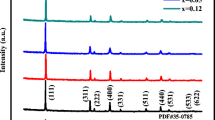
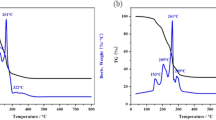
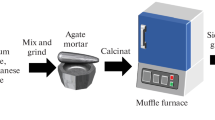
Abstract
The Mg-doped materials are synthesized by a novel ionothermal method using a kind of imidazolium-based ionic liquids as both reaction medium and structure-directing agent and successively followed by a calcination process. The tests show that the Mg-doped materials present uniform particles about 150 nm which are smaller than that of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. The result can be mostly due to MgCl2, which restrains the growth of the particles at high temperature. The electrochemical testing results demonstrate LiNi0.49Mg0.01Mn1.5O4 material has the capacity retention of higher than 96.9 % after 100 cycles, and high capacity of 105.3 mAh g−1 at 10 C rate, in comparison with the capacity retention of 91.2 % and capacity of 82.4 mAh g−1 for the pristine one. The excellent rate performance and cycling stability can be attributed to the small and uniform nanostructure, which can make the lithium-ion diffusion and electron transfer more easily across the LiNi0.49Mg0.01Mn1.5O4/electrolyte interfaces.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Etacheri V, Marom R, Elazari R, Salitra G, Aurbach D (2011) Challenges in the development of advanced Li-ion batteries: a review. Energ Environ Sci 4:3243–3262
Wu Y, Gao M, Li X, Liu Y, Pan H (2014) Preparation of mesohollow and microporous carbon nanofiber and its application in cathode material for lithium–sulfur batteries. J Phys Chem Solids 608:220–228
Caballero A, Hernan L, Melero M, Morales J, Moreno R, Ferrari B (2006) LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 thick-film electrodes prepared by electrophoretic deposition for use in high voltage lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 158:583–590
Liu G, Park KS, Song J, Goodenough JB (2013) Influence of thermal history on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. J Power Sources 243:260–266
Mauger A, Julien C (2014) Surface modifications of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries: status and trends. Ionics 20:751–787
Xiao J, Yu X, Zheng J, Zhou Y, Gao F, Chen X, Bai J, Yang XQ, Zhang JG (2013) Interplay between two-phase and solid solution reactions in high voltage spinel cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 242:736–741
Prakash D, Masuda Y, Sanjeeviraja C (2012) Structural and electrical studies of LiMnVO4 cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Ionics 18:31–37
Lafont U, Locati C, Kelder E (2006) Nanopowders of spinel-type electrode materials for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 177:3023–3029
Yang T, Zhang N, Lang Y, Sun K (2011) Enhanced rate performance of carbon-coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 56:4058–4064
Markovsky B, Talyossef Y, Salitra G, Aurbach D, Kim HJ, Choi S (2004) Cycling and storage performance at elevated temperatures of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 positive electrodes for advanced 5 V Li-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 6:821–826
Zhong G, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Chen C (2011) Effects of Al substitution for Ni and Mn on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. Electrochim Acta 56:6554–6561
Oh SH, Jeon SH, Cho WI, Kim CS, Cho BW (2008) Synthesis and characterization of the metal-doped high-voltage spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 by mechanochemical process. J Alloys Compd 452(2008):389–396
Alcantara R, Jaraba M, Lavela P, Tirado J (2004) X-ray diffraction and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of zinc coated LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 566:187–192
Xu H, Xie S, Ding N, Liu B, Shang Y, Chen C (2006) Improvement of electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel prepared by radiated polymer gel method. Electrochim Acta 51:4352–4357
Amdouni N, Zaghib K, Gendron F, Mauger A, Julien C (2006) Structure and insertion properties of disordered and ordered LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinels prepared by wet chemistry. Ionics 12:117–126
Fan Y, Wang J, Tang Z, He W, Zhang J (2007) Effects of the nanostructured SiO2 coating on the performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for high-voltage Li-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 52:3870–3875
Wang J, Lin WQ, Wu BH, Zhao JB (2014) Syntheses and electrochemical properties of the Na-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 145:245–253
Yi TF, Xie Y, Zhu YR, Zhu RS, Ye MF (2012) High rate micron-sized niobium-doped LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 as ultra high power positive-electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 211:59–65
Yi TF, Chen B, Zhu YR, Li XY, Zhu RS (2014) Enhanced rate performance of molybdenum-doped spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials for lithium ion battery. J Power Sources 247:778–785
Zeng YP, Wu XL, Mei P, Cong LN, Yao C, Wang RS, Xie HM, Sun LQ (2014) Effect of cationic and anionic substitutions on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 spinel cathode materials. Electrochim Acta 138:493–500
Ooms F, Keldera E, Schoonman J, Wagemaker M, Mulder F (2002) High-voltage LiMgdNi0.5ÀdMn1.5O4 spinels for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 152:143–153
Yi TF, Jiang LJ, Shu J, Yue CB, Zhu RS, Qiao HB (2010) Recent development and application of Li4Ti5O12 as anode material of lithium ion battery. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1236–1242
Alva G, Kim C, Yi T, Cook J, Xu L, Nolis G, Cabana J (2014) Surface chemistry consequences of Mg-based coatings on LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 electrode materials upon operation at high voltage. J Phys Chem C 118:10596–10605
Jian X, Wenren H, Huang S, Shi S, Wang X, Gu C, Tu J (2014) Oxalic acid-assisted combustion synthesized LiVO3 cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 246:417–422
Lin CY, Duh JG, Hsu CH, Chen JM (2010) LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material by low-temperature solid-state method with excellent cycleability in lithium ion battery. Mater Lett 64:2328–2330
Yoon S, Woo SG, Jung KN, Song H (2014) Conductive surface modification of cauliflower-like WO3 and its electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 613:187–192
Yi TF, Zhu YR, Zhu RS (2008) Density functional theory study of lithium intercalation for 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode materials. Solid State Ionics 179:2132–2136
Kishida I, Orita K, Nakamura A, Yokogawa Y (2013) Thermodynamic analysis using first-principles calculations of phases and structures of LixNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1). J Power Sources 241:1–5
Li X, Fang X, Chen X, Wang X, Li J, Fang F, Wei Z, Chu X, Wang F (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Mg-doped ZnO nanorods prepared by electrodeposition. Integr Ferroelectr 144:22–28
Park S, Oh SW, Kang S, Belharouak I, Amine K, Sun YK (2007) Comparative study of different crystallographic structure of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4-δ cathodes with wide operation voltage (2.0–5.0 V). Electrochim Acta 52:7226–7230
Mao J, Dai K, Zhai Y (2012) Electrochemical studies of spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathodes with different particle morphologies. Electrochim Acta 63:381–390
Liu J, Sun Z, Xie J, Chen H, Wu N, Wu B (2013) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.5-xCuxMn1.5-yAlyO4 (x = 0, 0.05, y = 0, 0.05). J Power Sources 240:95–100
Li J, Zhang Y, Li J, Wang L, He X, Gao J (2011) AlF3 coating of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 for high-performance Li-ion batteries. Ionics 17:671–675
Minakshi M, Kandhasamy S, Meyrick D (2012) Synthetic strategies for better battery performance through advances in materials and chemistry: olivine LiMn1/3Co1/3Ni1/3PO4. J Alloys Compd 544:62–66
Yi TF, Li CY, Zhu YR, Shu J, Zhu RS (2009) Comparison of structure and electrochemical properties for 5 V LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and LiNi0.4Cr0.2Mn1.4O4 cathode materials. J Solid State Electrochem 13:913–919
Liu G, Zhang L, Sun L, Wang L (2013) A new strategy to diminish the 4 V voltage plateau of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4. Mater Res Bull 48:4960–4962
Sun YK, SUNG WO, Yoon CS, HYUN JB, Prakash J (2006) Effect of sulfur and nickel doping on morphology and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4-xSx spinel material in 3-V region. J Power Sources 161:19–26
Wang L, Li H, Huang X, Baudrin E (2011) A comparative study of Fd-3 m and P4332 “LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4”. Solid State Ionics 193:32–38
Li XL, Liu YF, Xiao ZH, Guo W, Zhang R (2014) Ionothermal synthesis and characterization of Li2MnSiO4/C composites as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Ceram Int 40:289–296
Li XL, He WX, Xiao ZH, Peng FF, Chen JJ (2013) Ionothermal synthesis and rate performance studies of nanostructured Li3V2(PO4)3/C composites as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 17:1991–2000
Jafta Charl J, Mathe Mkhulu K, Ncholu M, Roos Wiets D, Ozoemena Kenneth I (2013) Microwave-assisted synthesis of high-voltage nanostructured LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinel: tuning the Mn3+ content and electrochemical performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7592–7598
Yang T, Sun K, Lei Z, Zhang N, Lang Y (2010) The influence of holding time on the performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode for lithium ion battery. J Alloys Compd 502:215–219
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Project of Land and Resources of Anhui Province (2011-k-11 and 2012-k-12) and the Soft Science project of Land and Resources of Anhui Province (2012021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, ZH., Cui, QQ., Li, XL. et al. Ionothermal synthesis for Mg-doped LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 spinel with structural stability and high-rate performance. Ionics 21, 1261–1267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1305-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1305-y