:10.1007/s10812-012-9634-y
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Bhuvaneswari M (2004) Dielectric and conductivity relaxations in PVAc based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 10:129–134. doi:10.1007/BF02410321
Arof AK, Osman Z, Morni NM, Kamarulzaman N, Ibrahim ZA, Muhamad MR (2001) Chitosan-based electrolyte for secondary lithium cells. J Mater Sci 36:791–793. doi:10.1023/A:1004869815261
Raphael E, Avellaneda CO, Manzolli B, Pawlicka A (2010) Agar-based films for application as polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 55:1455–1459. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.06.010
Khiar A, Puteh R, Arof A (2006) Conductivity studies of a chitosan-based polymer electrolyte. Physica B: Cond Matter 373:23–27. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2005.10.104
Robitaille C, Fauteux D (1986) Phase diagrams and conductivity characterization of some PEO-LiX electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 133:315–325. doi:10.1149/1.2108569
Mishra K, Pundir SS, Rai D (2017) Effect of polysorbate plasticizer on the structural and ion conduction properties of PEO–NH4PF6 solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 23:105–112
Pawlicka A, Danczuk M, Wieczorek W, Zygadlo-Monikowska E (2008) Influence of plasticizer type on the properties of polymer electrolytes based on chitosan. J Phys Chem A 112:8888–8895. doi:10.1021/jp801573h
Carvalho LA, Andrade AR, Bueno PR (2006) Espectroscopia de impedância eletroquímica aplicada ao estudo das reações heterogêneas em ânodos dimensionalmente estáveis. Química Nova 29:796–804. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422006000400029
Takahash Y, Sumita I, Tadokoro H (1973) Structural Studies of Polyethers .9. Planar zigzag modification of poly(ethylene oxide). J Polym Sci B 11:2113–2122. doi:10.1002/pol.1973.180111103
Kumar M, Sekhon S (2002) Role of plasticizer's dielectric constant on conductivity modification of PEO–NH 4 F polymer electrolytes. Europ Polym J 38:1297–1304. doi:10.1016/S0014-3057(01)00310-X
Tavares FC (2015) Preparação e Caracterização de Eletrólitos Sólidos Poliméricos à base de Goma Xantana. Dissertation, Universidade Federal de Pelotas-RS, Brazil
Iwaki Y, Escalona MH, Briones J, Pawlicka A (2012) Sodium alginate-based ionic conducting membranes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 554:221–231. doi:10.1080/15421406.2012.634329
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to FAPERGS (grant 12/2239-9) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq; grant 305029/2013-4) for the financial support given to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caldeira, I., Lüdtke, A., Tavares, F. et al. Ecologically friendly xanthan gum-PVA matrix for solid polymeric electrolytes. Ionics 24, 413–420 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2223-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2223-6