Abstract
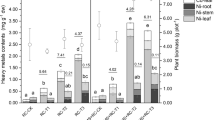
To investigate the remediation potential of spent mushroom substrate (SMS) on Cd pollution in a paddy soil, a rice pot experiment was conducted to study the effects of SMS addition on the availability of Cd in soil and the uptake of Cd in rice tissues. Five percent of SMS from Pleurotus eryngii (SMS-A, treatment: A), SMS from Agaricus bisporus (SMS-B, treatment: B), or SMS-A plus SMS-B (1:1, treatment: A+B) were added into a Cd-contaminated paddy soil before planting, respectively. The treatment of no SMS amendment was set up as the control (CK). At the four main growth stages of rice, the soils and plant samples were collected to detect the soil properties, Cd concentration in soils and rice tissues, and Cd fractions in soils. Results indicated that the application of SMS-A, SMS-B, and A+B significantly increased soil pH by 14.0–22.9, 23.9–32.9, and 22.7–30%, organic matter (OM) contents by 12.9–31.5, 22.1–34.5, and 26.1–36.9% comparing with CK. While cation exchange capacities (CECs) were increased by 3.6–8.5, 4.9–13.1, and 0.4–10.0% in A, B, and A+B treatments, respectively, except those at the maturation stage in A and B treatments. However, the CaCl2-Cd concentrations in soils were significantly decreased by 64.8–77.9, 76.1–98.9, 73.2–98.9% in A, B, and A+B treatments, respectively, comparing with CK. The reduced availability of Cd was attributed to the changes of Cd from soluble to insoluble fractions in soils amended with SMS and resulted in the decreased Cd uptake in rice tissues. The Cd concentrations in roots significantly decreased by 22.8–36.9, 28.6–36.6, and 26.8–42.6%, while the Cd concentrations in straw decreased by 20.1–46.4, 9.3–41.6, and 16.0–49.1% in A, B, and A+B treatments, respectively. At the maturation stage, the Cd concentrations in brown rice were reduced by 17.7, 15.9, and 19.4% in A, B, and A+B treatments, respectively. Correlation analysis revealed that the Cd concentrations in rice roots, straws, and brown rice were all positively correlated with CaCl2-Cd concentrations of soils. Moreover, soil pH and OM were significantly negatively correlated with the Cd concentration in rice tissues, except that between soil pH and the Cd concentration in rice straws. Therefore, the reduced Cd availability in soil and uptake in rice plant tissues together with better soil nutrient conditions by SMS application improved the biomass of root and straw at heading, filling, and maturation stages and the rice production by 32.9–38.8% at the maturation stage. The combined application of SMS-A and SMS-B can be used as a potential method for remediation of Cd-contaminated paddy soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bian R, Chen D, Liu X, Cui L, Li L, Pan G, Xie D, Zheng J, Zhang X, Zheng J, Chang A (2013) Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: results from a cross-site field experiment. Ecol Eng 58:378–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.07.031
Bian R, Li L, Bao D, Zheng J, Zhang X, Zheng J, Liu X, Cheng K, Pan G (2016) Cd immobilization in a contaminated rice paddy by inorganic stabilizers of calcium hydroxide and silicon slag and by organic stabilizer of biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:10028–10036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6214-3
Cao F, Cai Y, Liu L, Zhang M, He X, Zhang G, Wu F (2015) Differences in photosynthesis, yield and grain cadmium accumulation as affected by exogenous cadmium and glutathione in the two rice genotypes. Plant Growth Regul 75:715–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9973-1
Cheng X, ChiQuan H, Shi Z, Chen X, Oh K, Xia L, Liu X, Xiong P, Muo Q (2018) Effect of spent mushroom substrate on strengthening the phytoremediation potential of Ricinus communis to Cd- and Zn-polluted soil. Int J Phytoremediation 20(14):1389–1399. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1474439
CMEE (China Ministry of Ecology and Environment) (2018) Soil environmental quality: risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (GB 15618-2018). Standards Press of China, Beijing (In Chinese)
Corral-Bobadilla M, Gonzalez-Marcos A, Vergara-Gonzalez EP, Alba-Elias F (2019) Bioremediation of waste water to remove heavy metals using the spent mushroom substrate of Agaricus bisporus. Water 11:454. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030454
Fahmi AH, Samsuri AW, Jol H, Singh D (2018) Bioavailability and leaching of Cd and Pb from contaminated soil amended with different sizes of biochar. R Soc Open Sci 5:181328. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181328
Fan Z, Neff JC, Harden JW, Zhang T, Veldhuis H, Czimczik CI, Winston GC, O’Donnell JA (2011) Water and heat transport in boreal soils: implications for soil response to climate change. Sci Total Environ 409:1836–1842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.02.009
Fidel RB, Laird DA, Thompson ML, Lawrinenko M (2017) Characterization and quantification of biochar alkalinity. Chemosphere 167:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.151
Frutos I, García-Delgado C, Gárate A, Eymar E (2016) Biosorption of heavy metals by organic carbon from spent mushroom substrates and their raw materials. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:2713–2720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1100-6
Frutos I, García-Delgado C, Cala V, Gárate A, Eymar E (2017) The use of spent mushroom compost to enhance the ability of Atriplex halimus to phytoremediate contaminated mine soils. Environ Technol 38:1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1217938
Gu JF, Zhou H, Yang WT, Peng PQ, Zhang P, Zeng M, Liao BH (2018) Effects of an additive (hydroxyapatite–biochar–zeolite) on the chemical speciation of Cd and As in paddy soils and their accumulation and translocation in rice plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:8608–8619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0921-2
Guo F, Ding C, Zhou Z, Huang G, Wang X (2018) Effects of combined amendments on crop yield and cadmium uptake in two cadmium contaminated soils under rice-wheat rotation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.043
Hanafi FHM, Rezania S, Taib SM, Din MFM, Yamauchi M, Sakamoto M, Hara H, Park J, Ebrahimi SS (2018) Environmentally sustainable applications of agro-based spent mushroom substrate (SMS): an overview. J Mater Cycles Waste 20:1383–1396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0739-0
He H, Tam NFY, Yao A, Qiu R, Li WC, Ye Z (2017) Growth and Cd uptake by rice (Oryza sativa) in acidic and Cd-contaminated paddy soils amended with steel slag. Chemosphere 189:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.069
Herrero-Hernández E, Andrades MS, Rodríguez-Cruz MS, Sánchez-Martín MJ (2011) Effect of spent mushroom substrate applied to vineyard soil on the behaviour of copper-based fungicide residues. J Environ Manag 92:1849–1857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.03.011
Herrero-Hernandez E, Andrades MS, Rodriguez-Cruz MS, Arienzo M, Sanchez-Martin MJ (2012) Long-term variability of metals from fungicides applied in amended young vineyard fields of La Rioja (Spain). Environ Monit Assess 184:3359–3371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2194-4
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Beneficial effects of biochar application to contaminated soils on the bioavailability of Cd, Pb and Zn and the biomass production of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Biomass Bioenergy 57:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.07.019
Huang Q, Yu Y, Wan Y, Wang Q, Luo Z, Qiao Y, Su D, Li H (2018) Effects of continuous fertilization on bioavailability and fractionation of cadmium in soil and its uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Environ Manag 215:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.036
Huang J, Liu J, Kuo J, Xie W, Zhang X, Chang K, Buyukada M, Evrendilek F (2019) Kinetics, thermodynamics, gas evolution and empirical optimization of (co-)combustion performances of spent mushroom substrate and textile dyeing sludge. Bioresour Technol 280:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.011
Jalali M, Latifi Z (2018) Measuring and simulating effect of organic residues on the transport of cadmium, nickel, and zinc in a calcareous soil. J Geochem Explor 184:372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.05.001
Jia Z, Deng J, Chen N, Shi W, Tang X, Xu H (2017) Bioremediation of cadmium-dichlorophen co-contaminated soil by spent Lentinus edodes substrate and its effects on microbial activity and biochemical properties of soil. J Soils Sediments 17:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1562-7
Jordan SN, Mullen GJ, Courtney RG (2008) Utilization of spent mushroom compost for the revegetation of lead-zinc tailings: effects on physico-chemical properties of tailings and growth of Lolium perenne. Bioresour Technol 99:8125–8129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.03.054
Li X, Lin X, Zhang J, Wu Y, Yin R, Feng Y, Wang Y (2010) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by crude extracts from spent mushroom substrate and its possible mechanisms. Curr Microbiol 60:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9546-0
Li X, Zhang D, Sheng F, Qing H (2018) Adsorption characteristics of copper (II), zinc (II) and mercury (II) by four kinds of immobilized fungi residues. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.058
Liang J, Yang Z, Tang L, Zeng GM, Yu M, Li XD, Wu HP, Qian YY, Li XM, Luo YA (2017) Changes in heavy metal mobility and availability from contaminated wetland soil remediated with combined biochar-compost. Chemosphere 181:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.081
Lou Z, Sun Y, Zhou X, Baig SA, Hu B, Xu X (2017) Composition variability of spent mushroom substrates during continuous cultivation, composting process and their effects on mineral nitrogen transformation in soil. Geoderma 307:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.07.033
Lu RK (1999) Methods of soil agricultural chemistry analyses. China Agriculture Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Lu K, Yang X, Gielen G, Bolan N, Ok YS, Niazi NK, Xu S, Yuan GD, Chen X, Zhang XK, Liu D, Song ZL, Liu XY, Wang HL (2017) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 186:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.05.068
Luo N, Li X, Chen AY, Zhang LJ, Zhao HM, Xiang L, Cai YQ, Mo CH, Wong MH, Li H (2017) Does arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus affect cadmium uptake and chemical forms in rice at different growth stages? Sci Total Environ 599-600:1564–1572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.047
Ma P, Gu B, Zhang D, Cao Z, Zhang J (2013) Comparative study on treating wastewater containing lead by free and immobilized Lentinus Edodes Residue. J Agro-Environ Sci 32:653–660 (In Chinese)
Meng J, Zhong L, Wang L, Liu XM, Tang CX, Chen HJ, Xu JM (2018) Contrasting effects of alkaline amendments on the bioavailability and uptake of Cd in rice plants in a Cd-contaminated acid paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:8827–8835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1148-y
Mohamed I, Ahamadou B, Li M, Gong C, Cai P, Liang W, Huang Q (2010) Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in a contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J Soils Sediments 10:973–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0199-1
Paredes C, Medina E, Moral R, Pérez-Murcia MD, Moreno-Caselles J, Bustamante MA, Cecilia JA (2009) Characterization of the different organic matter fractions of spent mushroom substrate. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 40:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620802625575
Qiao JT, Liu TX, Wang XQ, Li FB, Lv YH, Cui JH, Zeng XD, Yuan YZ, Liu CP (2018) Simultaneous alleviation of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice by applying zero-valent iron and biochar to contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere 195:260–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.081
Qin R, Chen F, Gao J (2011) Long-term application of chemical fertilizers and rice straw on soil aluminum toxicity. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 42:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2011.528487
Rahman MA, Rahman MM, Reichman SM, Lim RP, Naidu R (2014) Heavy metals in Australian grown and imported rice and vegetables on sale in Australia: health hazard. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.11.024
Rodda MS, Li G, Reid RJ (2011) The timing of grain Cd accumulation in rice plants: the relative importance of remobilisation within the plant and root Cd uptake post-flowering. Plant Soil 347:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0829-4
Shi J, Pan G, Zhang N (2013) Effect of cadmium stress on Cd and Zn uptake and accumulation of different cultivars of hybrid rice. Acta Sci Circumst 33:2904–2910. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4044932 (In Chinese)
Stewart DPC, Cameron KC, Cornforth IS (1998) Effects of spent mushroom substrate on soil chemical conditions and plant growth in an intensive horticultural system: a comparison with inorganic fertiliser. Aust J Soil Res 36:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1071/s97076
Sun YQ, Wen CF, Liang X, He CQ (2018) Determination of the phytoremediation efficiency of Ricinus communis L. and methane uptakefrom cadmium and nickel-contaminated soil using spent mushroom substrate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:32603–32616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3128-2
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50043a017
USDA (1987) Soil mechanics level I. Module 3 – USDA textural soil classification study guide. Washington, DC
van Herwijnen R, Laverye T, Poole J, Hodson ME, Hutchings TR (2007) The effect of organic materials on the mobility and toxicity of metals in contaminated soils. Appl Geochem 22:2422–2434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.06.013
Wang W, Lai DYF, Li S, Kim PJ, Zeng C, Li P, Liang Y (2014) Steel slag amendment reduces methane emission and increases rice productivity in subtropical paddy fields in China. Wetl Ecol Manag 22:683–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-014-9364-4
Wang R, Guo J, Xu Y, Ding Y, Shen Y, Zheng X, Feng R (2016) Evaluation of silkworm excrement and mushroom dreg for the remediation of multiple heavy metal/metalloid contaminated soil using pakchoi. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 124:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.10.014
Wang L, Meng J, Li Z, Liu X, Fang X, Xu J (2017) First “charosphere” view towards the transport and transformation of Cd with addition of manure derived biochar. Environ Pollut 227:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.04.024
Wang F, Zhang S, Cheng P, Zhang S, Sun Y (2020) Effects of soil amendments on heavy metal immobilization and accumulation by maize grown in a multiple-metal-contaminated soil and their potential for safe crop production. Toxics 8:102. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040102
Wei Y, Jin Z, Zhang M, Li Y, Huang S, Liu X, Jin Y, Wang H, Qu J (2020) Impact of spent mushroom substrate on Cd immobilization and soil property. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:3007–3022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07138-y
Wu J, Li H, Li F, Zhang Y, Lu H, Zhuang P, Mo Q, Li Z (2016a) Distribution and fractionation of cadmium in soil aggregates affected by earthworms (Eisenia fetida) and manure compost. J Soils Sediments 16:2286–2295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1433-2
Wu YJ, Zhou H, Zou ZJ, Zhu W, Yang WT, Peng PQ, Zeng M, Liao BH (2016b) A three-year in-situ study on the persistence of a combined amendment (limestone + sepiolite) for remedying paddy soil polluted with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 130:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.04.018
Xu RK, Zhao AZ (2013) Effect of biochars on adsorption of Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) by three variable charge soils from southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:8491–8501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1769-8
Xu P, Sun CX, Ye XZ, Xiao WD, Zhang Q, Wang Q (2016) The effect of biochar and crop straws on heavy metal bioavailability and plant accumulation in a Cd and Pb polluted soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 132:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.05.031
Xu Y, Liang X, Xu Y, Xu Q, Huang Q, Wang L, Sun Y (2017) Remediation of heavy metal-polluted agricultural soils using clay minerals: a review. Pedosphere 27:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60310-2
Xu C, Chen H, Xiang Q, Zhu H, Wang S, Zhu Q, Huang D, Zhang Y (2018) Effect of peanut shell and wheat straw biochar on the availability of Cd and Pb in a soil–rice (Oryza sativa L.) system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0495-z
Xue Y, Gao B, Yao Y, Inyang M, Zhang M, Zimmerman AR, Ro KS (2012) Hydrogen peroxide modification enhances the ability of biochar (hydrochar) produced from hydrothermal carbonization of peanut hull to remove aqueous heavy metals: batch and column tests. Chem Eng J 200-202:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.116
Yang S, Cao J, Li F, Peng X, Peng Q, Yang Z, Chai L (2016) Field evaluation of the effectiveness of three industrial by-products as organic amendments for phytostabilization of a Pb/Zn mine tailings. Environ Sci Process Impacts 18:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5em00471c
Yu HY, Liu C, Zhu J, Li F, Deng DM, Wang Q, Liu C (2016) Cadmium availability in rice paddy fields from a mining area: the effects of soil properties highlighting iron fractions and pH value. Environ Pollut 209:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.021
Zhang X, Fang L, Li F, Yu H, Liu C, Du Y (2020) Synergistic passivating effects and mechanisms of zero valent iron and biochar on cadmium and arsenic in paddy soil over a whole growth period of rice. Eco Environ Sci 29(7):1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.07.021 (In Chinese)
Zhou H, Zhou X, Zeng M, Liao BH, Liu L, Yang WT, Wu YM, Qiu QY, Wang YJ (2014) Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.01.001
Zhou H, Zhu W, Yang WT, Gu JF, Gao ZX, Chen LW, Du WQ, Zhang P, Peng PQ, Liao BH (2018) Cadmium uptake, accumulation, and remobilization in iron plaque and rice tissues at different growth stages. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 152:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.01.031
Acknowledgements
We thank the support by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant number: 2018YFC1902105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Wei Shan, Panyang Liu, and Dean Rao. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hongyan Yu, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Liu, P., Shan, W. et al. Remediation potential of spent mushroom substrate on Cd pollution in a paddy soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 36850–36860 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13266-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13266-1