Abstract
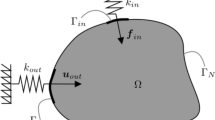
In topology optimization of structures considering flexibility, degenerated optimal solutions, such as hinges, gray areas and disconnected structures may appear. In this paper, built upon the newly developed morphable component based topology optimization approach, a novel representation using connected morphable components (CMC) and a linkage scheme are proposed to prevent degenerating designs and to ensure structure integrity. A lower bound condition of the thickness of each component is also incorporated to completely remove the smallest components in an optimal configuration. Designs of flexible structures, such as compliant mechanism design, maximum compliance structure design, and design of low-frequency resonating micro devices are studied to validate the proposed methodology. Our work demonstrates that the new methodology can successfully prevent degeneration solutions and possesses other advantages, such as minimum member size control in topology optimization of flexible structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo X, Cheng G D. Recent development in structural design and optimization. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2010; 26: 807–823
Sigmund O, Maute K. Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidiscip O, 2013; 48: 1031–1055
Bendsøe M P, Kikuchi N. Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Method Appl M, 1988; 71: 197–224
Bendsøe M P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optimiz, 1989; 1: 193–202
Zhou M, Rozvany G. The COC algorithm, Part II: topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Method Appl M, 1991; 89: 309–336
Rozvany G, Zhou M, Birker T. Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optimiz, 1992; 4: 250–252
Bendsøe M P, Sigmund O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech, 1999; 69: 635–654
Bendsøe M P, Sigmund O. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2003
Rogers J A, Someya T, Huang Y. Materials and mechanics for stretchable electronics. Science, 2010; 327: 1603–1607
Fan J A, Yeo W H, Su Y W, et al. Fractal design concepts for stretchable electronics. Nature Communications, 2014. 5
Suo Z. Mechanics of stretchable electronics and soft machines. MRS Bull, 2012; 37: 218–225
Deng J D, Rorschach K, Baker E, et al. Topology optimization and fabrication of low frequency vibration energy harvesting microdevices. Smart Mater Struct, 2015, 24: 025005
Pedersen N L. Maximization of eigenvalues using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip O, 2000; 20: 2–11
Du J B, Olhoff N. Topological design of freely vibrating continuum structures for maximum values of simple and multiple eigenfrequencies and frequency gaps. Struct Multidiscip O, 2007; 34: 91–110
Ma Z D, Kikuchi N, Hagiwara I. Structural topology and shape optimization for a frequency response problem. Comput Mech, 1993; 13: 157–174
Ma Z D, Kikuchi N, Cheng H C. Topological design for vibrating structures. Comput Method Appl M, 1995; 121: 259–280
Min S, Kikuchi N, Park Y C, et al. Optimal topology design of structures under dynamic loads. Struct Optimiz, 1999; 17: 208–218
Tai K, Chee T H. Design of structures and compliant mechanisms by evolutionary optimization of morphological representations of topology. J Mech Design, 2000. 122: 560–566
Tai K, Cui G Y, Ray T. Design synthesis of path generating compliant mechanisms by evolutionary optimization of topology and shape. J Mech Design, 2002; 124: 492–500
Zhou S W, Li Q. Microstructural design of connective base cells for functionally graded materials. Mater Lett, 2008; 62: 4022–4024
Friis K S, Sigmund O. Robust topology design of periodic grating surfaces. J Opt Soc Am B, 2012; 29: 2935–2943
Andreasen C S, Andreassen E, Jensen J S, et al. On the realization of the bulk modulus bounds for two-phase viscoelastic composites. J Mech Phys Solids, 2014; 63: 228–241
Nishiwaki S, Saitou K, Min S, et al. Topological design considering flexibility under periodic loads. Struct Multidiscip O, 2000; 19: 4–16
Tcherniak D. Topology optimization of resonating structures using SIMP method. Int J Numer Meth Eng, 2002; 54: 1605–1622
Tsai T D, Cheng C C. Structural design for desired eigenfrequencies and mode shapes using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip O, 2013; 47: 673–686
Tai K, Chee T. Design of structures and compliant mechanisms by evolutionary optimization of morphological representations of topology. J Mech Design, 2000; 122: 560–566
Tai K, Prasad J. Target-matching test problem for multiobjective topology optimization using genetic algorithms. Struct Multidiscip O, 2007; 34: 333–345
Nishiwaki S, Silva E, Saitou K, et al. Topology optimization of actuators using structural flexibility. In: Proceedings of 3rd WCSMO’99, Buffalo, 1999. 4–6
Zhou S W, Li Q. Design of graded two-phase microstructures for tailored elasticity gradients. J Mater Sci, 2008; 43: 5157–5167
Chen S, Wang M Y, Liu A Q. Shape feature control in structural topology optimization. Comput Aided Design, 2008; 40: 951–962
Wang F, Lazarov B S, Sigmund O. On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip O, 2011; 43: 767–784
Allaire G, Jouve F, Michailidis G. Thickness control in structural optimization via a level set method. 2014. https://hal.archivesouvertes. fr/hal-00985000.
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhong W. Explicit feature control in structural topology optimization via level set method. Comput Method Appl M, 2014; 272: 354–378
Zhang W, Zhong W, Guo X. An explicit length scale control approach in SIMP-based topology optimization. Comput Method Appl M, 2014; 282: 71–86
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhong W. Doing topology optimization explicitly and geometrically—A new moving morphable components based framework. J Appl Mech, 2014, 81: 081009
Zhu J, Zhang W, Beckers P. Integrated layout design of multi-component system. Int J Numer Meth Eng, 2009; 78: 631–651
Bell B, Norato J, Tortorelli D. A geometry projection method for continuum-based topology optimization of structures. In: 12th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations (ATIO) Conference and 14th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, Indianapolis, 2012
Norato J, Bell B, Tortorelli D. A geometry projection method for continuum-based topology optimization with discrete elements. Comput Method Appl M, 2015; 293: 306–327
Wei P, Wang M Y, Xing X. A study on X-FEM in continuum structural optimization using a level set model. Comput Aided Design, 2010; 42: 708–719
Kreissl S, Maute K. Levelset based fluid topology optimization using the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip O, 2012; 46: 311–326
Belytschko T, Liu W K, Moran B, et al. Nonlinear Finite Elements for Continua and Structures. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2013
Svanberg K. The method of moving asymptotes—A new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Meth Eng, 1987; 24: 359–373
Svanberg K. A globally convergent version of MMA without linesearch. In: Proceedings of the First World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, Goslar, Germany, 1995
Wen X. High order numerical methods to two dimensional delta function integrals in level set methods. J Comput Phys, 2009; 228: 4273–4290
Wen X. High order numerical methods to three dimensional delta function integrals in level set methods. SIAM J Sci Comput, 2010; 32: 1288–1309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, J., Chen, W. Design for structural flexibility using connected morphable components based topology optimization. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59, 839–851 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-016-6027-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-016-6027-0